* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 30 Study Notes
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
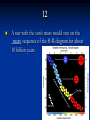
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
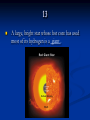
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
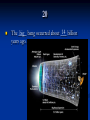
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
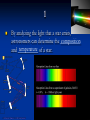
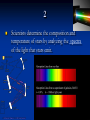
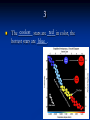
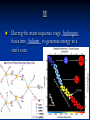
Study Notes for Chapter 30: Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Chapter 30 Section 1: Characteristics of Stars 1 By analyzing the light that a star emits, composition astronomers can determine the __________ temperature of a star. and __________ 2 Scientists determine the composition and spectra temperature of stars by analyzing the ______ of the light that stars emit. 3 coolest stars are ____ red in color, the The _______ blue hottest stars are _____. 4 appear to move in the sky because Stars _______ Earth is moving. ______ 5 A star moving away from the Earth has a red spectrum that is shifted toward ______. 6 light travels in a A light-year is the distance _____ year. 7 6,000 stars are visible from Earth About ______ without a telescope. 8 ________ Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. 9 Absolute magnitude is the true brightness of ________ a star. Chapter 30 Section 2: Stellar Evolution 10 After its temperature rises to 10,000,000°C, a protostar becomes a star when nuclear _________ fusion begins. 11 During the main sequence stage, ________ hydrogen helium to generate energy in a fuses into _______ star’s core. 12 A star with the sun’s mass would stay on the main sequence of the H-R diagram for about _____ 10 billion years. 13 A large, bright star whose hot core has used giant most of its hydrogen is a _____. 14 A small, hot, extremely dense core left after a white dwarf. star collapses is a _____ 15 A white ______ dwarf is a hot, extremely dense core collapses of matter left after a star _________. 16 Many astronomers believe that black _______ dwarfs do not exist. Chapter 30 Section 3: Star Groups 17 A galaxy is made of stars, dust, and gas bound gravity together by _______. Chapter 30 Section 4: The Big Bang Theory 18 red shift in Hubble’s discovery that there was ____ the spectra of galaxies lead to an expanding understanding that the universe is _________. 19 Red shift in the spectra of galaxies told Hubble that the universe is expanding. ________ 20 14 billion The ____ big bang occurred about ___ years ago. 21 Astronomers believe that cosmic background radiation formed shortly after the big bang. ________ 22 dark energy Most of the universe is made of _____ matter and dark _______. THE END