Massive Stars - University of Washington
... These stars pop off in an astronomical blink of the eye ...
... These stars pop off in an astronomical blink of the eye ...
File - SMIC Physics
... Center of the solar system. It is an enormous ball of gas. It is yellow in color. It is in the main sequence. ...
... Center of the solar system. It is an enormous ball of gas. It is yellow in color. It is in the main sequence. ...
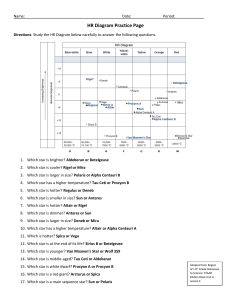
Apparent Magnitude
... In 125 B.C., a famous astronomer of that time, named Hipparchus, was making a star map of the “celestial sphere”. Hipparchus not only wanted to locate each star’s position on his map, but also to indicate the brightness of each star. To do this Hipparchus invented the concept of stellar magnitude. H ...
... In 125 B.C., a famous astronomer of that time, named Hipparchus, was making a star map of the “celestial sphere”. Hipparchus not only wanted to locate each star’s position on his map, but also to indicate the brightness of each star. To do this Hipparchus invented the concept of stellar magnitude. H ...
At the Heart of the Matter: The Blue White Dwarf in M 57. Paul Temple
... molecular or atomic carbon in any part of the spectrum. These stars are cool enough so that H atoms can join together into molecules, and so the signature of molecular H may also be observed. DZ Stars exhibiting only metal lines from species such as Ca and Fe. No H or He present. ...
... molecular or atomic carbon in any part of the spectrum. These stars are cool enough so that H atoms can join together into molecules, and so the signature of molecular H may also be observed. DZ Stars exhibiting only metal lines from species such as Ca and Fe. No H or He present. ...
JPL Small-Body Database Browser
... Classification of Stars • Furthermore, the classifications are each divided into tenths, with labels going from 0 to 9 – e.g. If a star is said to be a G-class star, it could, at its brightest, be classified as a G9 star, and at its dimmest, be classified as a G0 star. • The Sun is classified as a ...
... Classification of Stars • Furthermore, the classifications are each divided into tenths, with labels going from 0 to 9 – e.g. If a star is said to be a G-class star, it could, at its brightest, be classified as a G9 star, and at its dimmest, be classified as a G0 star. • The Sun is classified as a ...
Characteristics of stars
... • Many stars are about the size of the sun, which is a medium sized star. • White dwarfs are about the size of Earth. • Neutron stars are about 20KM (smallest) • Giant stars and super giant stars. If our sun were a super giant star it would fill our solar system as far out as Jupiter. ...
... • Many stars are about the size of the sun, which is a medium sized star. • White dwarfs are about the size of Earth. • Neutron stars are about 20KM (smallest) • Giant stars and super giant stars. If our sun were a super giant star it would fill our solar system as far out as Jupiter. ...
Size Color and Temperature
... Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse i ...
... Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse i ...
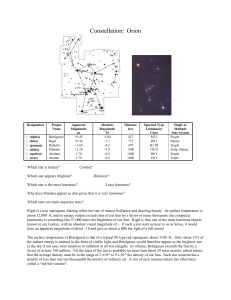
Orion
... Why does Mintaka appear so dim given that it is very luminous? Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of ma ...
... Why does Mintaka appear so dim given that it is very luminous? Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of ma ...
lifedeath - University of Glasgow
... Hydrogen fusion – fuelling a star’s nuclear furnace H = Hydrogen He = Helium ...
... Hydrogen fusion – fuelling a star’s nuclear furnace H = Hydrogen He = Helium ...
Chapter 28 – Stars and Galaxies
... 2. Stellar mass is expressed as multiples of the sun’s mass Betelgeuse’s mass – 20 solar masses F. Temperature and Color 1. Blue stars are hot 2. Red stars are cool G. Luminosity 1. The actual brightness of the star is luminosity 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star w ...
... 2. Stellar mass is expressed as multiples of the sun’s mass Betelgeuse’s mass – 20 solar masses F. Temperature and Color 1. Blue stars are hot 2. Red stars are cool G. Luminosity 1. The actual brightness of the star is luminosity 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star w ...
The Milky Way
... Constellations The stars in constellations are not physically close to each other in space. They were believed to represent great heroes and mythological figures. Their position in the sky seemed to tell stories that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years. Different ...
... Constellations The stars in constellations are not physically close to each other in space. They were believed to represent great heroes and mythological figures. Their position in the sky seemed to tell stories that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years. Different ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... • Supergiants that run out of fuel end in a massive explosion • Many nuclear fusion reactions occur and new elements form and explode into space • The debris from the explosion is the source for a new nebula • What remains of the star depends on the original size of the star ...
... • Supergiants that run out of fuel end in a massive explosion • Many nuclear fusion reactions occur and new elements form and explode into space • The debris from the explosion is the source for a new nebula • What remains of the star depends on the original size of the star ...
Stellar Evolution
... • If the core’s mass is even greater/denser than a neutron star, it collapses. • Surface gravity is so great that no matter can escape it…not even electromagnetic ...
... • If the core’s mass is even greater/denser than a neutron star, it collapses. • Surface gravity is so great that no matter can escape it…not even electromagnetic ...
Stars and Constellations
... • They are formed in space in large clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. • Atoms inside the nebula accelerate inward due to the force of gravity and they collide rapidly with each other, causing the center of the nebula to become very dense and hot, causing the temperature of the protostar to rise ...
... • They are formed in space in large clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. • Atoms inside the nebula accelerate inward due to the force of gravity and they collide rapidly with each other, causing the center of the nebula to become very dense and hot, causing the temperature of the protostar to rise ...
Table Number: _____
... Using the distance modulus equation, d= 10 x 10(m-M)/5 , in the Introduction to calculate the distance to the cluster in parsecs. Then convert your answer to light years. Show all work in the ...
... Using the distance modulus equation, d= 10 x 10(m-M)/5 , in the Introduction to calculate the distance to the cluster in parsecs. Then convert your answer to light years. Show all work in the ...
Light from stars part II
... Flux: the total light Energy emitted by one square meter of an object every second ...
... Flux: the total light Energy emitted by one square meter of an object every second ...
Death of Stars
... Birth Place of Stars: Dark and cold inter-stellar clouds These clouds are made of more hydrogen than helium. These clouds have very small amount of heavier elements. ...
... Birth Place of Stars: Dark and cold inter-stellar clouds These clouds are made of more hydrogen than helium. These clouds have very small amount of heavier elements. ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.