introduction to astronomy phys 271
... Circumpolar Stars or constellations • They never set, 23 hours 56 minute clock ...
... Circumpolar Stars or constellations • They never set, 23 hours 56 minute clock ...
The Life of a Star
... a red super giant. After this stage things become more violent. Instead of gentle billowing gas shells being ejected into space (a planetary nebula) the red super giant tears itself apart in an unbelievably violent explosion called a supernova. As the radiation and debris clear, a neutron star emerg ...
... a red super giant. After this stage things become more violent. Instead of gentle billowing gas shells being ejected into space (a planetary nebula) the red super giant tears itself apart in an unbelievably violent explosion called a supernova. As the radiation and debris clear, a neutron star emerg ...
A Red Giant - Cloudfront.net
... Becoming a Red Supergiant for about 15 million years. In the cool outer layers flakes of Carbon and Silicon form They are blown away by photons from the Core taking the outer layers of gas with them forming a … ...
... Becoming a Red Supergiant for about 15 million years. In the cool outer layers flakes of Carbon and Silicon form They are blown away by photons from the Core taking the outer layers of gas with them forming a … ...
Star Vocabulary
... 1. Apparent Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star appears to an observer. 2. Absolute Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star would be if all stars were at the same distance. 3. Luminosity- the actual brightness of a star. Depends only on the size and temperature of the star. 4.Doppler Effect- ...
... 1. Apparent Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star appears to an observer. 2. Absolute Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star would be if all stars were at the same distance. 3. Luminosity- the actual brightness of a star. Depends only on the size and temperature of the star. 4.Doppler Effect- ...
here - Boise State University
... Which size stars dim and not as bright???? 11. List another term scientist’s use to describe the true brightness of a star: 12. What do all stars form in? 13. What is a nebula? 14. What is the cycle or phase a star will spend most of its life in? 15. If our sun is currently 5 billion years old, how ...
... Which size stars dim and not as bright???? 11. List another term scientist’s use to describe the true brightness of a star: 12. What do all stars form in? 13. What is a nebula? 14. What is the cycle or phase a star will spend most of its life in? 15. If our sun is currently 5 billion years old, how ...
Lab 21.1 Classifying Stars
... Plot the 36 closest stars on the graph paper and mark each star’s location with a small “x”. Plot the 20 brightest stars on the graph paper and mark each star’s location with a small “o”. Using the diagram on page 382 of the text, label the five groups (four of them are circled). The third group fro ...
... Plot the 36 closest stars on the graph paper and mark each star’s location with a small “x”. Plot the 20 brightest stars on the graph paper and mark each star’s location with a small “o”. Using the diagram on page 382 of the text, label the five groups (four of them are circled). The third group fro ...
Document
... 20. Which of the following nuclear fuels does a one solar mass star use over the course of its entire evolution? a. hydrogen, b. hydrogen and helium, c. hydrogen, helium and carbon d. hydrogen, helium, carbon, and neon, e. hydrogen, helium, carbon, neon, and oxygen. 21. A planetary nebula is a. the ...
... 20. Which of the following nuclear fuels does a one solar mass star use over the course of its entire evolution? a. hydrogen, b. hydrogen and helium, c. hydrogen, helium and carbon d. hydrogen, helium, carbon, and neon, e. hydrogen, helium, carbon, neon, and oxygen. 21. A planetary nebula is a. the ...
Document
... The Milky Way Galaxy is a giant disk of stars 160,000 light-years across and 1,000 light-years thick. The Sun is located at the edge of a spiral arm, 30,000 light-years from the center It takes 250 Million years for the Sun to complete one orbit ...
... The Milky Way Galaxy is a giant disk of stars 160,000 light-years across and 1,000 light-years thick. The Sun is located at the edge of a spiral arm, 30,000 light-years from the center It takes 250 Million years for the Sun to complete one orbit ...
Sample Exam Questions
... d) cold gas and dust clouds 31. A galaxy that has just a little dust, but lots of red stars and a spheroidal shape, would be classified as a(n) ____ galaxy. a) elliptical b) irregular c) peculiar d) spiral 32. In a large cluster of galaxies, the mass of the very hot, x-ray-emitting gas between the g ...
