How do stars form?
... and the H-R Diagram • What happens when a star exhausts its nuclear fuel? • Depends on size • Star core collapses on itself, but heats the outer envelope. • Result may be: White dwarf, white dwarf with planetary nebula, red giant, neutron star or black hole. ...
... and the H-R Diagram • What happens when a star exhausts its nuclear fuel? • Depends on size • Star core collapses on itself, but heats the outer envelope. • Result may be: White dwarf, white dwarf with planetary nebula, red giant, neutron star or black hole. ...
Arcturus and Pollux
... • “Castor and Pollux” according to Roman mythology. Zeus seduced Leda by disguising himself as a swan. Castor was born by King of Sparta, Pollux by Zeus. Castor died, Pollux wanted to join him in Hades, so Zeus was sympathetic and placed both in the sky. • 17th Brightest star in the sky • 33.7 light ...
... • “Castor and Pollux” according to Roman mythology. Zeus seduced Leda by disguising himself as a swan. Castor was born by King of Sparta, Pollux by Zeus. Castor died, Pollux wanted to join him in Hades, so Zeus was sympathetic and placed both in the sky. • 17th Brightest star in the sky • 33.7 light ...
11.1 Stars - St John Brebeuf
... It is estimated there are more stars in the universe than there are grains of sand on all the beaches on Earth. By peering through the interstellar matter (dust and gases), astronomers can observe the birth of stars. ...
... It is estimated there are more stars in the universe than there are grains of sand on all the beaches on Earth. By peering through the interstellar matter (dust and gases), astronomers can observe the birth of stars. ...
Stars and telescopes
... c)No more H(very little), He turns into C More energy HHe and HeC, gravity cant hold on ahhh! ...
... c)No more H(very little), He turns into C More energy HHe and HeC, gravity cant hold on ahhh! ...
8th Grade Midterm Test Review
... condensed to form a central core and a protoplanetary disk. The central core became a protostar that was compressed by gravity until it became hot enough to begin nuclear fusion, at which point it became a star (the sun). In the protoplanetary disk, the matter collided to form ...
... condensed to form a central core and a protoplanetary disk. The central core became a protostar that was compressed by gravity until it became hot enough to begin nuclear fusion, at which point it became a star (the sun). In the protoplanetary disk, the matter collided to form ...
Study Guide - Universe Exam key 2014-15 v2
... 4. Make a drawing of each type of galaxy and label them. Include 1-2 facts about each one. Indicate which one represents our own galaxy. Spiral Galaxy looks like a pinwheel and is the type of galaxy we live in. Elliptical galaxies look like flattened balls. The most common. Irregular Galaxies have n ...
... 4. Make a drawing of each type of galaxy and label them. Include 1-2 facts about each one. Indicate which one represents our own galaxy. Spiral Galaxy looks like a pinwheel and is the type of galaxy we live in. Elliptical galaxies look like flattened balls. The most common. Irregular Galaxies have n ...
20081 Study Guide_77-120
... Similarly, astronomers detect black holes by their gravitational effects on nearby stars, gas, or dust. ...
... Similarly, astronomers detect black holes by their gravitational effects on nearby stars, gas, or dust. ...
PH142 - Mohawk Valley Community College
... This course covers these topics: the sun and other stars, multiple star systems, the Milky Way and other galaxies, nebulae, intergalactic material, cosmology and the evolution of stars, pulsars, and black holes. Laboratory sessions may be scheduled in the evening. II. Texts and Laboratory Materials ...
... This course covers these topics: the sun and other stars, multiple star systems, the Milky Way and other galaxies, nebulae, intergalactic material, cosmology and the evolution of stars, pulsars, and black holes. Laboratory sessions may be scheduled in the evening. II. Texts and Laboratory Materials ...
astronomy - Mr. Barnard
... At approximately which position is Earth’s solar system located? (1) A (3) C (2) B (4) D __2__7. The Milky Way galaxy is best described as (1)a constellation visible to everyone on Earth (2)a spiral-shaped formation composed of billions of stars (3)a region in space between the orbits of Mars and Ju ...
... At approximately which position is Earth’s solar system located? (1) A (3) C (2) B (4) D __2__7. The Milky Way galaxy is best described as (1)a constellation visible to everyone on Earth (2)a spiral-shaped formation composed of billions of stars (3)a region in space between the orbits of Mars and Ju ...
Notes on Sun-Earth-Moon (pg. 119)
... Only stars with more than 40 times the mass of the Sun form black holes when they die. This happens after a supernova. 10. Describe what happens to an average star and a massive star when each runs out of fuel. Small and medium stars become white dwarfs and eventually black dwarfs. A giant star can ...
... Only stars with more than 40 times the mass of the Sun form black holes when they die. This happens after a supernova. 10. Describe what happens to an average star and a massive star when each runs out of fuel. Small and medium stars become white dwarfs and eventually black dwarfs. A giant star can ...
