HW 5 Solutions What are “black smokers?” Where in our solar
... Black smokers are volcanic vents at the bottom of earth’s oceans. It was recently discovered that some of the oldest life forms on earth live in these harsh environments. This was a revolution in our understanding of life, since these organisms gain their energy not from the sun but from the interio ...
... Black smokers are volcanic vents at the bottom of earth’s oceans. It was recently discovered that some of the oldest life forms on earth live in these harsh environments. This was a revolution in our understanding of life, since these organisms gain their energy not from the sun but from the interio ...
Stellar Luminosity
... Stellar Luminosities • Stellar luminosities vary from 0.0001 L¤–1,000,000 L¤, ten orders of magnitude • Note that most of the stars in this image are at the same distance, so their relative apparent brightness is the same as their relative l ...
... Stellar Luminosities • Stellar luminosities vary from 0.0001 L¤–1,000,000 L¤, ten orders of magnitude • Note that most of the stars in this image are at the same distance, so their relative apparent brightness is the same as their relative l ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... between brightness and temp. Hotter things are brighter Hotter temp = more energy is radiated. Bigger stars are brighter. Bigger surface area = more energy radiated. ...
... between brightness and temp. Hotter things are brighter Hotter temp = more energy is radiated. Bigger stars are brighter. Bigger surface area = more energy radiated. ...
WebQuest-The-Life-Cycle-of-Stars-1
... and see pictures of the protostars of M16: The Eagle Nebula and other nebulae on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to other stars. 1) Compare the mass of our sun to Sirius? To Proxima Centauri? 2) Based on its mass, will our sun be aro ...
... and see pictures of the protostars of M16: The Eagle Nebula and other nebulae on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to other stars. 1) Compare the mass of our sun to Sirius? To Proxima Centauri? 2) Based on its mass, will our sun be aro ...
spectral-type
... increases on the Main Sequence as the temperature and luminosity increase. As theory predicts. ...
... increases on the Main Sequence as the temperature and luminosity increase. As theory predicts. ...
Eclipsing Binaries
... increases on the Main Sequence as the temperature and luminosity increase. As theory predicts. Furthermore, Mass does not correlate with luminosity for giant, evolved stars. Giants might have a large mass, or they might have a small mass, but still they are very luminous. Also the mass of a white dw ...
... increases on the Main Sequence as the temperature and luminosity increase. As theory predicts. Furthermore, Mass does not correlate with luminosity for giant, evolved stars. Giants might have a large mass, or they might have a small mass, but still they are very luminous. Also the mass of a white dw ...
Light Years Away
... 3. Reflected sunlight from the Moon's surface takes ______seconds to travel the distance to the Earth. A. 1.2 seconds B. 1.2 minutes C. 1.2 hours D. 1.2 days ...
... 3. Reflected sunlight from the Moon's surface takes ______seconds to travel the distance to the Earth. A. 1.2 seconds B. 1.2 minutes C. 1.2 hours D. 1.2 days ...
stars
... huge explosion. • This huge explosion was known as The Big Bang. • Scientist believe that this huge explosion gave birth to the stars and planets ...
... huge explosion. • This huge explosion was known as The Big Bang. • Scientist believe that this huge explosion gave birth to the stars and planets ...
Telescopes (continued). Properties of Stars.
... Spectral Type The surface temperature also determines the line spectrum of a star. Hot stars display lines of highly ionized elements, while cool stars show molecular lines. Stars are classified by assigning a spectral type. The hottest stars are called spectral type O, followed by B, A, F, G, K, M ...
... Spectral Type The surface temperature also determines the line spectrum of a star. Hot stars display lines of highly ionized elements, while cool stars show molecular lines. Stars are classified by assigning a spectral type. The hottest stars are called spectral type O, followed by B, A, F, G, K, M ...
a. Recognize the physical attributes of stars in the night sky such as
... a. they are so much dimmer than the sun b. they are so much smaller than the sun c. their light is lessened by our atmosphere d. they are so much further away than the sun Answer: d What are patterns of stars in the sky called? a. attributes b. constellations c. revolutions d. rotations Answer: b A ...
... a. they are so much dimmer than the sun b. they are so much smaller than the sun c. their light is lessened by our atmosphere d. they are so much further away than the sun Answer: d What are patterns of stars in the sky called? a. attributes b. constellations c. revolutions d. rotations Answer: b A ...
Stellar Properties
... what would be the distance to the star? A)1/5, b)1. c)5, d)25 pc 2. Star A and B have same luminosity. If star A is 4 times closer to Earth then star B, then _____ to earthly viewer.: a=A is 4 x brighter, b=B is 4x brighter, c=A is 16 times brighter d=B is 16 times brighter, e=A is 64x brighter 3. A ...
