John Forester, M.S., P.E. How To Find Your Position At Sea:
... Hour Angle of the Sun, for that day and time. Our chronometer tells us the time relative to the nearest noons. The navigation tables give us the Hour Angle for noon at that moment, the angle between the Sun and the zero plane. So we add or subtract, as appropriate, to combine the Hour Angles of the ...
... Hour Angle of the Sun, for that day and time. Our chronometer tells us the time relative to the nearest noons. The navigation tables give us the Hour Angle for noon at that moment, the angle between the Sun and the zero plane. So we add or subtract, as appropriate, to combine the Hour Angles of the ...
The Classification of Stellar Spectra
... Background: The History And Nature Of Spectral Classification Patterns of absorption lines were first observed in the spectrum of the sun by the German physicist Joseph von Fraunhofer early in the 1800’s, but it was not until late in the century that astronomers were able to routinely examine the sp ...
... Background: The History And Nature Of Spectral Classification Patterns of absorption lines were first observed in the spectrum of the sun by the German physicist Joseph von Fraunhofer early in the 1800’s, but it was not until late in the century that astronomers were able to routinely examine the sp ...
www.worldsci.org
... Doppler red-shift is an expanding universe with rapidly receding stars, galaxies, etc. – Can a reasonably macroscopic and tenuous form of matter like a star, let alone an entire galaxy, possibly travel at speeds approaching that of light and remain ‘intact’ (except, perhaps, something as dense as a ...
... Doppler red-shift is an expanding universe with rapidly receding stars, galaxies, etc. – Can a reasonably macroscopic and tenuous form of matter like a star, let alone an entire galaxy, possibly travel at speeds approaching that of light and remain ‘intact’ (except, perhaps, something as dense as a ...
ASTR 111 Lab Manual - Ohio Wesleyan University
... An important difference between longitude and right ascension is that longitude is measured in degrees, while right ascension is measured in units of time. To understand this, we must digress a little. For an observer, the meridian is the circle on the sky which stretches from due north to due sout ...
... An important difference between longitude and right ascension is that longitude is measured in degrees, while right ascension is measured in units of time. To understand this, we must digress a little. For an observer, the meridian is the circle on the sky which stretches from due north to due sout ...
Adult education at Scienceworks
... The Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn mark the furthest points north and south of the equator where the Sun's rays fall vertically. The Arctic Circle and the Antarctic Circle mark the furthest points north or south of the equator where the Sun appears above the horizon each day of the yea ...
... The Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn mark the furthest points north and south of the equator where the Sun's rays fall vertically. The Arctic Circle and the Antarctic Circle mark the furthest points north or south of the equator where the Sun appears above the horizon each day of the yea ...
Ground-Based Astrometry 2010-2020
... proper motions of Milky Way satellite galaxies and improved numerical simulations, we will learn the size and mass of the disk, bulge, and dark matter halo of the Milky Way. • How many dwarf galaxies are orbiting the Milky Way and what are their orbits? Lambda cold-dark matter (LCDM) cosmological mo ...
... proper motions of Milky Way satellite galaxies and improved numerical simulations, we will learn the size and mass of the disk, bulge, and dark matter halo of the Milky Way. • How many dwarf galaxies are orbiting the Milky Way and what are their orbits? Lambda cold-dark matter (LCDM) cosmological mo ...
Topic 3 - Holy Cross Collegiate
... Remember that as light passes through a gas, parts of the light are absorbed. This creates the dark lines in the spectrum. Now think about the solar spectrum. If the Sun’s spectrum also has dark lines in it, it must mean that sunlight passes through some gases. The conclusion is that gases in the Su ...
... Remember that as light passes through a gas, parts of the light are absorbed. This creates the dark lines in the spectrum. Now think about the solar spectrum. If the Sun’s spectrum also has dark lines in it, it must mean that sunlight passes through some gases. The conclusion is that gases in the Su ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Nuclear Fusion reactions (2 atoms jammed togetherenergy emitted as light and heat)- converts 600,000,000 tons of hydrogen into helium every second 93 million miles or 150 million km from Earth (closer than any other star) A planet’s characteristics are often determined by distance from the Sun (e ...
... Nuclear Fusion reactions (2 atoms jammed togetherenergy emitted as light and heat)- converts 600,000,000 tons of hydrogen into helium every second 93 million miles or 150 million km from Earth (closer than any other star) A planet’s characteristics are often determined by distance from the Sun (e ...
