Stars and their Properties
... Cosmic horizon – Edge of the Observable Universe Age of the Universe is determined by the size of the Observable Universe (right now it’s between 14 and 15 billion years old) Astrometry – Measuring the distance of stars and how they move around Solar Neighborhood – Closest stars to the Sun If you kn ...
... Cosmic horizon – Edge of the Observable Universe Age of the Universe is determined by the size of the Observable Universe (right now it’s between 14 and 15 billion years old) Astrometry – Measuring the distance of stars and how they move around Solar Neighborhood – Closest stars to the Sun If you kn ...
1705 chart front
... astronomers sometimes call an asterism. The Big Dipper is a familiar name for this pattern of stars, especially known to observers in the United States, but it’s not one of the 88 constellations recognized by astronomers worldwide. Ursa Major the Great Bear is the official constellation here, but yo ...
... astronomers sometimes call an asterism. The Big Dipper is a familiar name for this pattern of stars, especially known to observers in the United States, but it’s not one of the 88 constellations recognized by astronomers worldwide. Ursa Major the Great Bear is the official constellation here, but yo ...
Due Date: Thursday, November 16, 2006
... The most significant difference between a high-mass star and the Sun will be their lifetime! Look at the HR diagram in Figure 11.1. The lifetime of Spica (10 Msun) is only about 10 million years. The lifetime of Achernar (6 Msun) is only 100 million years…so when we really should not expect the Sun ...
... The most significant difference between a high-mass star and the Sun will be their lifetime! Look at the HR diagram in Figure 11.1. The lifetime of Spica (10 Msun) is only about 10 million years. The lifetime of Achernar (6 Msun) is only 100 million years…so when we really should not expect the Sun ...
CHAPTER 2 NOTES (STARS AND GALAXIES)
... Our Sun- single star system, which is the closest star to Earth Constellations- groups of stars in which people at one time thought they saw imaginary figures of animals and people: ex Ursa Minor (Little Bear)- containing the Polaris (North Star) Orion (Hunter)- containing the bright supergiant star ...
... Our Sun- single star system, which is the closest star to Earth Constellations- groups of stars in which people at one time thought they saw imaginary figures of animals and people: ex Ursa Minor (Little Bear)- containing the Polaris (North Star) Orion (Hunter)- containing the bright supergiant star ...
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
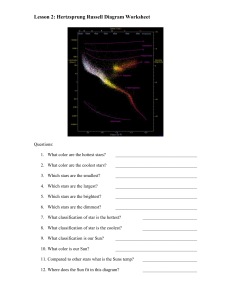
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
Novel technique water on exoplanets
... of worlds without the need for space-basedtelescopes. Since the early 1990s scientists have found almost 1000 planets in orbit around other stars.These so-calledexoplanets are mostly much larger than the Earth and many are much closer to their stars than we are to the Sun, leadingthem to be d e s c ...
... of worlds without the need for space-basedtelescopes. Since the early 1990s scientists have found almost 1000 planets in orbit around other stars.These so-calledexoplanets are mostly much larger than the Earth and many are much closer to their stars than we are to the Sun, leadingthem to be d e s c ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... the gas and dust into a spinning disk with a bulge in the middle. • A warm protostar forms as the center collapses under its ...
... the gas and dust into a spinning disk with a bulge in the middle. • A warm protostar forms as the center collapses under its ...
25 Study Guide
... • Binary stars can be used to determine stellar mass. • The nearest stars have the largest parallax angles, while those of distant stars are too small to measure. • Three factors control the apparent brightness of a star as seen from Earth: how big it is, how hot it is, and how far away it is. • A H ...
... • Binary stars can be used to determine stellar mass. • The nearest stars have the largest parallax angles, while those of distant stars are too small to measure. • Three factors control the apparent brightness of a star as seen from Earth: how big it is, how hot it is, and how far away it is. • A H ...
Name: ______________________________# __________ Study Guide is due WEDNESDAY November 2
... h. The stars that fall in a band in the middle are called_____________________________. i. Which star has the greatest absolute magnitude or brightness? ____________________. j. Which star has the least absolute magnitude or brightness? _______________________. k. Which star has the lowest surface t ...
... h. The stars that fall in a band in the middle are called_____________________________. i. Which star has the greatest absolute magnitude or brightness? ____________________. j. Which star has the least absolute magnitude or brightness? _______________________. k. Which star has the lowest surface t ...
Slide 1
... • If a star is seven times the size of the sun, it will become a red giant fairly quickly. • When its fusion stops, a central iron core remains. • The temperature heats up dramatically and causes a supernova. • A neutron star is the mass that remains. ...
... • If a star is seven times the size of the sun, it will become a red giant fairly quickly. • When its fusion stops, a central iron core remains. • The temperature heats up dramatically and causes a supernova. • A neutron star is the mass that remains. ...
Measuring the Stars pages 813-820
... that the axis of the Earth is pointing to for about the next 2,000 years. The Earth has a wobble, and the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be north. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a compass. ...
... that the axis of the Earth is pointing to for about the next 2,000 years. The Earth has a wobble, and the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be north. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a compass. ...
properties of stars 2012
... So… if apparent brightness is determined (by using a light meter) and d is known (perhaps by parallax), luminosity can be determined. Apparent Magnitude: Hipparchus, in 150 B.C. classified stars by magnitude, with 1 being the brightest, and six being the dimmest. With the advent of technology, brigh ...
... So… if apparent brightness is determined (by using a light meter) and d is known (perhaps by parallax), luminosity can be determined. Apparent Magnitude: Hipparchus, in 150 B.C. classified stars by magnitude, with 1 being the brightest, and six being the dimmest. With the advent of technology, brigh ...
Star Life Cycle and classroom textbooks for research!
... How does our sun compare in size and temp. to other stars? What phase in the life cycle of a star is our sun in right now? What is the next phase of our sun’s life cycle? How long will it be before our sun becomes this type of star? How long (in years) is the typical lifetime of a star? Where are th ...
... How does our sun compare in size and temp. to other stars? What phase in the life cycle of a star is our sun in right now? What is the next phase of our sun’s life cycle? How long will it be before our sun becomes this type of star? How long (in years) is the typical lifetime of a star? Where are th ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... – The closer the star is to the earth the greater the shift – Astronomers use a photo to determine the shift (photographed twice in a 6 month time) Then calculate the distance to within 1000 ly ...
... – The closer the star is to the earth the greater the shift – Astronomers use a photo to determine the shift (photographed twice in a 6 month time) Then calculate the distance to within 1000 ly ...
Red Giants and White Dwarfs
... “Planetary” Nebulae Slowly expanding shells of gas, ejected by pulsating stars, still heated by what’s left of the star’s core ...
... “Planetary” Nebulae Slowly expanding shells of gas, ejected by pulsating stars, still heated by what’s left of the star’s core ...
Sample exam 2
... 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You notice a power dial on the side of emission lamp and, just for fun, decide to turn up the power. The color of the helium lamp changes and you look through the spectroscop ...
... 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You notice a power dial on the side of emission lamp and, just for fun, decide to turn up the power. The color of the helium lamp changes and you look through the spectroscop ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.