Analyzing Spectra
... 2. What are the five known substances in this activity? ________________________________________ Look closely at the spectrum below. Those black lines are caused by elements in the star's atmosphere. As light emitted from a star passes through the star's atmosphere, some of it is absorbed by element ...
... 2. What are the five known substances in this activity? ________________________________________ Look closely at the spectrum below. Those black lines are caused by elements in the star's atmosphere. As light emitted from a star passes through the star's atmosphere, some of it is absorbed by element ...
Stars Notes
... Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition and brightness Color – red, red-orange, yellow, white, blue Temperature – ranges from 3,000 to 50,000 Size – super giant, giant, medium, dwarf, neutron Composition – what makes up the star (elements) Brightn ...
... Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition and brightness Color – red, red-orange, yellow, white, blue Temperature – ranges from 3,000 to 50,000 Size – super giant, giant, medium, dwarf, neutron Composition – what makes up the star (elements) Brightn ...
The new europian project ROPACS (Rocky Planets Around …
... Feedback to the network. assessments. ...
... Feedback to the network. assessments. ...
Red Giants
... Eventually, the layer just outside the core called the ``shell layer'' gets hot and dense enough for fusion to start. The fusion in the layer just outside the core is called shell burning. This fusion is very rapid because the shell layer is still compressing and increasing in temperature. The lumin ...
... Eventually, the layer just outside the core called the ``shell layer'' gets hot and dense enough for fusion to start. The fusion in the layer just outside the core is called shell burning. This fusion is very rapid because the shell layer is still compressing and increasing in temperature. The lumin ...
Navigation by the North Star - Science
... You can find the North Star by locating the two bowl stars of the Big Dipper. Follow those stars in a straight line to the first bright star you see. That is Polaris. ...
... You can find the North Star by locating the two bowl stars of the Big Dipper. Follow those stars in a straight line to the first bright star you see. That is Polaris. ...
The star and the trees prostrate
... electromagnetic radiation, including photons, the particles of light. This radiation exerts an outward pressure that exactly balances the inward pull of gravity caused by the star's mass. As the nuclear fuel is exhausted, the outward forces of radiation diminish, allowing the gravitation to compress ...
... electromagnetic radiation, including photons, the particles of light. This radiation exerts an outward pressure that exactly balances the inward pull of gravity caused by the star's mass. As the nuclear fuel is exhausted, the outward forces of radiation diminish, allowing the gravitation to compress ...
File - Mr. Fifield`s Corner
... Orbit is a regular, repeating path that one object in space takes as it revolves around another one. All orbits are elliptical, which means they are an ellipse, similar to an oval. These orbits result from gravitational forces ...
... Orbit is a regular, repeating path that one object in space takes as it revolves around another one. All orbits are elliptical, which means they are an ellipse, similar to an oval. These orbits result from gravitational forces ...
25drake3s
... fp -- Finding Planets Studies of star forming regions reveal that circumstellar disks are common around young stars ...
... fp -- Finding Planets Studies of star forming regions reveal that circumstellar disks are common around young stars ...
Chapter 26.4
... Very distant objects that release energy in outputs = to that of hundreds of GALAXIES combined Quasars may be powered by SUPERMASSIVE black holes that “accrete” galaxies. ...
... Very distant objects that release energy in outputs = to that of hundreds of GALAXIES combined Quasars may be powered by SUPERMASSIVE black holes that “accrete” galaxies. ...
E5 stellar processes and stellar evolution (HL only)
... • Neutron stars with masses substantially more than the Oppenheimer-Volkoff limit continue to collapse as the neutron pressure is insufficient. They become Black holes • At the centre of the black hole is a singularity • The boundary around the singularity where even light does not have sufficient e ...
... • Neutron stars with masses substantially more than the Oppenheimer-Volkoff limit continue to collapse as the neutron pressure is insufficient. They become Black holes • At the centre of the black hole is a singularity • The boundary around the singularity where even light does not have sufficient e ...
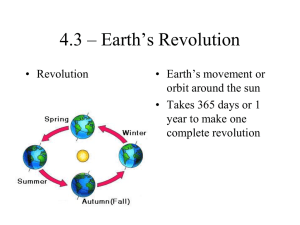
4.3 – Earth`s Revolution
... • Evidence the Earth is revolving around the sun • Stars seem to change position throughout the course of the year – look closer or father away • ACTUALLY!! Earth is moving – not the star ...
... • Evidence the Earth is revolving around the sun • Stars seem to change position throughout the course of the year – look closer or father away • ACTUALLY!! Earth is moving – not the star ...
