What To See Telescope(Jul-Sept) v1 - One
... The guide assumes you are at least somewhat familiar with the set-up and operation of your telescope. If your telescope has a larger aperture than 4 inches, then you will see more detail in most objects. Sights that benefit from larger-aperture telescopes, and descriptions of what you will see with ...
... The guide assumes you are at least somewhat familiar with the set-up and operation of your telescope. If your telescope has a larger aperture than 4 inches, then you will see more detail in most objects. Sights that benefit from larger-aperture telescopes, and descriptions of what you will see with ...
Integrated Science Names (Do with ONE partner or by yourself) How
... large a container would you need to hold all the stars in all the galaxies? Multiply 100 billion x 100 billion x your answer to Analysis Q#3 _______________________________ cubic meters 6. If all the stars in our galaxy were shrunk to about 1 mm in diameter (the size of an aluminum pellet) how far a ...
... large a container would you need to hold all the stars in all the galaxies? Multiply 100 billion x 100 billion x your answer to Analysis Q#3 _______________________________ cubic meters 6. If all the stars in our galaxy were shrunk to about 1 mm in diameter (the size of an aluminum pellet) how far a ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... event in detail. Astrophysical jets of matter are part of cosmic events and usually observed in combination with compact objects like neutron stars. These jets leave the object on the rotation axis and are therefore highly stable in the direction. ...
... event in detail. Astrophysical jets of matter are part of cosmic events and usually observed in combination with compact objects like neutron stars. These jets leave the object on the rotation axis and are therefore highly stable in the direction. ...
Results from the search for tidal disruption flares in the GALEX Deep
... • Designed to complement future ground-based TDS (PanStarrs, LSST) • All time-domain products, notably variable object alerts, will be immediately made public for community follow-up • Produce automated pipeline triggers to generate IAU and/or GCN circulars • Prevalence of UV-bright early evolution ...
... • Designed to complement future ground-based TDS (PanStarrs, LSST) • All time-domain products, notably variable object alerts, will be immediately made public for community follow-up • Produce automated pipeline triggers to generate IAU and/or GCN circulars • Prevalence of UV-bright early evolution ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
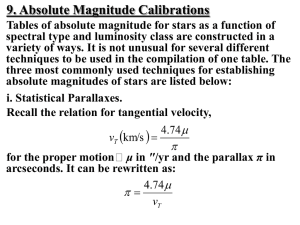
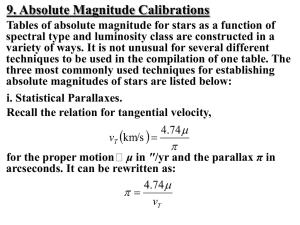
... of stars of different spectral types and luminosity classes. The general method of using a calibrated zero-age mainsequence (ZAMS) to derive cluster distances is outlined by Blaauw in Basic Astronomical Data. However, the necessary zero-point calibration involves the independent determination of the ...
... of stars of different spectral types and luminosity classes. The general method of using a calibrated zero-age mainsequence (ZAMS) to derive cluster distances is outlined by Blaauw in Basic Astronomical Data. However, the necessary zero-point calibration involves the independent determination of the ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... of stars of different spectral types and luminosity classes. The general method of using a calibrated zero-age mainsequence (ZAMS) to derive cluster distances is outlined by Blaauw in Basic Astronomical Data. However, the necessary zero-point calibration involves the independent determination of the ...
... of stars of different spectral types and luminosity classes. The general method of using a calibrated zero-age mainsequence (ZAMS) to derive cluster distances is outlined by Blaauw in Basic Astronomical Data. However, the necessary zero-point calibration involves the independent determination of the ...
Searching for Dwarf Galaxies and Population III Star
... Metal-free stars in the early universe will inhabit regions of space that have not yet been chemically enriched by earlier supernovae. However, the easiest regions to characterize at early times are volumes that have been ionized by flux from nearby, bright galaxies or proto-clusters of galaxies. Th ...
... Metal-free stars in the early universe will inhabit regions of space that have not yet been chemically enriched by earlier supernovae. However, the easiest regions to characterize at early times are volumes that have been ionized by flux from nearby, bright galaxies or proto-clusters of galaxies. Th ...
the magellanic clouds newsletter - Keele University Astrophysics
... have initial substructure. Furthermore, both clusters may be evolving along a very similar dynamical sequence, with the key difference that NGC 1805 is dynamically older than NGC 1818. The F-type binaries in NGC 1818 still show evidence of an initial period of rapid dynamical disruptions (which occu ...
... have initial substructure. Furthermore, both clusters may be evolving along a very similar dynamical sequence, with the key difference that NGC 1805 is dynamically older than NGC 1818. The F-type binaries in NGC 1818 still show evidence of an initial period of rapid dynamical disruptions (which occu ...
