The Life Cycle of Stars
... mass to other stars like Sirius, and Proxima Centauri. Based on its mass, will our sun be around for a while, WHY? Realize that once our Sun starts to run out of hydrogen fuel and has exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size t ...
... mass to other stars like Sirius, and Proxima Centauri. Based on its mass, will our sun be around for a while, WHY? Realize that once our Sun starts to run out of hydrogen fuel and has exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size t ...
Unit 6--Astronomy
... b. blue d. orange 3.Gamma rays, X-rays, visible light, and radio waves are all types of ____. a. nuclear energy c. ultraviolet radiation b. chromatic aberration d. electromagnetic radiation 4.Which of the following refers to the change in wavelength that occurs when an object moves toward or away fr ...
... b. blue d. orange 3.Gamma rays, X-rays, visible light, and radio waves are all types of ____. a. nuclear energy c. ultraviolet radiation b. chromatic aberration d. electromagnetic radiation 4.Which of the following refers to the change in wavelength that occurs when an object moves toward or away fr ...
1. Star A has a distance of 3 parsecs. What is its parallax angle? 1a
... Star I is of spectral type O2 and star II is of spectral type O3. Which star is hotter? Star I. Which of the following stars is the most massive: a) G2V b) K8V c) O1V? c) because its the hottest and hence brightest and hence most luminous. What do all the stars in question 13) have in common? They a ...
... Star I is of spectral type O2 and star II is of spectral type O3. Which star is hotter? Star I. Which of the following stars is the most massive: a) G2V b) K8V c) O1V? c) because its the hottest and hence brightest and hence most luminous. What do all the stars in question 13) have in common? They a ...
05spectralclasses
... • Some are very luminous compared to main sequence stars of their spectral class (implied large radius) giants • Some are very underluminous for their class white dwarfs ...
... • Some are very luminous compared to main sequence stars of their spectral class (implied large radius) giants • Some are very underluminous for their class white dwarfs ...
IV International Astronomy Olympiad
... military ships: to construct very small black holes from their material (patent yzarc048UA7). Estimate the diameter of a black hole constructed using this patent from a ship with the mass of 5000 tn (1 tn = 1000 kg). What physical object has a size of the same order of magnitude? Describe propagatio ...
... military ships: to construct very small black holes from their material (patent yzarc048UA7). Estimate the diameter of a black hole constructed using this patent from a ship with the mass of 5000 tn (1 tn = 1000 kg). What physical object has a size of the same order of magnitude? Describe propagatio ...
chapter-30-pp
... Notice that the lower the number of the star on the chart, the brighter it will appear to us. Absolute magnitude: the brightness that a star would have at a distance of 32.6 lightyears from Earth---in other words, if all stars were the same distance from Earth this is how they would look. So, the br ...
... Notice that the lower the number of the star on the chart, the brighter it will appear to us. Absolute magnitude: the brightness that a star would have at a distance of 32.6 lightyears from Earth---in other words, if all stars were the same distance from Earth this is how they would look. So, the br ...
Phys133-Sample MT2
... 6) No stars have been found with masses greater than 200-300 times our Sun because A) they would fragment into binary stars because of their rapid rotation. B) they would generate so much power that they would blow themselves apart. C) they are not bright enough to be seen nearby. D) molecular cloud ...
... 6) No stars have been found with masses greater than 200-300 times our Sun because A) they would fragment into binary stars because of their rapid rotation. B) they would generate so much power that they would blow themselves apart. C) they are not bright enough to be seen nearby. D) molecular cloud ...
The Sun and Stardust
... How are other elements made? Massive stars burn their hydrogen (and helium and carbon-nitrogen-oxygen) very quickly. At the end of their life heavier (metals) are formed such as vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, and nickel etc. Then massive stars (about ten times more massive than the Su ...
... How are other elements made? Massive stars burn their hydrogen (and helium and carbon-nitrogen-oxygen) very quickly. At the end of their life heavier (metals) are formed such as vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, and nickel etc. Then massive stars (about ten times more massive than the Su ...
Study Guide
... State magnitudes of stars from the H-R diagram. White dwarfs, main sequence, giants, supergiants (be able to use the H-R diagram to label and classify) List the spectral classes for stars in order. O,B,A,F,G,K,M State the name and shape of our galaxy. The Milky Way – it is spiral shaped Desc ...
... State magnitudes of stars from the H-R diagram. White dwarfs, main sequence, giants, supergiants (be able to use the H-R diagram to label and classify) List the spectral classes for stars in order. O,B,A,F,G,K,M State the name and shape of our galaxy. The Milky Way – it is spiral shaped Desc ...