Stars and Their Characteristics
... • Constellation- groups of stars that appear to form patterns – 88 constellations can be seen from n. and s. hemispheres – So far away that only after thousands of years might the motions be observed – Big Dipper- asterism (small-star grouping) • Part of Ursa Major- Great Bear ...
... • Constellation- groups of stars that appear to form patterns – 88 constellations can be seen from n. and s. hemispheres – So far away that only after thousands of years might the motions be observed – Big Dipper- asterism (small-star grouping) • Part of Ursa Major- Great Bear ...
Final Exam Review (Word doc)
... 44. If two stars are on the main sequence, and one is more luminous than the other, we can be sure that the more luminous star is the more massive. 45. Giant stars are more rare than main sequence stars because the giant stage is very short compared to the main sequence stage. 46. The event that mar ...
... 44. If two stars are on the main sequence, and one is more luminous than the other, we can be sure that the more luminous star is the more massive. 45. Giant stars are more rare than main sequence stars because the giant stage is very short compared to the main sequence stage. 46. The event that mar ...
14_creationism
... Quantum mechanics says these electrons can only have discrete energies when they are orbiting the nucleus. A spectral line is emitted when an electron jumps from one energy to another. ...
... Quantum mechanics says these electrons can only have discrete energies when they are orbiting the nucleus. A spectral line is emitted when an electron jumps from one energy to another. ...
Astronomy
... 22. Which spectral class of stars (which letter) have the lowest temperature? _____________ ...
... 22. Which spectral class of stars (which letter) have the lowest temperature? _____________ ...
Study Guide for Quiz on Astronomy: The Moon, Sun and Stars
... 18. In which galaxy do we live? __________________________________What kind of galaxy is it? ___________ At what location in our galaxy is our solar system?________________________ 19. Which planet is considered Earth’s twin due to its size? _____________________________Besides its diameter, what el ...
... 18. In which galaxy do we live? __________________________________What kind of galaxy is it? ___________ At what location in our galaxy is our solar system?________________________ 19. Which planet is considered Earth’s twin due to its size? _____________________________Besides its diameter, what el ...
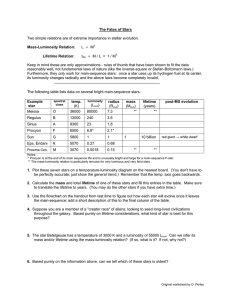
The Fates of Stars Mass-Luminosity Relation: Lifetime Relation:
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
Problem set 2
... specific intensity), you do not need to know the distance or luminosity, but only the temperature and angle subtended! Both of these are direct observables, unlike distance and luminosity . . . (c) Show that the answer to the previous part is the same as you would get by the more obvious but unneces ...
... specific intensity), you do not need to know the distance or luminosity, but only the temperature and angle subtended! Both of these are direct observables, unlike distance and luminosity . . . (c) Show that the answer to the previous part is the same as you would get by the more obvious but unneces ...
Astronomy Campus Assessment
... C. Galaxies can collide together, helping to create new stars in the process. D. Our galaxy, The Milky Way Galaxy, is one of billions of other galaxies located in the universe ...
... C. Galaxies can collide together, helping to create new stars in the process. D. Our galaxy, The Milky Way Galaxy, is one of billions of other galaxies located in the universe ...
Life cycle of a star
... When the helium core runs out, and the outer layers drift of away from the core as a gaseous shell, this gas that surrounds the core is called a ...
... When the helium core runs out, and the outer layers drift of away from the core as a gaseous shell, this gas that surrounds the core is called a ...
HELP
... even when the Moon is shining. Venus is covered with white clouds but Mars is not. a Suggest two reasons why Venus should be so bright. b Indicate which reason is likely to be the more important and say why. ...
... even when the Moon is shining. Venus is covered with white clouds but Mars is not. a Suggest two reasons why Venus should be so bright. b Indicate which reason is likely to be the more important and say why. ...
Support worksheet – Topic 3 Questions
... Suggest why the stellar parallax method is limited to distances of about 300 pc for Earth-based telescopes but can be extended to 1000 pc for satellite-based telescopes. ...
... Suggest why the stellar parallax method is limited to distances of about 300 pc for Earth-based telescopes but can be extended to 1000 pc for satellite-based telescopes. ...
Which has a hotter temperature, a red star or a blue star? How do
... The moon takes a full month to cycle through all of its phases (29.5 days, really). If the moon is a waining gibbous tonight, what will the phase be 2 weeks from now? Draw the position of the Earth, Moon, and Sun when the moon appears as a waining gibbous from the Earth. What fraction of a full cyc ...
... The moon takes a full month to cycle through all of its phases (29.5 days, really). If the moon is a waining gibbous tonight, what will the phase be 2 weeks from now? Draw the position of the Earth, Moon, and Sun when the moon appears as a waining gibbous from the Earth. What fraction of a full cyc ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.