Science 8 Name: Unit 2 Astronomy Date: Period: LAB
... 1. Using the data in the table, plot the location of each star and label it with its name. 2. Complete the data table based on the location of the star on the HR Diagram. 3. Color the columns of the HR Diagram. 4. Answer the questions. Background: The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram is actually an elabo ...
... 1. Using the data in the table, plot the location of each star and label it with its name. 2. Complete the data table based on the location of the star on the HR Diagram. 3. Color the columns of the HR Diagram. 4. Answer the questions. Background: The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram is actually an elabo ...
hw4
... Most stars are less massive than the Sun. On the HR Diagram, spectral type M main sequence stars are most common. If you mean temperature, then the answer is yes, sort of. The Sun sits in the mid-range represented on the HR Diagram. Clearly there are many kinds/types of stars that are hotter or cool ...
... Most stars are less massive than the Sun. On the HR Diagram, spectral type M main sequence stars are most common. If you mean temperature, then the answer is yes, sort of. The Sun sits in the mid-range represented on the HR Diagram. Clearly there are many kinds/types of stars that are hotter or cool ...
ppt
... • From there we can calculate how much further away the star must be than the Sun to make it the brightness we see from Earth • Delta Cephei shows has a period of about 5 days • This is a reasonably bright star in the constellation of Cepheus • Cepheids are in other galaxies also, and used similarly ...
... • From there we can calculate how much further away the star must be than the Sun to make it the brightness we see from Earth • Delta Cephei shows has a period of about 5 days • This is a reasonably bright star in the constellation of Cepheus • Cepheids are in other galaxies also, and used similarly ...
The Sun . . .
... where it expands and grows cooler and more luminous. Its final stage is white dwarf, after it collapses upon itself and only the hot, dense core will remain. ...
... where it expands and grows cooler and more luminous. Its final stage is white dwarf, after it collapses upon itself and only the hot, dense core will remain. ...
SNC 1PW - TeacherWeb
... 3. Our ___________________ consists of eight planets and all the objects that travel around the planets. 4. Many planets have ______________ orbiting them. 5. Planets and moons are __________________ because they do not emit their own light. 6. A ________ is matter that emits huge amounts of energy. ...
... 3. Our ___________________ consists of eight planets and all the objects that travel around the planets. 4. Many planets have ______________ orbiting them. 5. Planets and moons are __________________ because they do not emit their own light. 6. A ________ is matter that emits huge amounts of energy. ...
HOMEWORK 5 SOLUTIONS CHAPTER 9 4.A A red giant star will
... the Earth’s orbit will not change. Since the Sun is so far away, it appears to the Earth to be a point source. The black hole will also appear to be a point source so the orbit will not change. CHAPTER 11 1.C The halo is home to old, metal-poor stars. Globular clusters contain some of the oldest sta ...
... the Earth’s orbit will not change. Since the Sun is so far away, it appears to the Earth to be a point source. The black hole will also appear to be a point source so the orbit will not change. CHAPTER 11 1.C The halo is home to old, metal-poor stars. Globular clusters contain some of the oldest sta ...
A Star is Born!
... are based on the evolutionary phase of a star — whether it is a dwarf, subgiant, giant, or supergiant • Main sequence → Subgiant/Red giant: From burning hydrogen in the core to burning hydrogen in a shell that surrounds an inert (i.e., non-burning) helium core • Red giant → Horizontal Branch: Helium ...
... are based on the evolutionary phase of a star — whether it is a dwarf, subgiant, giant, or supergiant • Main sequence → Subgiant/Red giant: From burning hydrogen in the core to burning hydrogen in a shell that surrounds an inert (i.e., non-burning) helium core • Red giant → Horizontal Branch: Helium ...
Name: Astronomy Study Guide Part 1 Define Astronomy
... Describe how color of a star indicates temperature. Describe how stars are classified (o, g, m) The color of a star is indicative of the temperature and the composition of a star. For example blue stars burn the hottest of all stars. They are made up mostly of helium. ...