PHY 150
... blown off after leaving the main sequence, probably becoming a planetary nebula. The white dwarf will probably be about 0.8 MSun. ...
... blown off after leaving the main sequence, probably becoming a planetary nebula. The white dwarf will probably be about 0.8 MSun. ...
Universe 8e Lecture Chapter 17 Nature of Stars
... Main-sequence stars are stars like the Sun but with different masses. The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation between mass and luminosity for mainsequence stars. The greater the mass of a mainsequence star, the greater its luminosity (and also the greater its radius and surface t ...
... Main-sequence stars are stars like the Sun but with different masses. The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation between mass and luminosity for mainsequence stars. The greater the mass of a mainsequence star, the greater its luminosity (and also the greater its radius and surface t ...
Patterns in the Sky - Plano Independent School District
... stars that make up the pan or dipper and the 3 stars in the tail. You use the 2 stars on the end of the pan as the pointing stars to find Polaris the North Star in the tail of the Little Dipper. The 2 stars that are the pointers are Dubhe—the top star and Merak—the bottom star in the pan. The handle ...
... stars that make up the pan or dipper and the 3 stars in the tail. You use the 2 stars on the end of the pan as the pointing stars to find Polaris the North Star in the tail of the Little Dipper. The 2 stars that are the pointers are Dubhe—the top star and Merak—the bottom star in the pan. The handle ...
Section 25.2 Stellar Evolution
... remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and collapse into a white dwarf. Death of Medium-Mass Stars Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as lowmass stars. During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium- ...
... remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and collapse into a white dwarf. Death of Medium-Mass Stars Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as lowmass stars. During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium- ...
Chapter 28 – Stars and Galaxies
... There are millions of light years between galaxies Sun belongs to the Milky Way Galaxy which is a spiral galaxy Milky Way belongs to the Local Group of about 30 galaxies ...
... There are millions of light years between galaxies Sun belongs to the Milky Way Galaxy which is a spiral galaxy Milky Way belongs to the Local Group of about 30 galaxies ...
Mountain Skies - Pisgah Astronomical Research Institute
... in particular at the middle star and you will notice it is a bit fuzzy;; it is called the “smoking star” in some Native American traditions. A pair of binoculars or a telescope reveals this to be the beautiful “Great Nebula of Orion,” an immense cloud ...
... in particular at the middle star and you will notice it is a bit fuzzy;; it is called the “smoking star” in some Native American traditions. A pair of binoculars or a telescope reveals this to be the beautiful “Great Nebula of Orion,” an immense cloud ...
handout
... C. We receive _________ energy from the sun when it is shining onto the Earth’s surface under a ___________________ angle of incidence D. The seasons are ___________ related to Earth’s distance from the _____________. In fact, Earth is slightly ________________ to the sun in ____________ than in sum ...
... C. We receive _________ energy from the sun when it is shining onto the Earth’s surface under a ___________________ angle of incidence D. The seasons are ___________ related to Earth’s distance from the _____________. In fact, Earth is slightly ________________ to the sun in ____________ than in sum ...
Homework #2
... 4) Given below is a HR-diagram prepared from data taken by the Hipparcos satellite using 4477 stars whose parallax distance is accurately determined. Consider a main sequence star with color index B-V = 0.65. What would be its absolute magnitude (as accurately as you can read the graph)? If another ...
... 4) Given below is a HR-diagram prepared from data taken by the Hipparcos satellite using 4477 stars whose parallax distance is accurately determined. Consider a main sequence star with color index B-V = 0.65. What would be its absolute magnitude (as accurately as you can read the graph)? If another ...
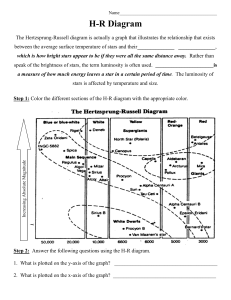
H-R Diagram Student
... H-R Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of ...
... H-R Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of ...
Word Pro - Smvocab
... Magnification - the apparent increase in size of an object viewed with a lens. Magnitude - the degree of brightness of a star. Mathematician - a scientist who deals with quantities and forms using numbers. Milky Way - a broad band of light across the heavens made up of stars and nebulae, our galaxy. ...
... Magnification - the apparent increase in size of an object viewed with a lens. Magnitude - the degree of brightness of a star. Mathematician - a scientist who deals with quantities and forms using numbers. Milky Way - a broad band of light across the heavens made up of stars and nebulae, our galaxy. ...
Document
... The Sun is a yellow dwarf star. It is believed to be over 4 billion years old. It is nearly 99% of the galaxy mass. ...
... The Sun is a yellow dwarf star. It is believed to be over 4 billion years old. It is nearly 99% of the galaxy mass. ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.