Stars and Galaxies Section 1 Stars
... A. Patterns of stars - constellations 1. Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations 2. Modern astronomy studies 88 constellations 3. Some constellations are not visible all year because Earth revolves around the Sun 4. Circumpolar constellations in the northern sky appe ...
... A. Patterns of stars - constellations 1. Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations 2. Modern astronomy studies 88 constellations 3. Some constellations are not visible all year because Earth revolves around the Sun 4. Circumpolar constellations in the northern sky appe ...
Ginger Dublin 6th Grade Science
... • Stars give off electromagnetic radiation in different forms • Each form has its own wavelength ...
... • Stars give off electromagnetic radiation in different forms • Each form has its own wavelength ...
Chapter 30 Study Notes
... During the main sequence stage, ________ hydrogen helium to generate energy in a fuses into _______ star’s core. ...
... During the main sequence stage, ________ hydrogen helium to generate energy in a fuses into _______ star’s core. ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... megatons/second • Let’s relate that to human scales. What would that be at one kilometer distance? • 77 x 1015 tons/(150 x 106km)2 = 3 tons • Picture a truckload of explosives a km away giving off a one-second burst of heat and light to rival the Sun ...
... megatons/second • Let’s relate that to human scales. What would that be at one kilometer distance? • 77 x 1015 tons/(150 x 106km)2 = 3 tons • Picture a truckload of explosives a km away giving off a one-second burst of heat and light to rival the Sun ...
August Evening Skies
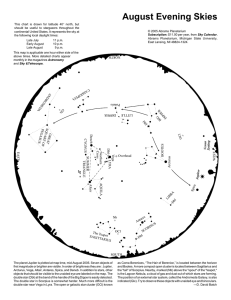
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2005. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2005. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
Northern Hemisphere – December 2012
... Jupiter rises at sunset at the beginning of the month and is visible throughout the night as it reaches opposition (opposite the Sun in the sky) during December. Shining at magnitude -2.8, it reaches 60 degrees' elevation in Taurus in the south, helping us to see it with little atmospheric interfere ...
... Jupiter rises at sunset at the beginning of the month and is visible throughout the night as it reaches opposition (opposite the Sun in the sky) during December. Shining at magnitude -2.8, it reaches 60 degrees' elevation in Taurus in the south, helping us to see it with little atmospheric interfere ...
Name: ____________________________ Date: _____________ Per. _________ Stars Study Guide (Ch. 21)
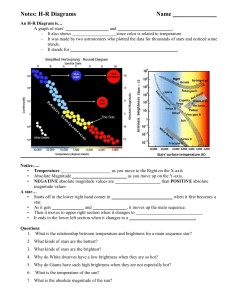
... Name: ____________________________ Date: _____________ Per. _________ 13. What is a graph that shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star? __________________ ...
... Name: ____________________________ Date: _____________ Per. _________ 13. What is a graph that shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star? __________________ ...
astronomy 2 review sheet - Hicksville Public Schools
... 18. Describe a meteor, meteoroid and a meteorite. METEOR- STREAK OF LIGHT AS A METE0ROID BURNS UP IN THE EARTH’S ATMOSPHERE. METEOROID- A CHUNK OF ROCK OR DUST IN SPACE. METEORITE- A METEOROID THAT HITS THE EARTH’S SURFACE. 19. What force pulls together matter in stars? GRAVITY 20. If you look at an ...
... 18. Describe a meteor, meteoroid and a meteorite. METEOR- STREAK OF LIGHT AS A METE0ROID BURNS UP IN THE EARTH’S ATMOSPHERE. METEOROID- A CHUNK OF ROCK OR DUST IN SPACE. METEORITE- A METEOROID THAT HITS THE EARTH’S SURFACE. 19. What force pulls together matter in stars? GRAVITY 20. If you look at an ...
Star Gazing
... region to the right of the sun (spring sunset). Use fist method (arm outstretched) to measure 30o (3 fist lengths) to the right/north of sunset now. • Specific directions on website for what you need to write down. • Turn in the picture with details listed in the ...
... region to the right of the sun (spring sunset). Use fist method (arm outstretched) to measure 30o (3 fist lengths) to the right/north of sunset now. • Specific directions on website for what you need to write down. • Turn in the picture with details listed in the ...
labex7
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
Star
... -Some dwarf stars are as small as the Earth. -Our sun is a medium size star (1,390,000 km). -Some stars are 1,000 times larger than our sun. -Density affects mass…no relationship between size and mass. Example: a star can be smaller than our sun, but have a greater mass…meaning it is more dense! ...
... -Some dwarf stars are as small as the Earth. -Our sun is a medium size star (1,390,000 km). -Some stars are 1,000 times larger than our sun. -Density affects mass…no relationship between size and mass. Example: a star can be smaller than our sun, but have a greater mass…meaning it is more dense! ...
Ch 28 Vocab cnp
... The most luminous, most massive stars, with diameters greater than 100 times the diameter of the sun A variable star that brightens and dims regularly, or pulses, and whose distance can be determined from its period of pulsation A large star with great luminosity and a diameter 10 to 100 times great ...
... The most luminous, most massive stars, with diameters greater than 100 times the diameter of the sun A variable star that brightens and dims regularly, or pulses, and whose distance can be determined from its period of pulsation A large star with great luminosity and a diameter 10 to 100 times great ...
Astronomy - The-A-List
... answer questions relating to orbital motions of binary and multiple star systems Use parallax, spectroscopic parallax, and the distance modulus to calculate distances to Type I and II Cepheids ...
... answer questions relating to orbital motions of binary and multiple star systems Use parallax, spectroscopic parallax, and the distance modulus to calculate distances to Type I and II Cepheids ...
Sagittarius - columbusastronomy
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
Variable and Binary Stars
... Some are variable even to the naked eye, once you know what you are looking for – Mira (o Ceti): T ~ 1 year AKA “Wonderful” in Latin ...
... Some are variable even to the naked eye, once you know what you are looking for – Mira (o Ceti): T ~ 1 year AKA “Wonderful” in Latin ...
May - RASC St. John`s Centre
... Familiar to everyone, the Big Dipper is the most prominent asterism (distinctive grouping of several stars) in the northern sky, and it can be used as a convenient guide to several constellations that surround it. Four stars form its bowl and three its curved handle. The two stars that form the fron ...
... Familiar to everyone, the Big Dipper is the most prominent asterism (distinctive grouping of several stars) in the northern sky, and it can be used as a convenient guide to several constellations that surround it. Four stars form its bowl and three its curved handle. The two stars that form the fron ...
1) Name the following: a) The smallest and largest planets of the
... d) The biggest star known to us present in Orion constellation. e))The brightest object in the night sky after the moon, which rotates from east to west. f)The planets closest and farthest to the sun. 2) If we join the group of stars shown in the picture below, the resulting figure will look like a ...
... d) The biggest star known to us present in Orion constellation. e))The brightest object in the night sky after the moon, which rotates from east to west. f)The planets closest and farthest to the sun. 2) If we join the group of stars shown in the picture below, the resulting figure will look like a ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.