Physical Science Lecture Notes
... 3. Spectrographs: break light into its visible components a. Astronomers use spectrograths to determine temperatures and chemical composition of the stars they are looking at. B. Characteristics of Stars 1. Constellation: a group or pattern of stars in the night sky that appeared as symbols or figur ...
... 3. Spectrographs: break light into its visible components a. Astronomers use spectrograths to determine temperatures and chemical composition of the stars they are looking at. B. Characteristics of Stars 1. Constellation: a group or pattern of stars in the night sky that appeared as symbols or figur ...
Main Sequence stars
... • a new way to classify stars • color, peak wavelength of the black body curve, and spectral class all of which are indicators of a star’s temperature ...
... • a new way to classify stars • color, peak wavelength of the black body curve, and spectral class all of which are indicators of a star’s temperature ...
File
... A white dwarf is a dead star that shines very dimly as it cools down. When our Sun turns into a white dwarf, it will shrink to about the size of Earth! The particles are very tightly packed. They are more than a million times as ...
... A white dwarf is a dead star that shines very dimly as it cools down. When our Sun turns into a white dwarf, it will shrink to about the size of Earth! The particles are very tightly packed. They are more than a million times as ...
LAB: Star Classification
... Table 3 - Spectral Class and Temperature Spectral Class O B A F G K M ...
... Table 3 - Spectral Class and Temperature Spectral Class O B A F G K M ...
chapter8
... intrinsic brightness or luminosity (L) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d): L ...
... intrinsic brightness or luminosity (L) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d): L ...
Thought Question
... The only direct way to measure the distance to a star is from the parallax By definition, a star with a parallax of 1 arcsecond (arcsec) is at a distance of 1 parsec (pc). 1 arcsec = 1/3,600 degree. ...
... The only direct way to measure the distance to a star is from the parallax By definition, a star with a parallax of 1 arcsecond (arcsec) is at a distance of 1 parsec (pc). 1 arcsec = 1/3,600 degree. ...
The Death of Stars
... • Perhaps the most famous is the “Crab Nebula” from a supernova in 1054 AD. It was so bright, Chinese, Japanese, and Arab astronomers saw it for months during the day, and could be seen for 2 years at night. • The remnant merges with other gas and forms new stars. • Supernovae occur 1 to 3 times per ...
... • Perhaps the most famous is the “Crab Nebula” from a supernova in 1054 AD. It was so bright, Chinese, Japanese, and Arab astronomers saw it for months during the day, and could be seen for 2 years at night. • The remnant merges with other gas and forms new stars. • Supernovae occur 1 to 3 times per ...
OTA System Report For June 4, 2009 8:30 AM
... Previous 24 hours: 1) All hardware nominal, but FGS Thermal E442 – Aft F/G Panel is hitting YLW Hi 2) The 4 previous Acquisitions that were pending ETR telemetry were successful 3) There were 5 successful Acquisitions, and 1 TRANS Mode Observation with FGS 2 to support the AMA move. 4) 1 GSACQ was a ...
... Previous 24 hours: 1) All hardware nominal, but FGS Thermal E442 – Aft F/G Panel is hitting YLW Hi 2) The 4 previous Acquisitions that were pending ETR telemetry were successful 3) There were 5 successful Acquisitions, and 1 TRANS Mode Observation with FGS 2 to support the AMA move. 4) 1 GSACQ was a ...
Branches of Earth Science Tools Used to Study Stars Constellations
... o Most stars have the same general composition 73% Hydrogen Most Common 25% Helium 2nd most common 2% Other Elements o Scientists use a spectroscope to identify characteristics Characteristic: Something that identifies an object Elements have “Fingerprint” color characteristics They have ...
... o Most stars have the same general composition 73% Hydrogen Most Common 25% Helium 2nd most common 2% Other Elements o Scientists use a spectroscope to identify characteristics Characteristic: Something that identifies an object Elements have “Fingerprint” color characteristics They have ...
Final Review Sheet - Astronomy Part 2
... 2. What is the difference between a constellation, binary star, and a star cluster? ...
... 2. What is the difference between a constellation, binary star, and a star cluster? ...
Earth-Space Vocabulary
... • Dec 21 (first day of winter) least amount of daylight • June 21 (first day of summer) most amount of daylight ...
... • Dec 21 (first day of winter) least amount of daylight • June 21 (first day of summer) most amount of daylight ...
Astronomy 360 - indstate.edu
... arcseconds) and indicate how far north or south of the celestial equator (defined by projecting the Earth's equator onto the celestial sphere) the object lies. Lines of longitude have their equivalent in lines of right ascension (RA), but whereas longitude is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds ...