... Describe how color of a star indicates temperature. Describe how stars are classified (o, g, m) The color of a star is indicative of the temperature and the composition of a star. For example blue stars burn the hottest of all stars. They are made up mostly of helium. ...
Today`s Class: Measuring temperatures of stars Astronomer`s
... • Important: the different spectral lines seen are NOT primarily because stars are made of different elements ...
... • Important: the different spectral lines seen are NOT primarily because stars are made of different elements ...
File
... 5. What is an astronomical unit? A unit of measure to measure distances in the solar system is the distance from the Earth to the Sun. 6. What is an asteroid? Chunks of rock and ice 7. What are comets? Rocks, ice and dust 8. What are meteors? A streak of light made by a glowing meteoroid 9. What is ...
... 5. What is an astronomical unit? A unit of measure to measure distances in the solar system is the distance from the Earth to the Sun. 6. What is an asteroid? Chunks of rock and ice 7. What are comets? Rocks, ice and dust 8. What are meteors? A streak of light made by a glowing meteoroid 9. What is ...
Chapter 16 Lesson 2: What is a Star
... Some galaxies are called irregular because they are not spiral or elliptical and do not have a definite shape. 1. Irregular galaxies are probably young galaxies with their stars are still forming. Constellations a. Ursa Major is a constellation, an area of the sky and all the stars seen in that area ...
... Some galaxies are called irregular because they are not spiral or elliptical and do not have a definite shape. 1. Irregular galaxies are probably young galaxies with their stars are still forming. Constellations a. Ursa Major is a constellation, an area of the sky and all the stars seen in that area ...
White Dwarf Stars Near The Earth
... the “ages” of the white dwarfs on this page, I mean how long they have been white dwarfs, not how long they were main-sequence stars before that.) 40 Eridani B is a member of a triple star system and was once the brightest and most massive of the three, since the other two are relatively cool K-clas ...
... the “ages” of the white dwarfs on this page, I mean how long they have been white dwarfs, not how long they were main-sequence stars before that.) 40 Eridani B is a member of a triple star system and was once the brightest and most massive of the three, since the other two are relatively cool K-clas ...
PHYS299B_Final_HudsonJustin
... luminosity of the target star and to graph the luminosity verses time. ...
... luminosity of the target star and to graph the luminosity verses time. ...
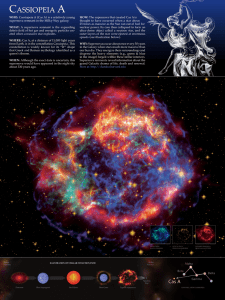
cassiopeia a - Chandra X
... WHAT: A supernova remnant is the expanding debris field of hot gas and energetic particles created when a massive star explodes. WHERE: Cas A, at a distance of 11,000 light years from Earth, is in the constellation Cassiopeia. This constellation is widely known for its “W” shape that Greek and Roman ...
... WHAT: A supernova remnant is the expanding debris field of hot gas and energetic particles created when a massive star explodes. WHERE: Cas A, at a distance of 11,000 light years from Earth, is in the constellation Cassiopeia. This constellation is widely known for its “W” shape that Greek and Roman ...
2b Astronomer space units
... earth, satellites orbiting around Earth, and sophisticated spacebased telescopes have shown us the immensity of objects in space and of distances across the universe. ...
... earth, satellites orbiting around Earth, and sophisticated spacebased telescopes have shown us the immensity of objects in space and of distances across the universe. ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Spring 2011
... of space because these stars are very rare. On the other hand, the least luminous stars are quite common, but are so faint they are hard to see even if they are close. 2. The parallax of the bright star Vega is 0.129 seconds of arc. What is the distance of Vega in parsecs ? In light-years ? We have ...
... of space because these stars are very rare. On the other hand, the least luminous stars are quite common, but are so faint they are hard to see even if they are close. 2. The parallax of the bright star Vega is 0.129 seconds of arc. What is the distance of Vega in parsecs ? In light-years ? We have ...
1000
... You have been sitting out watching the star and you notice that the star you are watching has moved about 15 degrees, how long have you been watching? ...
... You have been sitting out watching the star and you notice that the star you are watching has moved about 15 degrees, how long have you been watching? ...
