STARS Chapter 8 Section 1
... one year, or 186,282 miles per second, or 5.88 trillion miles**** This quasar is 10 billion light years from Earth ...
... one year, or 186,282 miles per second, or 5.88 trillion miles**** This quasar is 10 billion light years from Earth ...
Lifetimes of stars
... • The Sun (and all stars) will eventually run out of fuel (hydrogen in regions where it is hot enough for fusion). • If all the hydrogen in the Sun could fuse to helium, the Sun’s lifetime would be 100 billion years. • But, by the time about 10% of the Sun’s H has been converted into He the solar st ...
... • The Sun (and all stars) will eventually run out of fuel (hydrogen in regions where it is hot enough for fusion). • If all the hydrogen in the Sun could fuse to helium, the Sun’s lifetime would be 100 billion years. • But, by the time about 10% of the Sun’s H has been converted into He the solar st ...
Why Is the Sun a Star
... star? If an object is massive enough its gravity will be strong enough to begin crushing the matter at the core and a star is “born”. Imagine that we could pile everything we could get our hands on and throw it into a pile in the center of the grass field at school. Eventually if our pile got big en ...
... star? If an object is massive enough its gravity will be strong enough to begin crushing the matter at the core and a star is “born”. Imagine that we could pile everything we could get our hands on and throw it into a pile in the center of the grass field at school. Eventually if our pile got big en ...
DOC
... 12. I can compare how stars evolved based on their mass (examples black hole, neutron star and white dwarf). 13. I can recall why the length of a star’s life depends on its mass. 14. I can recall that parallax and the inverse square law are used to determine distance of stars and galaxies. 1 ...
... 12. I can compare how stars evolved based on their mass (examples black hole, neutron star and white dwarf). 13. I can recall why the length of a star’s life depends on its mass. 14. I can recall that parallax and the inverse square law are used to determine distance of stars and galaxies. 1 ...
File
... following causes the phases of the moon? A. Over the course of a month, different parts of the moon’s reflected sunlight are visible from Earth. B. The moon reflects differing amounts of sunlight as it revolves around the Earth. C. The moon rotates more slowly than the Earth, with one rotation every ...
... following causes the phases of the moon? A. Over the course of a month, different parts of the moon’s reflected sunlight are visible from Earth. B. The moon reflects differing amounts of sunlight as it revolves around the Earth. C. The moon rotates more slowly than the Earth, with one rotation every ...
EARTH SCIENCE KEY NOTES
... 2. OUTER PLANETS (JOVIAN PLANETS) – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune (also called the Gas Giants). Gas Surfaces Low density High Mass Evolution of the Solar System: Scientists believe that our solar system started to form approximately 4.6 billion years ago (see handout on beginning of the ...
... 2. OUTER PLANETS (JOVIAN PLANETS) – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune (also called the Gas Giants). Gas Surfaces Low density High Mass Evolution of the Solar System: Scientists believe that our solar system started to form approximately 4.6 billion years ago (see handout on beginning of the ...
Constellation
... pearls' surrounding an Exploding Star Two decades ago, astronomers spotted one of the brightest exploding stars in more than 400 years. This image shows the entire region around the supernova. The most prominent feature in the image is a ring with dozens of bright spots. A shock wave of material unl ...
... pearls' surrounding an Exploding Star Two decades ago, astronomers spotted one of the brightest exploding stars in more than 400 years. This image shows the entire region around the supernova. The most prominent feature in the image is a ring with dozens of bright spots. A shock wave of material unl ...
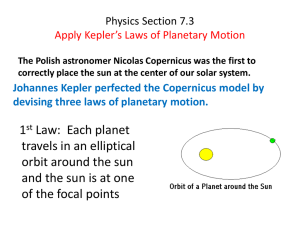
Physics Section 7.3 Apply Kepler*s Laws of Planetary
... A large planet orbiting a distant star is discovered. The planet’s orbital distance is 7.5 x 1010 m, and its period is 105.5 days. Calculate the mass of the star and the planets orbital speed. ...
... A large planet orbiting a distant star is discovered. The planet’s orbital distance is 7.5 x 1010 m, and its period is 105.5 days. Calculate the mass of the star and the planets orbital speed. ...
Patterns in the Night Sky Constellation: a grouping of stars, as
... geographical coordinates of their location. Geostationary Orbit Satellites: Directly above the equator; appear motionless in the sky, which makes them useful for communications and other commercial industries because they can be linked to antennas on Earth. Communication industries use geostationary ...
... geographical coordinates of their location. Geostationary Orbit Satellites: Directly above the equator; appear motionless in the sky, which makes them useful for communications and other commercial industries because they can be linked to antennas on Earth. Communication industries use geostationary ...
Earth, Space and all that jazz… A long time ago, in the second
... Are the rocky planets orbiting our nearest star. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune makes eight. The final four are full of gas and for their size they’re lightweight. As telescopes improved in strength and accuracy, Discoveries were made within our own galaxy. Like how the Earth keeps spinning whi ...