Chapter 21
... • radii of 20 to several hundred solar radii (they are about the size of Jupiter's orbit!!!!) • two types are red supergiants (Betelgeuse and Antares) and blue supergiants (Rigel) ...
... • radii of 20 to several hundred solar radii (they are about the size of Jupiter's orbit!!!!) • two types are red supergiants (Betelgeuse and Antares) and blue supergiants (Rigel) ...
Ch. 5 The Universe and Solar System
... – The dying star shrinks into a white dwarf and becomes dull and cold. ...
... – The dying star shrinks into a white dwarf and becomes dull and cold. ...
HERE
... and very great density. These white dwarf stars are intensely hot ... but they are cooling. Their interior nuclear fires no longer burn, so they will continue to cool until they fade away. 26 The white dwarfs are circled. ...
... and very great density. These white dwarf stars are intensely hot ... but they are cooling. Their interior nuclear fires no longer burn, so they will continue to cool until they fade away. 26 The white dwarfs are circled. ...
The Big Dipper is a
... If your astrological sign is Aries, the Sun should be in the constellation Aries on your birthday. The dates, according to astrological tradition, during which the Sun is in the constellation Aries are: March 21 to April 20th. In which constellation is the Sun actually in, during this time period? a ...
... If your astrological sign is Aries, the Sun should be in the constellation Aries on your birthday. The dates, according to astrological tradition, during which the Sun is in the constellation Aries are: March 21 to April 20th. In which constellation is the Sun actually in, during this time period? a ...
Extrasolar planets
... Distance = 150 light-years Period = 3.5 days => orbital distance of 0.05 AU Like the planet around 51Peg, the planet was found to be large and orbiting tightly around the star – these are also known as “hot Jupiters”. Mass = 0.62MJ ...
... Distance = 150 light-years Period = 3.5 days => orbital distance of 0.05 AU Like the planet around 51Peg, the planet was found to be large and orbiting tightly around the star – these are also known as “hot Jupiters”. Mass = 0.62MJ ...
Stellar Evolution - Hays High School
... form – More massive stars can completely form in a few hundred thousand years ...
... form – More massive stars can completely form in a few hundred thousand years ...
Binary Stars (Professor Powerpoint)
... location where a fulcrum would be placed to balance the stars on a seesaw. ...
... location where a fulcrum would be placed to balance the stars on a seesaw. ...
Grade 9 Science – Unit 4 Space Quiz
... c. Remnant heat from the original very hot expansion has been measured d. All of the above 18. What type of star forms after a Supernova explosion? In this star, the centre collapses so that protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. The star is so very, very dense that one teaspoon on Earth wo ...
... c. Remnant heat from the original very hot expansion has been measured d. All of the above 18. What type of star forms after a Supernova explosion? In this star, the centre collapses so that protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. The star is so very, very dense that one teaspoon on Earth wo ...
AnwerkeyChaper1516
... 9. Saturn rings: Billions of particles of rocks and ice 10. No, Neptune, Jupiter, Uranus also have rings 11. Solar system formed from same cloud of interstellar material. Smaller planets could not hold on their light gases (H, He) and their exposed core became rocky. 13. Pluto has strongly elliptica ...
... 9. Saturn rings: Billions of particles of rocks and ice 10. No, Neptune, Jupiter, Uranus also have rings 11. Solar system formed from same cloud of interstellar material. Smaller planets could not hold on their light gases (H, He) and their exposed core became rocky. 13. Pluto has strongly elliptica ...
Death of massive stars
... In November 1967, Jocelyn Bell found a new, regular pattern in data from a radio telescope. Originally she and her team suspected they had made the first detection of alien life, and named it LGM 1. What they really found was the first pulsar. ...
... In November 1967, Jocelyn Bell found a new, regular pattern in data from a radio telescope. Originally she and her team suspected they had made the first detection of alien life, and named it LGM 1. What they really found was the first pulsar. ...
Astronomy Final Exam Review
... • Supernova- how massive and supermassive stars begin the end of their lives (after red giant or supergiant phase) • Quasar- rare, starlike object that gives off radio waves as material is sucked toward a black hole • Light year- the distance light travels in a year • AU-(astronomical unit)- 1AU= di ...
... • Supernova- how massive and supermassive stars begin the end of their lives (after red giant or supergiant phase) • Quasar- rare, starlike object that gives off radio waves as material is sucked toward a black hole • Light year- the distance light travels in a year • AU-(astronomical unit)- 1AU= di ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.