ASTRO REVIEW 14
... spectrum Gamma ray X-ray Ultraviolet Visible light Infrared waves TV waves Radio waves Radiation ...
... spectrum Gamma ray X-ray Ultraviolet Visible light Infrared waves TV waves Radio waves Radiation ...
FSA school wide Science Olympiad 12/8/2007
... C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (the galactic equator) 3. On July 4, 1054, Chinese astronomers (and possibly Native Americans) recorded a supernova ...
... C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (the galactic equator) 3. On July 4, 1054, Chinese astronomers (and possibly Native Americans) recorded a supernova ...
KMS Universe Test Study Guide
... average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Because they are very large. 8) Why do white dwarf stars appear so dim, when they ...
... average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Because they are very large. 8) Why do white dwarf stars appear so dim, when they ...
Astronomy - Shelbyville Central Schools
... Light year = the distance light travels in 1 year • Light travels at 300,000 km/s, or about 9.5 trillion km in one year. ...
... Light year = the distance light travels in 1 year • Light travels at 300,000 km/s, or about 9.5 trillion km in one year. ...
Astronomy Learning Objectives and Study Questions for Chapter 12
... B. brown dwarf C. main-sequence star D. OB association E. emission nebula 3. Paradoxically, stars with the highest initial masses are the _____. A. farthest away B. nearest C. dimmest D. coolest E. first to move off the main sequence 4. Small stars with masses of 0.08-0.4 M that convect internally ...
... B. brown dwarf C. main-sequence star D. OB association E. emission nebula 3. Paradoxically, stars with the highest initial masses are the _____. A. farthest away B. nearest C. dimmest D. coolest E. first to move off the main sequence 4. Small stars with masses of 0.08-0.4 M that convect internally ...
File
... 23) What are the three classifications of galaxies? What do each look like? Which is most common? 24) What shape is the Milky Way? 25) What is the local group? 26) How many stars are in the Milky Way? 27) Approximately how big is the Milky Way 28) The largest known galaxy is what type of galaxy? 29) ...
... 23) What are the three classifications of galaxies? What do each look like? Which is most common? 24) What shape is the Milky Way? 25) What is the local group? 26) How many stars are in the Milky Way? 27) Approximately how big is the Milky Way 28) The largest known galaxy is what type of galaxy? 29) ...
Astronomical distances and Stellar magnitudes
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
How Do Astronomers Measure the Brightness of a Star?
... Apparent magnitude- brightness of a star as viewed from Earth A difference of 1 magnitude corresponds to a factor of 2.5 in brightness The smaller (more negative) the #, the brighter the star ...
... Apparent magnitude- brightness of a star as viewed from Earth A difference of 1 magnitude corresponds to a factor of 2.5 in brightness The smaller (more negative) the #, the brighter the star ...
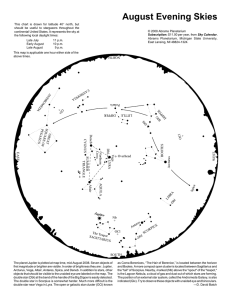
Level 4 Constellations North Star, South Star
... Five major constellations are always visible above the horizon from our latitudes: Ursa Minor, Ursa Major, Cassiopeia, Cepheus and Draco. They all revolve once in 24 hours around the North Star and stars in these are known as Circumpolar stars. Ursa Minor or the Little Bear is well known for being t ...
... Five major constellations are always visible above the horizon from our latitudes: Ursa Minor, Ursa Major, Cassiopeia, Cepheus and Draco. They all revolve once in 24 hours around the North Star and stars in these are known as Circumpolar stars. Ursa Minor or the Little Bear is well known for being t ...
the life cycle of stars
... • Energy is generated in the core and causes the star to shine. • The size of the star changes very little as long as its supply of hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei. ...
... • Energy is generated in the core and causes the star to shine. • The size of the star changes very little as long as its supply of hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei. ...
Chapter 24 Test:Stars/Galaxies
... of Magellan are two _____ galaxy fragments orbiting the the remnants of a larger galaxy we collided with over years ago. (a) elliptical, (b) normal spiral, (c) (d) barred spiral. ...
... of Magellan are two _____ galaxy fragments orbiting the the remnants of a larger galaxy we collided with over years ago. (a) elliptical, (b) normal spiral, (c) (d) barred spiral. ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.