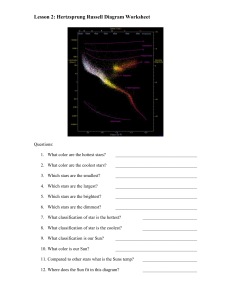
Question C:
... Other different combinations would include absolute or apparent magnitude for the vertical axis, along with some measure of temperature horizontally. Absolute magnitude is necessary to show the important features, but requires that we know the distance to each star on the diagram. Apparent magnitude ...
... Other different combinations would include absolute or apparent magnitude for the vertical axis, along with some measure of temperature horizontally. Absolute magnitude is necessary to show the important features, but requires that we know the distance to each star on the diagram. Apparent magnitude ...
Astronomy Review
... galaxy is at the center of the universe. 62. The __________________________________ theory states that the universe began when a dense, hot, supermassive ball violently exploded. 63. Circle the letter of each item that is evidence for the big bang theory. a. Red shift of galaxies b. Supernova explos ...
... galaxy is at the center of the universe. 62. The __________________________________ theory states that the universe began when a dense, hot, supermassive ball violently exploded. 63. Circle the letter of each item that is evidence for the big bang theory. a. Red shift of galaxies b. Supernova explos ...
Topic E: Astrophysics
... So maybe yesterday's spirals are todays ellipticals. This is an active research area. One problem is that if most of ...
... So maybe yesterday's spirals are todays ellipticals. This is an active research area. One problem is that if most of ...
Supernova’s
... • While the sun can burn helium and hydrogen to keep the star shinning, massive stars attain temperatures so great that Iron is produced in the core. • Iron is the most stable nuclei. • It is at this point where the core collapses and the imploding material produces a shock ...
... • While the sun can burn helium and hydrogen to keep the star shinning, massive stars attain temperatures so great that Iron is produced in the core. • Iron is the most stable nuclei. • It is at this point where the core collapses and the imploding material produces a shock ...
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
Problem Sheet for Introduction to Astrophysics
... a) If you could stand on the event horizon of a one-solar-mass black hole (M=1.991030 kg), what is the tidal force acting on you? (Assume your weight is 70kg and your height is 2 m) b) If you could stand on the event horizon of a 109 solar mass black hole, what is the tidal force acting on you (the ...
... a) If you could stand on the event horizon of a one-solar-mass black hole (M=1.991030 kg), what is the tidal force acting on you? (Assume your weight is 70kg and your height is 2 m) b) If you could stand on the event horizon of a 109 solar mass black hole, what is the tidal force acting on you (the ...
The “Big Bang” Theory
... • These life forms were the simplest form of life – _______ _________. • There is evidence of multi-cellular life as far back as ___________ years. • As organisms with _________ and eventually __________ arrive the fossil record becomes more detailed because these are more easily ___________. ...
... • These life forms were the simplest form of life – _______ _________. • There is evidence of multi-cellular life as far back as ___________ years. • As organisms with _________ and eventually __________ arrive the fossil record becomes more detailed because these are more easily ___________. ...
Stars and Their Characteristics
... Stars • mass can be determined by the inertial properties of the body or by its gravitational effect on the bodies around it ...
... Stars • mass can be determined by the inertial properties of the body or by its gravitational effect on the bodies around it ...
Space Key Word Search
... supermassive black holes; radiation is emitted into space as material falls into a black hole, usually at the center of a galaxy - this is referred to as an AGN - Active Galactic Nucleus; extremely far away. ...
... supermassive black holes; radiation is emitted into space as material falls into a black hole, usually at the center of a galaxy - this is referred to as an AGN - Active Galactic Nucleus; extremely far away. ...
2.7 - 2.9a
... include the Milky Way (our galaxy) all have a central nucleus have long curved arms contain a lot of gas and dust ...
... include the Milky Way (our galaxy) all have a central nucleus have long curved arms contain a lot of gas and dust ...
Life Cycle of Star EDpuzzle worksheet
... a. Red Giant b. White Dwarf 8. What happens to the outer layer of the Red Giant as it expands? a. It will drift off into space and become a Solar Nebula b. It will explode and become a Solar Nebula 9. The remaining core of the Sun will be called a White Dwarf. What is a White Dwarf like? a. It is de ...
... a. Red Giant b. White Dwarf 8. What happens to the outer layer of the Red Giant as it expands? a. It will drift off into space and become a Solar Nebula b. It will explode and become a Solar Nebula 9. The remaining core of the Sun will be called a White Dwarf. What is a White Dwarf like? a. It is de ...
LT 5: I can describe how astronomers determine the composition
... Parallax: an apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from different locations ...
... Parallax: an apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from different locations ...
FSA school wide Science Olympiad 12/8/2007
... C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (the galactic equator) 3. On July 4, 1054, Chinese astronomers (and possibly Native Americans) recorded a supernova ...
... C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (the galactic equator) 3. On July 4, 1054, Chinese astronomers (and possibly Native Americans) recorded a supernova ...
Stellar Magnitude, Distance, and Motion
... Actual star brightness The apparent magnitude that a star would have if it were (in our imagination) placed at a distance of 10 parsecs (which is 32.6 light years) from the Earth Used to describe luminosity - The amount of energy a star gives off each second The 20 Brightest Stars in the Sky C ...
... Actual star brightness The apparent magnitude that a star would have if it were (in our imagination) placed at a distance of 10 parsecs (which is 32.6 light years) from the Earth Used to describe luminosity - The amount of energy a star gives off each second The 20 Brightest Stars in the Sky C ...
Fusion in the Sun
... Solar flares send electrically charged particles into space called solar wind. Solar wind can cause magnetic storms that damage satellites. ...
... Solar flares send electrically charged particles into space called solar wind. Solar wind can cause magnetic storms that damage satellites. ...
Astronomy Toolkit
... appears in the sky – Some faint stars are intrinsically bright, but are very distant – Some bright stars are very faint but happen to lie close to us ...
... appears in the sky – Some faint stars are intrinsically bright, but are very distant – Some bright stars are very faint but happen to lie close to us ...
il 3 ~ )
... (c) Estimate the surface area of your body (in m2). You are welcome to make any reasonable assumptions and approximations, but be sure to state what they are! (d) Assuming your body radiates like a blackbody (OK within a factor of 2-3), estjmate the total power L radiated by your body in Watts. How ...
... (c) Estimate the surface area of your body (in m2). You are welcome to make any reasonable assumptions and approximations, but be sure to state what they are! (d) Assuming your body radiates like a blackbody (OK within a factor of 2-3), estjmate the total power L radiated by your body in Watts. How ...
Characteristics of Stars
... • Astronomers use a unit called the light year to measure distances between the stars • Light travels at a speed of 300,000 km/s • Light year- distance that light travels in one year =9.5 trillion km • Light year=unit of distance ...
... • Astronomers use a unit called the light year to measure distances between the stars • Light travels at a speed of 300,000 km/s • Light year- distance that light travels in one year =9.5 trillion km • Light year=unit of distance ...
1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light... limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of...
... 1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer p ...
... 1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer p ...
The Science behind the Stars ctY Astrophysics by Spencer McClung
... orbiting the star. Obviously we couldn’t see the planet, but it was thrilling to learn from the data that it was there. In addition to learning how to calculate the size of celestial objects, we discussed the life cycle of stars, from gaseous nebulas to rapidly spinning neutron stars. The process of ...
... orbiting the star. Obviously we couldn’t see the planet, but it was thrilling to learn from the data that it was there. In addition to learning how to calculate the size of celestial objects, we discussed the life cycle of stars, from gaseous nebulas to rapidly spinning neutron stars. The process of ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.