
General Astronomy - Stockton University
... Pickering. Pickering became frustrated with his male assistants at the Harvard College Observatory and, legend has it, famously declared his maid could do a better job. Turns out she could. In 1881, Pickering hired Fleming to do clerical work at the observatory. While there, she devised and helped i ...
... Pickering. Pickering became frustrated with his male assistants at the Harvard College Observatory and, legend has it, famously declared his maid could do a better job. Turns out she could. In 1881, Pickering hired Fleming to do clerical work at the observatory. While there, she devised and helped i ...
Loving The Universe
... Substance Of Life Life requires H, C, O, & N All elements of life came from stars that lived AND DIED before the sun formed. Sun is a 2nd or 3rd generation star o 1st stars were pure hydrogen and helium) ...
... Substance Of Life Life requires H, C, O, & N All elements of life came from stars that lived AND DIED before the sun formed. Sun is a 2nd or 3rd generation star o 1st stars were pure hydrogen and helium) ...
solar system
... A SEASON is one of the four periods of the year. Each eason--spring, summer, autumn, and winter--lasts about hree months and brings changes in temperature, weather, nd the length of daylight. During the spring, the days are warm in middle parts of the Northern Hemiphere, the northern half of the Ear ...
... A SEASON is one of the four periods of the year. Each eason--spring, summer, autumn, and winter--lasts about hree months and brings changes in temperature, weather, nd the length of daylight. During the spring, the days are warm in middle parts of the Northern Hemiphere, the northern half of the Ear ...
Space Unit - Questions and Answers
... Smallest – the millions of tiny meteoroids that produce spectacular displays called meteor showers probably come from the debris left behind by comets. ...
... Smallest – the millions of tiny meteoroids that produce spectacular displays called meteor showers probably come from the debris left behind by comets. ...
Chapter 19 I. The Sun, Earth and Moon A. Sun is our closest star B
... E. Gravity holds the solar system together 1. We usually think of gravity as the attractive force that pulls us to the Earth. 2. True definition of gravity is the attractive force between objects. 3. The more mass an object has the greater its gravitational pull. a. The Sun has more mass than any ob ...
... E. Gravity holds the solar system together 1. We usually think of gravity as the attractive force that pulls us to the Earth. 2. True definition of gravity is the attractive force between objects. 3. The more mass an object has the greater its gravitational pull. a. The Sun has more mass than any ob ...
Kepler`s Law - New Mexico Tech
... -Cepheid: Type F to K supergiant stars that pulsate with a period of 1 to 70 days. They are brighter than RR Lyrae Stars Two Types: Population 1: Young Massive Stars Population 2: Old Fainter Stars on an average of 1.5 in magnitude -RR Lyrae Variables: Type A stars that do not vary greatly in magnit ...
... -Cepheid: Type F to K supergiant stars that pulsate with a period of 1 to 70 days. They are brighter than RR Lyrae Stars Two Types: Population 1: Young Massive Stars Population 2: Old Fainter Stars on an average of 1.5 in magnitude -RR Lyrae Variables: Type A stars that do not vary greatly in magnit ...
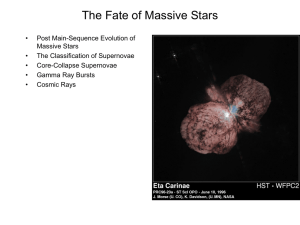
The Fate of Massive Stars
... reported location of the bright object seen in 1054 is now known as the Crab Supernova remnant A pulsar has been identified at this location as well ...
... reported location of the bright object seen in 1054 is now known as the Crab Supernova remnant A pulsar has been identified at this location as well ...
Solar System from Web
... -Cepheid: Type F to K supergiant stars that pulsate with a period of 1 to 70 days. They are brighter than RR Lyrae Stars Two Types: Population 1: Young Massive Stars Population 2: Old Fainter Stars on an average of 1.5 in magnitude -RR Lyrae Variables: Type A stars that do not vary greatly in magnit ...
... -Cepheid: Type F to K supergiant stars that pulsate with a period of 1 to 70 days. They are brighter than RR Lyrae Stars Two Types: Population 1: Young Massive Stars Population 2: Old Fainter Stars on an average of 1.5 in magnitude -RR Lyrae Variables: Type A stars that do not vary greatly in magnit ...
Sun: The Nearest Star
... Faculae are bright luminous hydrogen clouds which form above regions where sunspots are about to form. Flares are bright filaments of hot gas emerging from sunspot regions. Sunspots are dark depressions on the photosphere with a typical temperature of 4,000°C (7,000°F). Corona is the region that pro ...
... Faculae are bright luminous hydrogen clouds which form above regions where sunspots are about to form. Flares are bright filaments of hot gas emerging from sunspot regions. Sunspots are dark depressions on the photosphere with a typical temperature of 4,000°C (7,000°F). Corona is the region that pro ...
Ch 3 Sec 1 Tools of modern astronomy
... a) A dark star may show itself by passing in front of the brighter star – called an eclipsing binary b) Or, the brighter star may appear to wobble, as the 2 stars pull on each other 2. Planets have been found around other stars a) Same techniques as used for binary star systems b) Means that can’t f ...
