Stars and Galaxies Section 1 Stars
... Stars and Galaxies Section 1 Stars A. Patterns of stars - constellations 1. Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations 2. Modern astronomy studies 88 constellations 3. Some constellations are not visible all year because Earth revolves around the Sun 4. Circumpolar cons ...
... Stars and Galaxies Section 1 Stars A. Patterns of stars - constellations 1. Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations 2. Modern astronomy studies 88 constellations 3. Some constellations are not visible all year because Earth revolves around the Sun 4. Circumpolar cons ...
How the Universe Works Extreme Stars Name 1. When a star dies
... 4. Eventually, the helium in the core begins to fuse into (oxygen) (iron) (carbon). 5. After the sun blasts away its outer layers, all that remains is an intensely hot, core called a (planetary nebula) (white dwarf) (pulsar). 6. At the core of a white dwarf astronomers believe lies a core of (iron) ...
... 4. Eventually, the helium in the core begins to fuse into (oxygen) (iron) (carbon). 5. After the sun blasts away its outer layers, all that remains is an intensely hot, core called a (planetary nebula) (white dwarf) (pulsar). 6. At the core of a white dwarf astronomers believe lies a core of (iron) ...
Sky Notes - April 2012 - North Devon Astronomical Society
... and extra-galactic distances. Delta Cephei is around 887 light-years distant and has a magnitude +7.5 companion, (separation 41 arcseconds), which is visible in small telescopes. ...
... and extra-galactic distances. Delta Cephei is around 887 light-years distant and has a magnitude +7.5 companion, (separation 41 arcseconds), which is visible in small telescopes. ...
Figure 10-6 The same star field shown in Figure
... stars, however. When the magnitude scale was extended and expressed by a mathematical formula, it developed that the brighter stars are brighter than those of the first magnitude; indeed they are even brighter than those of zero magnitude. The only way to express these hitherto unsuspected magnitude ...
... stars, however. When the magnitude scale was extended and expressed by a mathematical formula, it developed that the brighter stars are brighter than those of the first magnitude; indeed they are even brighter than those of zero magnitude. The only way to express these hitherto unsuspected magnitude ...
What Can We See in the Night Sky?
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
homework assignment 3
... Due Monday, April 22, 2013 at 5 p.m., either electronically or on paper. 1. Most astronomy textbooks use planets orbiting the Sun to illustrate the relevance of Kepler’s third law of planetary motion. In a class on stars and galaxies, describe a more relevant example of Kepler’s third law (i.e., whe ...
... Due Monday, April 22, 2013 at 5 p.m., either electronically or on paper. 1. Most astronomy textbooks use planets orbiting the Sun to illustrate the relevance of Kepler’s third law of planetary motion. In a class on stars and galaxies, describe a more relevant example of Kepler’s third law (i.e., whe ...
Astronomy – Interpreting Main Sequence Star Data The
... Astronomy – Interpreting Main Sequence Star Data The classification of stars by surface temperature and spectral pattern is a painstaking process requiring the efforts of many scientists from hundreds of observatories around the world. To make it easier to refer to the different types of main sequen ...
... Astronomy – Interpreting Main Sequence Star Data The classification of stars by surface temperature and spectral pattern is a painstaking process requiring the efforts of many scientists from hundreds of observatories around the world. To make it easier to refer to the different types of main sequen ...
Chapter 28 Notes
... Why can’t we see Orion in June? Because of Earth’s movement around the sun Apparent Magnitude – What is it? How bright a star appears to be to an observer on Earth. ...
... Why can’t we see Orion in June? Because of Earth’s movement around the sun Apparent Magnitude – What is it? How bright a star appears to be to an observer on Earth. ...
STARS and GALAXIES
... heat and light. • Some stars are very old and the size of planets or moons, and some no longer ...
... heat and light. • Some stars are very old and the size of planets or moons, and some no longer ...
Slide 1
... • Binary Stars: when two stars orbit around each other • Stars of equal mass have their center of mass in the middle ...
... • Binary Stars: when two stars orbit around each other • Stars of equal mass have their center of mass in the middle ...
tire
... atom. In the process, energy is released. 2. A disk of gas orbiting a star or black hole. 3. The most common element in the universe and the major component of stars. 4. The bending of light from a distance star or galaxy by the gravity of a closer star, galaxy or galaxy cluster. 5. Large black hole ...
... atom. In the process, energy is released. 2. A disk of gas orbiting a star or black hole. 3. The most common element in the universe and the major component of stars. 4. The bending of light from a distance star or galaxy by the gravity of a closer star, galaxy or galaxy cluster. 5. Large black hole ...
Chapter 7 Vocabulary212
... 1. Spectroscope- used to study star’s characteristics by spreading light into different wavelengths 2. Nuclear fusion- nuclei of several atoms combine to form on large nucleus 3. astronomical unit- average distance between Earth and Sun (150 million km) 4. light year- distance light travels in 1 yea ...
... 1. Spectroscope- used to study star’s characteristics by spreading light into different wavelengths 2. Nuclear fusion- nuclei of several atoms combine to form on large nucleus 3. astronomical unit- average distance between Earth and Sun (150 million km) 4. light year- distance light travels in 1 yea ...
Sagittarius - columbusastronomy
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
Homework, November 16, 2006 AST110-6
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 • In this class we will ...
... MBol (!) − MBol (!) = 2.5 log10 [L(!)/L(!)] ...
... MBol (!) − MBol (!) = 2.5 log10 [L(!)/L(!)] ...
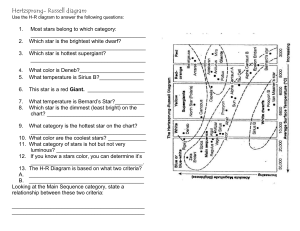
Hertzsprung - Russel Diagram
... Most stars belong to which category: _______________________________________ Which star is the brightest white dwarf? _______________________________________ Which star is hottest supergiant? _______________________________________ ...
... Most stars belong to which category: _______________________________________ Which star is the brightest white dwarf? _______________________________________ Which star is hottest supergiant? _______________________________________ ...
Astronomy Snakes and Ladders Earth, third planet in Solar System
... consist of dust and gas. Usually seen when it is close to the Sun ...
... consist of dust and gas. Usually seen when it is close to the Sun ...
Characteristics of Stars
... • Absolute Magnitude: the “Real” brightness of the star. How much light it really gives off.(Need to know the distance to the Star) • Apparent Magnitude: How bright the star appears to be. ...
... • Absolute Magnitude: the “Real” brightness of the star. How much light it really gives off.(Need to know the distance to the Star) • Apparent Magnitude: How bright the star appears to be. ...
Life Cycle of Star Flipbook
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.