... arcseconds) and indicate how far north or south of the celestial equator (defined by projecting the Earth's equator onto the celestial sphere) the object lies. Lines of longitude have their equivalent in lines of right ascension (RA), but whereas longitude is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds ...
16. Properties of Stars
... Note that Absolute Magnitude is a measure of the Luminosity of the Star Apparent visual Magnitude is a measure of the Apparent Brightness (or Intensity) of the starlight reaching the observer. ...
... Note that Absolute Magnitude is a measure of the Luminosity of the Star Apparent visual Magnitude is a measure of the Apparent Brightness (or Intensity) of the starlight reaching the observer. ...
Chap 11 Characterizing Stars v2
... A spectroscopic binary is a system detected from the periodic shift of its spectral lines. This shift is caused by the Doppler effect as the orbits of the stars carry them alternately toward and away from Earth. An eclipsing binary is a system whose orbits are viewed nearly edge-on from Earth, so th ...
... A spectroscopic binary is a system detected from the periodic shift of its spectral lines. This shift is caused by the Doppler effect as the orbits of the stars carry them alternately toward and away from Earth. An eclipsing binary is a system whose orbits are viewed nearly edge-on from Earth, so th ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... Mark scheme for Extension Worksheet – Option E, Worksheet 1 ...
... Mark scheme for Extension Worksheet – Option E, Worksheet 1 ...
The most important questions to study for the exam
... • From the absorption lines in the star's spectrum 14. Aldebaran, a star in the constellation Taurus, has a spectral-luminosity class of K5 III. This tells us that Aldebaran is • a hot supergiant. • a cool supergiant. • a cool giant. 15. An astronomer classifies a particular star as luminosity class ...
... • From the absorption lines in the star's spectrum 14. Aldebaran, a star in the constellation Taurus, has a spectral-luminosity class of K5 III. This tells us that Aldebaran is • a hot supergiant. • a cool supergiant. • a cool giant. 15. An astronomer classifies a particular star as luminosity class ...
Cosmic Distance Ladder
... the Earth causes nearby stars to appear to move relative to the more distant stars. • The annual parallax is defined as the difference in position of a star as seen from the Earth and Sun, i.e. the angle subtended at a star by the mean radius of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. ...
... the Earth causes nearby stars to appear to move relative to the more distant stars. • The annual parallax is defined as the difference in position of a star as seen from the Earth and Sun, i.e. the angle subtended at a star by the mean radius of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. ...
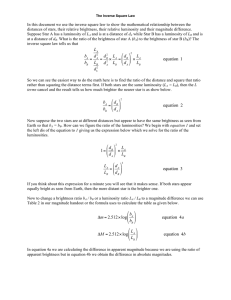
Inverse Square Law
... distances of stars, their relative brightness, their relative luminosity and their magnitude difference. Suppose Star A has a luminosity of LA and is at a distance of dA while Star B has a luminosity of LB and is at a distance of dB. What is the ratio of the brightness of star A (bA) to the brightne ...
... distances of stars, their relative brightness, their relative luminosity and their magnitude difference. Suppose Star A has a luminosity of LA and is at a distance of dA while Star B has a luminosity of LB and is at a distance of dB. What is the ratio of the brightness of star A (bA) to the brightne ...
IB_Op_F_04 - Effectsmeister
... Which spectral class is most common? Which spectral class is the least common? In general, what is the relationship between the temperature of a star and its brightness? Most of the stars seem to be along a line from the upper left corner to the lower right corner of the HR Diagram. Stars which fall ...
... Which spectral class is most common? Which spectral class is the least common? In general, what is the relationship between the temperature of a star and its brightness? Most of the stars seem to be along a line from the upper left corner to the lower right corner of the HR Diagram. Stars which fall ...
Notes on Precession in Astronomy
... and planets on the unevenly distributed mass of the Earth. The Earth slowly wobbles, much as a top, or gyroscope, does when spun. This wobble is called the Earth's Precession. ...
... and planets on the unevenly distributed mass of the Earth. The Earth slowly wobbles, much as a top, or gyroscope, does when spun. This wobble is called the Earth's Precession. ...
Star Formation
... • The time required for an interstellar cloud to become a main sequence star depends strongly on its mass • The most massive O stars reach the 10 million Kelvin needed to start fusion in a million years (1/50 time taken by sun) • An M-type star less massive than our sun takes one billion years to fo ...
... • The time required for an interstellar cloud to become a main sequence star depends strongly on its mass • The most massive O stars reach the 10 million Kelvin needed to start fusion in a million years (1/50 time taken by sun) • An M-type star less massive than our sun takes one billion years to fo ...
Classifying Stars (pages 753–754) Key Concept: Characteristics
... Classifying Stars (pages 753–754) Key Concept: Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and brightness. ...
... Classifying Stars (pages 753–754) Key Concept: Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and brightness. ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.