Old Sample Exam #2
... Each answer worth 5 points except last which is worth 10 points. All constants in mks units unless otherwise specified: c=3x108 G=6.7x10-11 h=6.6x10-34 =5.7x10-8 REarth=6400km ...
... Each answer worth 5 points except last which is worth 10 points. All constants in mks units unless otherwise specified: c=3x108 G=6.7x10-11 h=6.6x10-34 =5.7x10-8 REarth=6400km ...
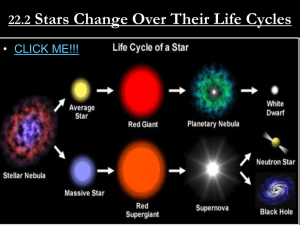
The Life Cycle of Stars
... expands to 10 – 100 times its original size The star has used all of its hydrogen fuel. The center shrinks. ...
... expands to 10 – 100 times its original size The star has used all of its hydrogen fuel. The center shrinks. ...
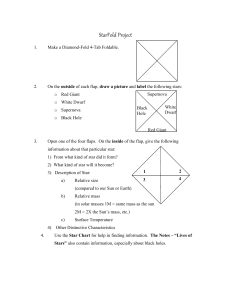
Life Cycle of Stars Flipbook Assignment
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
Unit 11 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
PH507 - University of Kent
... 1. Calculate the luminosity (in units of the solar luminosity) of a blackbody of Saturn’s radius that has a temperature of 1000 K? Explain the steps you take in the derivation. The surface temperature of the Sun is 5780 K. The radii of Saturn and the Sun are 6.00 x 107 m and 6.96 x 108 m, respective ...
... 1. Calculate the luminosity (in units of the solar luminosity) of a blackbody of Saturn’s radius that has a temperature of 1000 K? Explain the steps you take in the derivation. The surface temperature of the Sun is 5780 K. The radii of Saturn and the Sun are 6.00 x 107 m and 6.96 x 108 m, respective ...
Regulus the Star njw
... The star’s name regulus comes from the Latin word Rex which means King It is associated with many cultures like the Greeks , Arabs, and Ancient Babylon It also is know as one of the four Royal Stars of the Heavens ...
... The star’s name regulus comes from the Latin word Rex which means King It is associated with many cultures like the Greeks , Arabs, and Ancient Babylon It also is know as one of the four Royal Stars of the Heavens ...
Chapter 27 Review Guide// ESS
... 2. What is the relationship of color to a star’s surface temperature? 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different tim ...
... 2. What is the relationship of color to a star’s surface temperature? 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different tim ...
When Stars Blow Up
... •When the temperature reaches a few MK, fusion begins •Degenerate fusion is a runaway. •All the H fuses to He and heavier elements in a soundcrossing time (a few minutes) •The star increases in brightness ~ 10,000 times •Most of the matter is ejected ...
... •When the temperature reaches a few MK, fusion begins •Degenerate fusion is a runaway. •All the H fuses to He and heavier elements in a soundcrossing time (a few minutes) •The star increases in brightness ~ 10,000 times •Most of the matter is ejected ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... 20. What are the two main parts of the Sun? 21. Describe the following layers of the Sun: Corona Chromosphere Photosphere Convection zone Radiative zone Core 22. What are sunspots? 23. Prominences 24. Solar flares 25. How long does it take the light particles to reach the surface of the Earth? ...
... 20. What are the two main parts of the Sun? 21. Describe the following layers of the Sun: Corona Chromosphere Photosphere Convection zone Radiative zone Core 22. What are sunspots? 23. Prominences 24. Solar flares 25. How long does it take the light particles to reach the surface of the Earth? ...
Review_game_and_answers
... 7- How are all galaxies moving in relation to every other galaxy? Away from each other ...
... 7- How are all galaxies moving in relation to every other galaxy? Away from each other ...
chapter 18
... helium nuclei to form carbon nuclei. c) hydrogen nuclei to form helium nuclei. d) carbon nuclei to form magnesium nuclei. ...
... helium nuclei to form carbon nuclei. c) hydrogen nuclei to form helium nuclei. d) carbon nuclei to form magnesium nuclei. ...
Chapter 28 Vocabulary
... Main sequence star - A star that is at the point in its life cycle in which it is actively fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei; also the band of the Hertzsprun-Russell diagram depicting such stars. ...
... Main sequence star - A star that is at the point in its life cycle in which it is actively fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei; also the band of the Hertzsprun-Russell diagram depicting such stars. ...
Extra Questions Stellar properties
... How many times brighter or dimmer than the Sun is it? 3 Barnard’s star, the star with the largest known proper motion in the skjy can be seen only with a telescope because its apparent magnitude is +9.54. Its distance from Earth is 1.81 parsecs. How much closer to Earth would it have to be in order ...
... How many times brighter or dimmer than the Sun is it? 3 Barnard’s star, the star with the largest known proper motion in the skjy can be seen only with a telescope because its apparent magnitude is +9.54. Its distance from Earth is 1.81 parsecs. How much closer to Earth would it have to be in order ...
Use this form to take notes in class about stars
... Stars of Spectral Classes B to M 9. What color is our sun? ___________what class is it in? ...
... Stars of Spectral Classes B to M 9. What color is our sun? ___________what class is it in? ...
Chapter 29 Stellar Evolution
... How it would look if we were 10 parsecs away. “BeetleJuice” Rigel Spica Sirius ...
... How it would look if we were 10 parsecs away. “BeetleJuice” Rigel Spica Sirius ...
Main Sequence Stars
... Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate being absolute magnitude (equivalent to luminosity). The result, called th ...
... Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate being absolute magnitude (equivalent to luminosity). The result, called th ...
The Universe Constellations
... 4. Cepheid variable stars pulse in a regular pattern. In what way are these stars useful to astronomers? ...
... 4. Cepheid variable stars pulse in a regular pattern. In what way are these stars useful to astronomers? ...
Blank Jeopardy
... A rainbow of colors is produced when white light passes through a prism because the light ___ ...
... A rainbow of colors is produced when white light passes through a prism because the light ___ ...
Astronomy word grid
... 18. The apparent backwards movement of the planets in the sky 22. A type of variable star used to measure distance 25. The name used to describe the brightness of a star 26. The name given to a very large but cool star 29. He discovered the moons of Jupiter 30. A type of telescope using lenses 35. A ...
... 18. The apparent backwards movement of the planets in the sky 22. A type of variable star used to measure distance 25. The name used to describe the brightness of a star 26. The name given to a very large but cool star 29. He discovered the moons of Jupiter 30. A type of telescope using lenses 35. A ...
Physical properties of stars
... Too little mass-failed star (Brown dwarf) Too much mass- Blue Giants that fuse their fuel at incredible rates and have short lived lives. Pg 460 diagram of stellar masses Chemical Composition: Primarily hydrogen and helium Trace amounts of other elements Nuclear fusion is the source of energy for a ...
... Too little mass-failed star (Brown dwarf) Too much mass- Blue Giants that fuse their fuel at incredible rates and have short lived lives. Pg 460 diagram of stellar masses Chemical Composition: Primarily hydrogen and helium Trace amounts of other elements Nuclear fusion is the source of energy for a ...
Study Guide_galaxies, Tools, and Stars Test
... 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light year? 9. What contains all the matter and energy that exists? 10. Name two types of optical telescopes. 11. What do radio telescopes receive and where do they come from? 12. ...
... 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light year? 9. What contains all the matter and energy that exists? 10. Name two types of optical telescopes. 11. What do radio telescopes receive and where do they come from? 12. ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.