... what would be the distance to the star? A)1/5, b)1. c)5, d)25 pc 2. Star A and B have same luminosity. If star A is 4 times closer to Earth then star B, then _____ to earthly viewer.: a=A is 4 x brighter, b=B is 4x brighter, c=A is 16 times brighter d=B is 16 times brighter, e=A is 64x brighter 3. A ...
Stellar Evolution: After the Main Sequence
... ceases when the hydrogen has been exhausted in the core of a main-sequence star • This leaves a core of nearly pure helium surrounded by a shell through which hydrogen fusion works its way outward in the star • The core shrinks and becomes hotter, while the star’s outer layers expand and cool • The ...
... ceases when the hydrogen has been exhausted in the core of a main-sequence star • This leaves a core of nearly pure helium surrounded by a shell through which hydrogen fusion works its way outward in the star • The core shrinks and becomes hotter, while the star’s outer layers expand and cool • The ...
Review Guide
... 5. What type of galaxy contains both young and old stars? 6. What type of galaxy contains only old stars? 7. What type of galaxy contains only young stars? 8. Besides their shape what other characteristic distinguishes the different types of galaxies from each other? 9. Why do distant galaxies appea ...
... 5. What type of galaxy contains both young and old stars? 6. What type of galaxy contains only old stars? 7. What type of galaxy contains only young stars? 8. Besides their shape what other characteristic distinguishes the different types of galaxies from each other? 9. Why do distant galaxies appea ...
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Black Holes
... as plutonium-244, 244Pu, (81 million years). The short-lived isotopes are particularly interesting. If they formed in an exploding star, that explosion might have triggered the collapse of the huge interstellar cloud in which the Sun formed. ...
... as plutonium-244, 244Pu, (81 million years). The short-lived isotopes are particularly interesting. If they formed in an exploding star, that explosion might have triggered the collapse of the huge interstellar cloud in which the Sun formed. ...
- MrKowalik.com
... 4. If Earth and another celestial object were coming closer together, the electromagnetic waves are bunched together resulting in _____________________________________ 5. If Earth and another celestial object were moving apart, the electromagnetic waves are spread out causing a _____________________ ...
... 4. If Earth and another celestial object were coming closer together, the electromagnetic waves are bunched together resulting in _____________________________________ 5. If Earth and another celestial object were moving apart, the electromagnetic waves are spread out causing a _____________________ ...
The Inverse Square Law and Surface Area
... • There are several classes of stars with known power output. • Stars which have the same surface temperature ( and spectral characteristics) as the sun all have the same power output • We can readily calculate the power output of nearby stars and classify their power output and compare them with mo ...
... • There are several classes of stars with known power output. • Stars which have the same surface temperature ( and spectral characteristics) as the sun all have the same power output • We can readily calculate the power output of nearby stars and classify their power output and compare them with mo ...
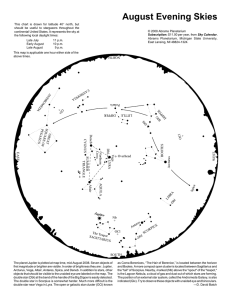
August Evening Skies
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2008. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2008. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
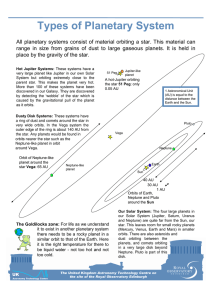
Types of Planetary System
... a ring of dust and comets around the star in very wide orbits. In the Vega system the outer edge of the ring is about 140 AU from the star. Any planets would be found in orbits nearer the star such as the Neptune-like planet in orbit around Vega. Orbit of Neptune-like planet around the star Vega: 65 ...
... a ring of dust and comets around the star in very wide orbits. In the Vega system the outer edge of the ring is about 140 AU from the star. Any planets would be found in orbits nearer the star such as the Neptune-like planet in orbit around Vega. Orbit of Neptune-like planet around the star Vega: 65 ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are double-star systems in which two stars revolve around e ...
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are double-star systems in which two stars revolve around e ...
Chapter 26
... 2. A star’s mass determines the star’s place on the main sequence and how long it will stay there. 3. A dwindling supply in a star’s core ultimately leads to the star’s death as a white dwarf, neutron star or black hole. ...
... 2. A star’s mass determines the star’s place on the main sequence and how long it will stay there. 3. A dwindling supply in a star’s core ultimately leads to the star’s death as a white dwarf, neutron star or black hole. ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.