Larger, high-res file, best for printing
... zero-point for the period-luminosity relation. Then if one found a Cepheid, one had only to determine its period, and one would know its absolute magnitude; comparing this to its apparent magnitude would give its distance. Extending this to cluster variables, which were fainter than Cepheids, sugges ...
... zero-point for the period-luminosity relation. Then if one found a Cepheid, one had only to determine its period, and one would know its absolute magnitude; comparing this to its apparent magnitude would give its distance. Extending this to cluster variables, which were fainter than Cepheids, sugges ...
How are a star`s temperature, color, and brightness related?
... The stellar classes (OBAFGKM) are further subdivided with a number 0 to 9 following the letter. Our sun, a G2 star, is slightly cooler than the F range. A G9 star would be just a bit warmer than the K range. ...
... The stellar classes (OBAFGKM) are further subdivided with a number 0 to 9 following the letter. Our sun, a G2 star, is slightly cooler than the F range. A G9 star would be just a bit warmer than the K range. ...
A Star`s Color, Temperature, and Brightness are Related!
... The stellar classes (OBAFGKM) are further subdivided with a number 0 to 9 following the letter. Our sun, a G2 star, is slightly cooler than the F range. A G9 star would be just a bit warmer than the K range. ...
... The stellar classes (OBAFGKM) are further subdivided with a number 0 to 9 following the letter. Our sun, a G2 star, is slightly cooler than the F range. A G9 star would be just a bit warmer than the K range. ...
copyright 2002 scientific american, inc.
... The two categories differ spectroscopically, with short bursts having relatively more high-energy gamma rays than long bursts do. The January 1999 burst emitted gamma rays for a minute and a half. Arguably the most important result from BATSE concerned the distribution of the bursts. They occur isot ...
... The two categories differ spectroscopically, with short bursts having relatively more high-energy gamma rays than long bursts do. The January 1999 burst emitted gamma rays for a minute and a half. Arguably the most important result from BATSE concerned the distribution of the bursts. They occur isot ...
Supernovae and Gamma-Ray Bursts (draft)
... the core pressure is independent of temperature. Therefore, a rise in central temperature (due to the carbon burning) does not produce an increase in pressure which would limit the increase in temperature (the valve mechanism that keeps burning in ordinary stars, supported by thermal pressure, stabl ...
... the core pressure is independent of temperature. Therefore, a rise in central temperature (due to the carbon burning) does not produce an increase in pressure which would limit the increase in temperature (the valve mechanism that keeps burning in ordinary stars, supported by thermal pressure, stabl ...
2013. CCAT. All Rights Reserved.
... generation of stars began enriching the medium, the Universe was reionized,, and the star formation rate increased to a what appears to have been a broad peak or plateau. This period of galaxy infancy witnessed the greatest logarithmic growth in the density of stars, black holes, and heavy elements, ...
... generation of stars began enriching the medium, the Universe was reionized,, and the star formation rate increased to a what appears to have been a broad peak or plateau. This period of galaxy infancy witnessed the greatest logarithmic growth in the density of stars, black holes, and heavy elements, ...
The Sun - Our Star
... Solar flares, much more explosive and energetic than prominences, are erupt releases of magnetic energy. Flares take place in active regions where a prominence is supported against gravity by magnetic field lines and then the magnetic field structure changes abruptly. Coronal gas may heat to 40 mill ...
... Solar flares, much more explosive and energetic than prominences, are erupt releases of magnetic energy. Flares take place in active regions where a prominence is supported against gravity by magnetic field lines and then the magnetic field structure changes abruptly. Coronal gas may heat to 40 mill ...
Chapter 5 Theory of Stellar Evolution
... concentrate on what is known with some certainty. Thus, we assume that stars can contract out of the interstellar medium, and generally we avoid most of the detailed description of the final, fatal collapse of massive stars. In addition, the fascinating field of the evolution of close binary stars, ...
... concentrate on what is known with some certainty. Thus, we assume that stars can contract out of the interstellar medium, and generally we avoid most of the detailed description of the final, fatal collapse of massive stars. In addition, the fascinating field of the evolution of close binary stars, ...
Estudio de Cúmulos de Galaxias en el Sloan Digital Sky Survey
... Baugh et al. 2005: - Reproduce the z=3 LF of LBGs - Reproduce the number of SMGs. ...
... Baugh et al. 2005: - Reproduce the z=3 LF of LBGs - Reproduce the number of SMGs. ...
1. The Birth of a Star
... toward a faint colored cloud in space named “M42”. Notice that in the same info display, the distance from you to that cloud is listed as 1,177.7 ly. The “ly” stands for “Light Year”. It is not a time, but a distance. It is the distance a beam of light will travel through space in one year. 13. Ligh ...
... toward a faint colored cloud in space named “M42”. Notice that in the same info display, the distance from you to that cloud is listed as 1,177.7 ly. The “ly” stands for “Light Year”. It is not a time, but a distance. It is the distance a beam of light will travel through space in one year. 13. Ligh ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.