+(J - cloudfront.net
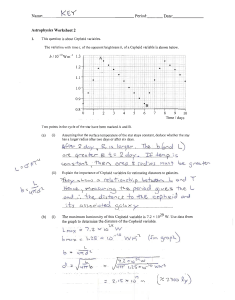
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
types of stars, luminosity, and brightness
... 13. You would NOT expect the same distribution of stars on the HR diagram if Apparent Brightness versus Temperature were plotted, because apparent brightness depends on the distance to each star, and every star is located at a different distance from us. So, some stars APPEAR dimmer, even though th ...
... 13. You would NOT expect the same distribution of stars on the HR diagram if Apparent Brightness versus Temperature were plotted, because apparent brightness depends on the distance to each star, and every star is located at a different distance from us. So, some stars APPEAR dimmer, even though th ...
2-2 wkst - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]
... ____________ 22. small hot stars that are dimmer than the sun ____________ 23. high-temperature stars that quickly use up their hydrogen ____________ 24. cool stars with high absolute magnitude ...
... ____________ 22. small hot stars that are dimmer than the sun ____________ 23. high-temperature stars that quickly use up their hydrogen ____________ 24. cool stars with high absolute magnitude ...
friends of the planetarium newsletter
... stars known, including one at more than 300 times the mass of our Sun; double the size that scientists thought heavyweight stars could reach. These colossal stars are millions of times brighter than the sun and shed mass through very powerful winds. A European research team discovered the massive st ...
... stars known, including one at more than 300 times the mass of our Sun; double the size that scientists thought heavyweight stars could reach. These colossal stars are millions of times brighter than the sun and shed mass through very powerful winds. A European research team discovered the massive st ...
SECTION 8: STARS- OBSERVING CONSTELLATIONS INTRODUCTION
... in 1 year. Light travels 300,000 km (186,000 miles) per second. It takes 8 ½ minutes for light to reach us from our Sun and 4.5 light years for light to reach us from the next closest star, Centauri Proxima. The distance between the Sun and Earth is 93 million miles. In this section, students will d ...
... in 1 year. Light travels 300,000 km (186,000 miles) per second. It takes 8 ½ minutes for light to reach us from our Sun and 4.5 light years for light to reach us from the next closest star, Centauri Proxima. The distance between the Sun and Earth is 93 million miles. In this section, students will d ...
Types of Stars
... determining the distance of stars. • The change in position of an object with respect to a distant background is called parallax. • As Earth moves in its orbit, astronomers are able to observe stars from two different positions. • Astronomers measure the parallax of nearby stars to ...
... determining the distance of stars. • The change in position of an object with respect to a distant background is called parallax. • As Earth moves in its orbit, astronomers are able to observe stars from two different positions. • Astronomers measure the parallax of nearby stars to ...
Night Sky Checklist April–May–June Unaided Eye Astronomy
... The Big Dipper is only a part of the large constellation Ursa Major, the Larger Bear, and seems to be known as a dipper only in North America and parts of Africa. This prominent group has had many other names in other parts of the world and in other times in history. The stars at the front of the Di ...
... The Big Dipper is only a part of the large constellation Ursa Major, the Larger Bear, and seems to be known as a dipper only in North America and parts of Africa. This prominent group has had many other names in other parts of the world and in other times in history. The stars at the front of the Di ...
Binary Orbits
... One star goes behind the other A. The two stars are sufficiently close B. One is large enough to block the other C. The inclination angle is close to 90 Stars are so close that thay cannot be distinguished, but detected due to reduction of light. ...
... One star goes behind the other A. The two stars are sufficiently close B. One is large enough to block the other C. The inclination angle is close to 90 Stars are so close that thay cannot be distinguished, but detected due to reduction of light. ...
SR Stellar Properties
... Name: ________________________________ Date: ___________________ Period: _________ H-R Diagram Scientists began to learn about stars by observing properties of stars, including brightness and color. Astronomers tried to make sense of the star data by grouping together stars with similar properties. ...
... Name: ________________________________ Date: ___________________ Period: _________ H-R Diagram Scientists began to learn about stars by observing properties of stars, including brightness and color. Astronomers tried to make sense of the star data by grouping together stars with similar properties. ...
Prep Homework Solutions for HW due 10/04/10
... in a close binary causes its mass to exceed the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.4 Msun, which is the maximum mass possible for a white dwarf. Above this mass, gravitational compression ignites fusion in the core, converting C and O to Nickel. The fusion blows the white dwarf apart since it is not composed ...
... in a close binary causes its mass to exceed the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.4 Msun, which is the maximum mass possible for a white dwarf. Above this mass, gravitational compression ignites fusion in the core, converting C and O to Nickel. The fusion blows the white dwarf apart since it is not composed ...
Name - MIT
... A) The rate that visible light from the Sun is being absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere B) The rate that hydrogen is being fused into helium in the Sun C) The rate that gamma rays are hitting the Earth’s atmosphere D) The rate that white dwarfs are being formed in the galaxy E) The rate that stars f ...