... d) cold gas and dust clouds 31. A galaxy that has just a little dust, but lots of red stars and a spheroidal shape, would be classified as a(n) ____ galaxy. a) elliptical b) irregular c) peculiar d) spiral 32. In a large cluster of galaxies, the mass of the very hot, x-ray-emitting gas between the g ...
Brighter than the average star?
... On average, very bright stars are rare in space but they are the most common stars listed in star catalogues because they are easy to find. The vast majority of stars we see in the sky are brighter than the Sun. Stars are classified by a letter called their spec- ...
... On average, very bright stars are rare in space but they are the most common stars listed in star catalogues because they are easy to find. The vast majority of stars we see in the sky are brighter than the Sun. Stars are classified by a letter called their spec- ...
chapter 28 pages 747-752
... • After the main sequence stage, these stars will undergo a supernova • After this, they could either form a neutron star after everything collapses or a REALLY large star will become a black hole • Both are extremely dense ...
... • After the main sequence stage, these stars will undergo a supernova • After this, they could either form a neutron star after everything collapses or a REALLY large star will become a black hole • Both are extremely dense ...
Name
... The Apparent Magnitude Scale The apparent magnitude of stars was first recorded by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus about 160 B.C. Hipparchus grouped stars according to their brightness or magnitude. He called the twenty brightest stars first magnitude stars. Stars half that bright were second magnit ...
... The Apparent Magnitude Scale The apparent magnitude of stars was first recorded by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus about 160 B.C. Hipparchus grouped stars according to their brightness or magnitude. He called the twenty brightest stars first magnitude stars. Stars half that bright were second magnit ...
Celestial Bodies
... The Sun The Sun provides our world with the warmth and light needed to survive. Our Sun is an average ...
... The Sun The Sun provides our world with the warmth and light needed to survive. Our Sun is an average ...
Chapter 28.3 Topic questions
... 11. Red Super Giant stars have surface temperatures that are cooler than our earth, so why do they have greater luminosity than the sun? 12. The H-R diagram also includes which stars that are near the end of their life, what are these stars called? 13. A star begins it life in a cloud of gas and dus ...
... 11. Red Super Giant stars have surface temperatures that are cooler than our earth, so why do they have greater luminosity than the sun? 12. The H-R diagram also includes which stars that are near the end of their life, what are these stars called? 13. A star begins it life in a cloud of gas and dus ...
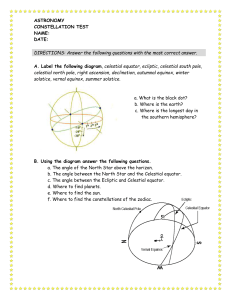
ASTRONOMY
... 1. To which constellation does the big dipper belong? 2. Which stars in Ursa Major point to Polaris? 3. How can one find the constellation Cassiopeia? 4. To what constellation do Castor and Pollux belong? 5. Where was the first planet outside our solar system found? 6. In what constellation did the ...
... 1. To which constellation does the big dipper belong? 2. Which stars in Ursa Major point to Polaris? 3. How can one find the constellation Cassiopeia? 4. To what constellation do Castor and Pollux belong? 5. Where was the first planet outside our solar system found? 6. In what constellation did the ...
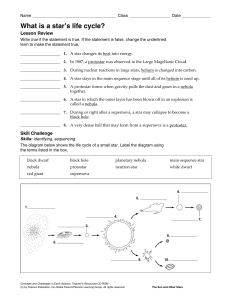
What is a star`s life cycle?
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
Stellar Evolution
... We do not know that all stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity Low Mass Stars – consume fuel at a slow rate, may remain on main-sequence for up to 100 billion years, end up collapsing into white dwarfs Medium Mass Stars – go into red-giant stage, foll ...
... We do not know that all stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity Low Mass Stars – consume fuel at a slow rate, may remain on main-sequence for up to 100 billion years, end up collapsing into white dwarfs Medium Mass Stars – go into red-giant stage, foll ...
Jeopardy - University of Nebraska–Lincoln
... This coordinate gives an object’s east-west location on the Celestial Sphere and ranges from 0-360 degrees (with 0 degrees being the north point and increasing ...
... This coordinate gives an object’s east-west location on the Celestial Sphere and ranges from 0-360 degrees (with 0 degrees being the north point and increasing ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.