Earth Science 11 Chapter 28 Answers: 28.1 1. All are forms of
... 1. Galaxies are natural groupings of stars in space, whereas constellations are not. A constellation is a group of stars that appear to be together as viewed from Earth. 2. A light-year is the distance a ray of light travels in one year, equal to 9.5 x 1012 kilometers. A parsec equals 3.258 light ye ...
... 1. Galaxies are natural groupings of stars in space, whereas constellations are not. A constellation is a group of stars that appear to be together as viewed from Earth. 2. A light-year is the distance a ray of light travels in one year, equal to 9.5 x 1012 kilometers. A parsec equals 3.258 light ye ...
Due Date: Thursday, November 16, 2006
... generated in the core of the Sun takes about one million years to get to the surface. This means that the thermal energy generated in the last minute of the fusion will last for about a million years, and the Sun will just very slowly contract. So, we will not see changes on the surface until a mill ...
... generated in the core of the Sun takes about one million years to get to the surface. This means that the thermal energy generated in the last minute of the fusion will last for about a million years, and the Sun will just very slowly contract. So, we will not see changes on the surface until a mill ...
April - Bristol Astronomical Society
... There are no Messier objects in Crater, however there are a number of galaxies from the NGC catalogue. NGC 3887 and NGC 3511 and NGC 3513 are the among the easier targets for amateur observers. NGC 3887 is an 11th magnitude barred spiral which lies within the bowl of Crater, to the northwest of zeta ...
... There are no Messier objects in Crater, however there are a number of galaxies from the NGC catalogue. NGC 3887 and NGC 3511 and NGC 3513 are the among the easier targets for amateur observers. NGC 3887 is an 11th magnitude barred spiral which lies within the bowl of Crater, to the northwest of zeta ...
Review 2
... Solar system formation. What is a nebula? What evidence do we have that stars form within dark interstellar clouds? What triggers the collapse of interstellar clouds to form stars? What is a protostar and how does it form? What stops a protostar from growing even more? What are the various types of ...
... Solar system formation. What is a nebula? What evidence do we have that stars form within dark interstellar clouds? What triggers the collapse of interstellar clouds to form stars? What is a protostar and how does it form? What stops a protostar from growing even more? What are the various types of ...
new_qwk11
... A. When a star finishes burning all the hydrogen in its core, it ceases to be a main sequence star B. The “helium flash” (ignition of the helium core) takes place at the tip of the red giant branch C. A planetary nebula is formed when a star loses part of its outer envelope in a stellar wind and thi ...
... A. When a star finishes burning all the hydrogen in its core, it ceases to be a main sequence star B. The “helium flash” (ignition of the helium core) takes place at the tip of the red giant branch C. A planetary nebula is formed when a star loses part of its outer envelope in a stellar wind and thi ...
SAMPLE TEST: Stars and Galaxies Multiple Choice Identify the letter
... ____ 19. According to Figure 25-1, the sun has an absolute magnitude of ____. a. –5 c. 5 b. 0 d. 5000 ____ 20. Another name for the interstellar matter that will eventually form a star is ____. a. supernova c. black hole b. red giant d. nebula ____ 21. A star is said to be born when ____. a. a prot ...
... ____ 19. According to Figure 25-1, the sun has an absolute magnitude of ____. a. –5 c. 5 b. 0 d. 5000 ____ 20. Another name for the interstellar matter that will eventually form a star is ____. a. supernova c. black hole b. red giant d. nebula ____ 21. A star is said to be born when ____. a. a prot ...
The coolest White Dwarf— older than the age of the universe?
... Figure 2. The pulsar has two beams along magnetic axes which are misaligned with the poles of rotation. The earth observer sees a stronger flash from the beam which is pointed nearer the earth than the other. So every rotation results in two flashes. The bottom plot is the observed light curve of th ...
... Figure 2. The pulsar has two beams along magnetic axes which are misaligned with the poles of rotation. The earth observer sees a stronger flash from the beam which is pointed nearer the earth than the other. So every rotation results in two flashes. The bottom plot is the observed light curve of th ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.