... Are the rocky planets orbiting our nearest star. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune makes eight. The final four are full of gas and for their size they’re lightweight. As telescopes improved in strength and accuracy, Discoveries were made within our own galaxy. Like how the Earth keeps spinning whi ...
Space Science Distance Definitions
... that as light travels towards you, it is spreading out and covering a larger area. This idea is illustrated in this figure: ...
... that as light travels towards you, it is spreading out and covering a larger area. This idea is illustrated in this figure: ...
The Danger of Deadly Cosmic Explosions
... • Not much harm if further. • SN material in sediments. • 1 SN/100 years in our galaxy • Close 1 per 100million years. • Good news: our neighbors are peaceful. • Bad news: when one shows signs of blowing, it is time to migrate. ...
... • Not much harm if further. • SN material in sediments. • 1 SN/100 years in our galaxy • Close 1 per 100million years. • Good news: our neighbors are peaceful. • Bad news: when one shows signs of blowing, it is time to migrate. ...
PowerPoint - Earth Science with Mrs. Wilson
... get a view without them in the way. These stars are in our view as we are looking out of our galaxy! ...
... get a view without them in the way. These stars are in our view as we are looking out of our galaxy! ...
Sun, Stars, HR Diagram
... cooler and more luminous the same temperature and larger hotter and larger ...
... cooler and more luminous the same temperature and larger hotter and larger ...
After Dark in Allenspark
... January 9: Since January 1, Venus has been getting much lower in the sky at sunset each night. This is probably the last night to see Venus, but only if you have a good Western horizon. January 12: In the morning eastern sky, Jupiter is less than 1 degree North of the star Alpha Libra (that is, the ...
... January 9: Since January 1, Venus has been getting much lower in the sky at sunset each night. This is probably the last night to see Venus, but only if you have a good Western horizon. January 12: In the morning eastern sky, Jupiter is less than 1 degree North of the star Alpha Libra (that is, the ...
Test #3
... a. the ratio of the angular separation from the center of mass of each of the stars. b. the distance to the binary and its radial velocity. c. the semi major axis and period of the orbit. d. the radial velocities of the two stars. 15. Blue stars are _____ than red stars a. hotter b. cooler c. larger ...
... a. the ratio of the angular separation from the center of mass of each of the stars. b. the distance to the binary and its radial velocity. c. the semi major axis and period of the orbit. d. the radial velocities of the two stars. 15. Blue stars are _____ than red stars a. hotter b. cooler c. larger ...
Part I: Moons, Asteroids, and Comets
... 1. What is a moon? _________________________________________________________________________ 2. How many moons are in our solar system? _________________________________________________________________________ 3. Do all planets have moons? _________________________________________________________ ...
... 1. What is a moon? _________________________________________________________________________ 2. How many moons are in our solar system? _________________________________________________________________________ 3. Do all planets have moons? _________________________________________________________ ...
SOLUTIONS ASTROPHYSICS – OPTION D 2015-17
... The question is meaningless within the big bang model since by definition time started with the big bang. It is as meaningless as to ask for a place 1 km north of the north pole. However, recent developments within string theory suggest that the question may not be as meaningless as it appears. See ...
... The question is meaningless within the big bang model since by definition time started with the big bang. It is as meaningless as to ask for a place 1 km north of the north pole. However, recent developments within string theory suggest that the question may not be as meaningless as it appears. See ...
Stars - Madison County Schools
... Life Cycle of Stars • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it ...
... Life Cycle of Stars • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it ...
class17
... How would the apparent brightness of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times farther away? ...
... How would the apparent brightness of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times farther away? ...
The H-R Diagram
... larger, and more massive than the Sun. The Sun is near with an absolute magnitude of MV=+5 and a spectral type G2. Like all m.s. stars it is of luminosity class V. Those stars to the lower right are less massive, cooler, and smaller than the Sun. The main sequence contains about 80% of all stars. St ...
... larger, and more massive than the Sun. The Sun is near with an absolute magnitude of MV=+5 and a spectral type G2. Like all m.s. stars it is of luminosity class V. Those stars to the lower right are less massive, cooler, and smaller than the Sun. The main sequence contains about 80% of all stars. St ...
Interstellar clouds
... • It has an extremely low density of 1 atom per cm3, about 10 billionth the density of gas created by our best vacuums here on earth. ...
... • It has an extremely low density of 1 atom per cm3, about 10 billionth the density of gas created by our best vacuums here on earth. ...
Distance and Luminosity (new 2012)
... Proxima Centauri (4.3ly away) Astronomical Unit, AU = average distance between Earth and Sun (1 AU=150 million km) Parsec, pc ...
... Proxima Centauri (4.3ly away) Astronomical Unit, AU = average distance between Earth and Sun (1 AU=150 million km) Parsec, pc ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.