Binocular Universe: Bikini Bottom
... The second double star is Dabih, or Beta (β) Capricorni, is just south of Algedi in the same field of view. While Algedi's two stars appear identically bright, Dabih's two stars look markedly different. The brighter sun, called Dabih-Major, shines at 3rd magnitude, while its companion, Dabih-Minor, ...
... The second double star is Dabih, or Beta (β) Capricorni, is just south of Algedi in the same field of view. While Algedi's two stars appear identically bright, Dabih's two stars look markedly different. The brighter sun, called Dabih-Major, shines at 3rd magnitude, while its companion, Dabih-Minor, ...
Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram March 16 −
... If stars A-D replaced the sun, would people be able to live in Michigan? a. b. c. d. e. ...
... If stars A-D replaced the sun, would people be able to live in Michigan? a. b. c. d. e. ...
Astronomy HOMEWORK Chapter 12 - 9th Edition 1. Consider a star
... Earth and life on it? What effects would moving Earth closer to the lower-mass Sun have? A 0.5 M⊙ star would have about 0.03 L⊙ (3% of the Sun’s luminosity). This makes things much colder, maybe -70 Celsius. No need for freezers, lots of ice for winter sports, and the year would be longer. Most like ...
... Earth and life on it? What effects would moving Earth closer to the lower-mass Sun have? A 0.5 M⊙ star would have about 0.03 L⊙ (3% of the Sun’s luminosity). This makes things much colder, maybe -70 Celsius. No need for freezers, lots of ice for winter sports, and the year would be longer. Most like ...
Star Gazing
... Cassiopeia: left V eats Polaris Cassiopeia: right V points to Andromeda (only galaxy visible to the naked eye); then Andromeda curves to Great Square of Pegasus • Deneb (NE) to Altair (southern tip of Summer Triangle) points to bottom left of The Teapot handle ...
... Cassiopeia: left V eats Polaris Cassiopeia: right V points to Andromeda (only galaxy visible to the naked eye); then Andromeda curves to Great Square of Pegasus • Deneb (NE) to Altair (southern tip of Summer Triangle) points to bottom left of The Teapot handle ...
Brightness + Magnitude of Stars
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
bYTEBoss lesson 3 life of star
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
Unit 1
... • We can follow a stars evolution on the HR diagram. • Lower mass stars move on to the main sequence, stay for a while, and eventually move through giant stages before becoming white dwarfs • Higher mass stars move rapidly off the main sequence and into the giant stages, eventually exploding in a su ...
... • We can follow a stars evolution on the HR diagram. • Lower mass stars move on to the main sequence, stay for a while, and eventually move through giant stages before becoming white dwarfs • Higher mass stars move rapidly off the main sequence and into the giant stages, eventually exploding in a su ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... Red 8. What type of star has a high temperature but a low luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) White dwarf 9. What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) Red supergiant 10. According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, what relationship exist b ...
... Red 8. What type of star has a high temperature but a low luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) White dwarf 9. What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) Red supergiant 10. According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, what relationship exist b ...
Astronomy Unit Study Guide
... B. the “star” in the middle of our solar system C. he formed three law’s of planetary motion D. a cloud of dust and gas in space E. the idea that the sun is the center of the solar system F. he developed a model of a sun-centered solar system G. a pattern of stars in the sky H. color that is emitted ...
... B. the “star” in the middle of our solar system C. he formed three law’s of planetary motion D. a cloud of dust and gas in space E. the idea that the sun is the center of the solar system F. he developed a model of a sun-centered solar system G. a pattern of stars in the sky H. color that is emitted ...
lecture12
... visible wavelengths. The same emission lines for Star B are observed to be at ultraviolet wavelengths. From these observations you conclude that: ...
... visible wavelengths. The same emission lines for Star B are observed to be at ultraviolet wavelengths. From these observations you conclude that: ...
Nov 2009
... (d) State the differences between the eventual fate of the Sun and Becrux after they leave the main sequence. ...
... (d) State the differences between the eventual fate of the Sun and Becrux after they leave the main sequence. ...
The Brightness of Stars
... a certain color range The filters are simply colored glass that goes over the mirror or lens of a telescope Astronomers say Vega has an MV of 0, which means Vega has an absolute magnitude of 0 in the V (for visible--no filters) color band ...
... a certain color range The filters are simply colored glass that goes over the mirror or lens of a telescope Astronomers say Vega has an MV of 0, which means Vega has an absolute magnitude of 0 in the V (for visible--no filters) color band ...
$doc.title
... cruising with a speed of 477 km/s outward from the center of our Galaxy. If the spectral type of the star is B5V, and the apparent magnitude is mV = 13.0 mag, estimate that this star is fr ...
... cruising with a speed of 477 km/s outward from the center of our Galaxy. If the spectral type of the star is B5V, and the apparent magnitude is mV = 13.0 mag, estimate that this star is fr ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 1
... A. They go through first red giant, helium burning in the core, and double shell burning phases. B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhil ...
... A. They go through first red giant, helium burning in the core, and double shell burning phases. B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhil ...
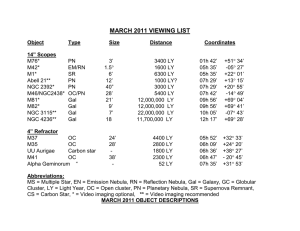
March
... M82 is an irregular galaxy of 8th magnitude in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh-MAY-jer). Also known as the Cigar Galaxy for it’s elongated shape, M82 is also about 12 million Light Years distant. The close encounter with M81 described above distorted the shape of this irregular galaxy, creatin ...
... M82 is an irregular galaxy of 8th magnitude in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh-MAY-jer). Also known as the Cigar Galaxy for it’s elongated shape, M82 is also about 12 million Light Years distant. The close encounter with M81 described above distorted the shape of this irregular galaxy, creatin ...
www.NewYorkScienceTeacher.org/review
... What causes the dark bands observed in a solar spectrum? a. the emission of specific elements b. different chemical elements which absorb light at specific wavelengths c. highly compressed, glowing gas d. warmer gas in front of a source that emits a continuous spectrum The apparent shift in a star’s ...
... What causes the dark bands observed in a solar spectrum? a. the emission of specific elements b. different chemical elements which absorb light at specific wavelengths c. highly compressed, glowing gas d. warmer gas in front of a source that emits a continuous spectrum The apparent shift in a star’s ...
Stars
... • The distance which a ray of light would travel in one ‘Earth’ year • About 6,000,000,000,000 (6 trillion) miles • 186,000 miles per second ...
... • The distance which a ray of light would travel in one ‘Earth’ year • About 6,000,000,000,000 (6 trillion) miles • 186,000 miles per second ...
Star Properties and Stellar Evolution
... 1. Pulsating stars – expand and contract 2. Cepheid Variables – used to find distances to galaxies that contain them 3. Eclipsing Binaries – 2 stars revolve around each other ...
... 1. Pulsating stars – expand and contract 2. Cepheid Variables – used to find distances to galaxies that contain them 3. Eclipsing Binaries – 2 stars revolve around each other ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.