NSDL/NSTA Web Seminar: Celebrating Astronomy: A Star`s Story
... Astronomy is a dynamic science. New discoveries add to our knowledge of the universe and our own solar system. • New images brought to use by the Hubble Space Telescope show that star formation is more complex and violent than anyone had believed. • Supersonic jets of particles and dense clots of d ...
... Astronomy is a dynamic science. New discoveries add to our knowledge of the universe and our own solar system. • New images brought to use by the Hubble Space Telescope show that star formation is more complex and violent than anyone had believed. • Supersonic jets of particles and dense clots of d ...
Celebrating Astronomy: The Life of a Star
... Astronomy is a dynamic science. New discoveries add to our knowledge of the universe and our own solar system. • New images brought to use by the Hubble Space Telescope show that star formation is more complex and violent than anyone had believed. • Supersonic jets of particles and dense clots of d ...
... Astronomy is a dynamic science. New discoveries add to our knowledge of the universe and our own solar system. • New images brought to use by the Hubble Space Telescope show that star formation is more complex and violent than anyone had believed. • Supersonic jets of particles and dense clots of d ...
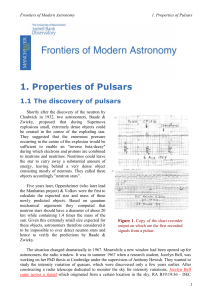
1: Properties of Pulsars
... dwarfs. Only neutron stars were left as a possible explanation. Periods for radial oscillations of neutron stars were predicted to be larger than 1 second and were hence incompatible with the periods of the first discovered pulsars. Finally, another property of pulsars, also most easily observed in ...
... dwarfs. Only neutron stars were left as a possible explanation. Periods for radial oscillations of neutron stars were predicted to be larger than 1 second and were hence incompatible with the periods of the first discovered pulsars. Finally, another property of pulsars, also most easily observed in ...
Chapter 15
... Elliptical galaxies have no spiral arms and no disk. They come in many sizes, from giant ellipticals of trillions of stars, down to dwarf ellipticals of less than a million stars. Ellipticals also contain very little, if any, cool gas and dust, and they show no evidence of ongoing star formation. El ...
... Elliptical galaxies have no spiral arms and no disk. They come in many sizes, from giant ellipticals of trillions of stars, down to dwarf ellipticals of less than a million stars. Ellipticals also contain very little, if any, cool gas and dust, and they show no evidence of ongoing star formation. El ...
New Worlds Ahead: The Discovery of Exoplanets
... perpendicular to this plane, and the direction of the Sun rotation is the same as the planets revolution around the Sun. These observations gave birth to the Solar nebula theory, which was proposed by Kant and Laplace more that two hundred years ago, but, although correct, it has been for decades th ...
... perpendicular to this plane, and the direction of the Sun rotation is the same as the planets revolution around the Sun. These observations gave birth to the Solar nebula theory, which was proposed by Kant and Laplace more that two hundred years ago, but, although correct, it has been for decades th ...
Astrophysical parameters of ten poorly studied open star clusters
... with the 2MASS J, H and Ks filters (Bonatto et al. 2004; Bica et al. 2006) to derive the cluster parameters. The simultaneous fittings were attempted on the J ∼ (J − H) and Ks ∼ (J − Ks ) diagrams for the inner stars, which should be less contaminated by the background field. If the number of stars ...
... with the 2MASS J, H and Ks filters (Bonatto et al. 2004; Bica et al. 2006) to derive the cluster parameters. The simultaneous fittings were attempted on the J ∼ (J − H) and Ks ∼ (J − Ks ) diagrams for the inner stars, which should be less contaminated by the background field. If the number of stars ...
Complete Lecture Notes (pdf file)
... Exercise 1.1: The V magnitudes of two main-sequence stars are both observed to be 7.5, but their blue magnitudes are B1 = 7.2 and B2 = 8.65. (a) What are the colour indices of the two stars. (b) Which star is the bluer and by what factor is it brighter at blue wavelength. (c) Making reasonable assum ...
... Exercise 1.1: The V magnitudes of two main-sequence stars are both observed to be 7.5, but their blue magnitudes are B1 = 7.2 and B2 = 8.65. (a) What are the colour indices of the two stars. (b) Which star is the bluer and by what factor is it brighter at blue wavelength. (c) Making reasonable assum ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.