... a) A dark star may show itself by passing in front of the brighter star – called an eclipsing binary b) Or, the brighter star may appear to wobble, as the 2 stars pull on each other 2. Planets have been found around other stars a) Same techniques as used for binary star systems b) Means that can’t f ...
Planetary Configurations
... For normal stars, bigger M yields bigger R, but opposite for WDs Radius is fixed, and WD still glows, so it just continues to cool and fade (i.e., temperature drops over time) ...
... For normal stars, bigger M yields bigger R, but opposite for WDs Radius is fixed, and WD still glows, so it just continues to cool and fade (i.e., temperature drops over time) ...
Astronomy Unit Test Review Sheet
... 2. What is an optical telescope? What is the difference between a reflecting and a refracting telescope? What other types of telescopes do scientists use to gather information? Optical telescopes are used to see visible light from far away. Refracting uses a glass lens and a reflecting telescope use ...
... 2. What is an optical telescope? What is the difference between a reflecting and a refracting telescope? What other types of telescopes do scientists use to gather information? Optical telescopes are used to see visible light from far away. Refracting uses a glass lens and a reflecting telescope use ...
light energy
... • Distances can be deceiving: Bright stars look close, but may be very far away Star Approx. Distance (LY) P. Centari ...
... • Distances can be deceiving: Bright stars look close, but may be very far away Star Approx. Distance (LY) P. Centari ...
GeoDome Notes
... making it much cooler than our Sun (~6000 degrees Kelvin). It is a dying star having used up most of its fuel. It expands and contracts which changes its magnitude (measure of brightness) over a 6 year period. At its largest if placed in our Solar System, it would engulf Jupiter. It is about 650 lig ...
... making it much cooler than our Sun (~6000 degrees Kelvin). It is a dying star having used up most of its fuel. It expands and contracts which changes its magnitude (measure of brightness) over a 6 year period. At its largest if placed in our Solar System, it would engulf Jupiter. It is about 650 lig ...
presentation source
... cloud. Pressure builds till nuclear fusion ignites in centre, becoming a star. • Associated with disks (planetary systems), outflows and jets. • Disperse their cocoon to become visible. • Typically form in clusters, dominated by light from 1-2 brightest members. GENS4001 1999-X1 ...
... cloud. Pressure builds till nuclear fusion ignites in centre, becoming a star. • Associated with disks (planetary systems), outflows and jets. • Disperse their cocoon to become visible. • Typically form in clusters, dominated by light from 1-2 brightest members. GENS4001 1999-X1 ...
Name - MIT
... A) The rate that visible light from the Sun is being absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere B) The rate that hydrogen is being fused into helium in the Sun C) The rate that gamma rays are hitting the Earth’s atmosphere D) The rate that white dwarfs are being formed in the galaxy E) The rate that stars f ...
... A) The rate that visible light from the Sun is being absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere B) The rate that hydrogen is being fused into helium in the Sun C) The rate that gamma rays are hitting the Earth’s atmosphere D) The rate that white dwarfs are being formed in the galaxy E) The rate that stars f ...
Unit 1
... • You may be asking, “If light cannot escape a black hole, how can we see one?” • If a black hole is in orbit around a companion star, the black hole can pull material away from it. ...
... • You may be asking, “If light cannot escape a black hole, how can we see one?” • If a black hole is in orbit around a companion star, the black hole can pull material away from it. ...
Name
... A) The rate that visible light from the Sun is being absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere B) The rate that gamma rays are hitting the Earth’s atmosphere C) The rate that hydrogen is being fused into helium in the Sun D) The rate that white dwarfs are being formed in the galaxy E) The rate that stars f ...
... A) The rate that visible light from the Sun is being absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere B) The rate that gamma rays are hitting the Earth’s atmosphere C) The rate that hydrogen is being fused into helium in the Sun D) The rate that white dwarfs are being formed in the galaxy E) The rate that stars f ...
Bellringer - Madison County Schools
... • The brightness of a star depends on both its SIZE and TEMPERATURE. ...
... • The brightness of a star depends on both its SIZE and TEMPERATURE. ...
Stars and Galaxies
... The stars in a galaxy are very far apart. Scientists believe there may be as many as 100 000 million other galaxies beyond ours. Because gravity attracts them together, the stars in a galaxy are clustered. There are vast expanses of nothing between different galaxies. ...
... The stars in a galaxy are very far apart. Scientists believe there may be as many as 100 000 million other galaxies beyond ours. Because gravity attracts them together, the stars in a galaxy are clustered. There are vast expanses of nothing between different galaxies. ...
What is a Scientist? - Cockeysville Middle School
... 2. Surface Temperature What pattern exists for main sequence stars based upon these two characteristics? For main sequence stars, as the surface temperature increases, the absolute brightness increases. ESS-5B ...
... 2. Surface Temperature What pattern exists for main sequence stars based upon these two characteristics? For main sequence stars, as the surface temperature increases, the absolute brightness increases. ESS-5B ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.






![Test ticket - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010793453_1-3f96ef5ee7d4646c2142d92e4dc3c3f6-300x300.png)