... A) The rate that visible light from the Sun is being absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere B) The rate that hydrogen is being fused into helium in the Sun C) The rate that gamma rays are hitting the Earth’s atmosphere D) The rate that white dwarfs are being formed in the galaxy E) The rate that stars f ...
Astronomy 110 Announcements: 11.1 Properties of Stars
... 330 (change from original schedule) • Homework #3 due Friday • Remember to hand in any extra-credit from observing ...
... 330 (change from original schedule) • Homework #3 due Friday • Remember to hand in any extra-credit from observing ...
25 August: Getting Oriented, Astronomical Coordinate Systems
... altitude angle due south, sets in the west • When the Sun sets, it gets dark and we see the stars and planets • The Moon “ “ “ “ “ • The Moon rises at a different time each night and is seen against a different constellation • The constellations in the evening sky are different in different seasons ...
... altitude angle due south, sets in the west • When the Sun sets, it gets dark and we see the stars and planets • The Moon “ “ “ “ “ • The Moon rises at a different time each night and is seen against a different constellation • The constellations in the evening sky are different in different seasons ...
Astronomy Unit Period
... __________ 4. Which of the following statements is true about a star? a. A star’s outer layers are hot and thin. b. A star’s outer layers are hot and dense. c. A star’s inner layers are cool and dense. d. A star’s inner layers are hot and dense. __________ 5. Some of the light that radiates from a s ...
... __________ 4. Which of the following statements is true about a star? a. A star’s outer layers are hot and thin. b. A star’s outer layers are hot and dense. c. A star’s inner layers are cool and dense. d. A star’s inner layers are hot and dense. __________ 5. Some of the light that radiates from a s ...
The Sun
... Light-Year: The distance light travels in a year. It is used to measure distances between stars. ...
... Light-Year: The distance light travels in a year. It is used to measure distances between stars. ...
binary star
... Death of Massive Stars • In contrast to sunlike stars, stars that are over three times the sun’s mass have relatively short life spans, which end in a supernova event. • A supernova is an exploding massive star that increases in brightness many thousands of times. • The massive star’s interior con ...
... Death of Massive Stars • In contrast to sunlike stars, stars that are over three times the sun’s mass have relatively short life spans, which end in a supernova event. • A supernova is an exploding massive star that increases in brightness many thousands of times. • The massive star’s interior con ...
measure
... Light travels 300,000 km every Second…… ……That’s about 10 million, million kilometres every year!!! ...
... Light travels 300,000 km every Second…… ……That’s about 10 million, million kilometres every year!!! ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... production rate and available fuel (mass) – Example: Star with 4L and 3M uses 4 times more mass for energy production, but has 3 times more mass, so its life time is a factor ¾=0.75 compared to the sun: 7.5 billion years ([0.75] goes in the box) ...
... production rate and available fuel (mass) – Example: Star with 4L and 3M uses 4 times more mass for energy production, but has 3 times more mass, so its life time is a factor ¾=0.75 compared to the sun: 7.5 billion years ([0.75] goes in the box) ...
(AU): Average distance from Earth to Sun
... Iron core of a high-mass star continues to collapse and becomes a super-dense Neutron Star. A teaspoon weighs 10 million tons! BUT iron core of a very-high-mass star collapses further and becomes … a Black Hole. ...
... Iron core of a high-mass star continues to collapse and becomes a super-dense Neutron Star. A teaspoon weighs 10 million tons! BUT iron core of a very-high-mass star collapses further and becomes … a Black Hole. ...
Note Taking Guide #2: Characteristics of Stars Welcome back! As
... A star’s apparent magnitude is how much light a star appears to give off when viewed from Earth. The closer a star is to Erath, the more light it appears to give off. Think of our sun versus Alpha Centauri; the sun appears to give off much more light, even though the two stars are actually very simi ...
... A star’s apparent magnitude is how much light a star appears to give off when viewed from Earth. The closer a star is to Erath, the more light it appears to give off. Think of our sun versus Alpha Centauri; the sun appears to give off much more light, even though the two stars are actually very simi ...
Introduction to the EarthESci 100Dr. Albanese, Tuesdays and
... 14. The large size of some of the volcanoes on Mars is due to an earlier period of plate tectonics. 15. Comets are not part of our solar system, but rather interstellar objects which occasionally pass by the sun. 16. The high surface temperature of Venus is caused largely by the presence of ammonia. ...
... 14. The large size of some of the volcanoes on Mars is due to an earlier period of plate tectonics. 15. Comets are not part of our solar system, but rather interstellar objects which occasionally pass by the sun. 16. The high surface temperature of Venus is caused largely by the presence of ammonia. ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.


![2-2 wkst - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009700019_1-9e7a7c15444658cfc76a04a9cf1ba291-300x300.png)




















