life and death of a high mass star 2
... AFTER THAT, THEY LOSE THEIR MASS AND HEAT AND BEGIN TO DIE. THIS PROCESS TAKES BILLIONS AND BILLIONS OF YEARS. ...
... AFTER THAT, THEY LOSE THEIR MASS AND HEAT AND BEGIN TO DIE. THIS PROCESS TAKES BILLIONS AND BILLIONS OF YEARS. ...
Distance measurement in astronomy
... Cepheid variables are one particular type of variable star (one whose brightness changes with time) called after delta Cephei, the first star of this type to be observed. The variation in brightness of this star was discovered by John Goodricke in 1784. Goodricke lived in York and was a promising yo ...
... Cepheid variables are one particular type of variable star (one whose brightness changes with time) called after delta Cephei, the first star of this type to be observed. The variation in brightness of this star was discovered by John Goodricke in 1784. Goodricke lived in York and was a promising yo ...
Characteristics of stars powerpoint
... • The distance that light travels in one year • It travels about 9.5 million million km • Travels at a speed of 300,000 km per second ...
... • The distance that light travels in one year • It travels about 9.5 million million km • Travels at a speed of 300,000 km per second ...
The magnitudes of stars
... However this does not give a true impression of the actual brightness of a star. A nearby faint star may well look brighter than another star that is actually brighter but more distant. (A good example of this is shown by Rigel and Sirius in the following table. Sirius looks brighter than Rigel when ...
... However this does not give a true impression of the actual brightness of a star. A nearby faint star may well look brighter than another star that is actually brighter but more distant. (A good example of this is shown by Rigel and Sirius in the following table. Sirius looks brighter than Rigel when ...
Sample exam 2
... 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You notice a power dial on the side of emission lamp and, just for fun, decide to turn up the power. The color of the helium lamp changes and you look through the spectroscop ...
... 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You notice a power dial on the side of emission lamp and, just for fun, decide to turn up the power. The color of the helium lamp changes and you look through the spectroscop ...
A Brief History of Planetary Science
... The magnitude scales is logarithmic and is related to the flux by: m2 – m1 = 2.5 log10 (f1/f2) ...
... The magnitude scales is logarithmic and is related to the flux by: m2 – m1 = 2.5 log10 (f1/f2) ...
Problem set 1 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56Fe is 8.8MeV
... 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56 Fe is 8.8 MeV per nucleon. Estimate the total energy released per kilogram of matter by the sequence of reactions which fuse hydrogen to iron. 2. The main sequence of the Pleiades cluster of stars consists of stars with mass less than 6M ; the more massive s ...
... 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56 Fe is 8.8 MeV per nucleon. Estimate the total energy released per kilogram of matter by the sequence of reactions which fuse hydrogen to iron. 2. The main sequence of the Pleiades cluster of stars consists of stars with mass less than 6M ; the more massive s ...
Can We Make A Star?
... • They are made of cosmic dust, mostly hydrogen and helium • They are very unstable • The are very violent • They give off an extremely large amount of energy ...
... • They are made of cosmic dust, mostly hydrogen and helium • They are very unstable • The are very violent • They give off an extremely large amount of energy ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY Dr. Uri Griv Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University
... • The responce of the human eye works on the basis of a geometric progression rather than an arithmetic progression • The modern magnitude classification: a difference of 5 magnitudes to equal exactly a factor of 100 in apparent brightness • If m1 and m2 are the apparent magnitudes with apparent bri ...
... • The responce of the human eye works on the basis of a geometric progression rather than an arithmetic progression • The modern magnitude classification: a difference of 5 magnitudes to equal exactly a factor of 100 in apparent brightness • If m1 and m2 are the apparent magnitudes with apparent bri ...
15.3 The Lives of Stars
... have dissipated (spreads out) • Size of earth, with same mass as our sun • Turns into a black dwarf when fuel runs out • Neutron Stars • Left over from a supernova ...
... have dissipated (spreads out) • Size of earth, with same mass as our sun • Turns into a black dwarf when fuel runs out • Neutron Stars • Left over from a supernova ...
Lifecycle of a Star
... Stars with masses of 25 to 50 times of the Sun form black holes after a supernova. The leftover core of the star is so dense that it causes gravitational collapse. ...
... Stars with masses of 25 to 50 times of the Sun form black holes after a supernova. The leftover core of the star is so dense that it causes gravitational collapse. ...
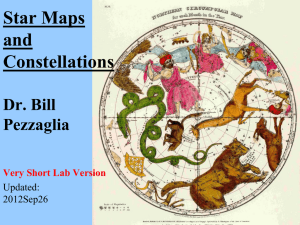
Star Maps and Constellations
... chases the bears (Ursa Major, Ursa Minor) around in circles, i.e. keeps them at the North pole ...
... chases the bears (Ursa Major, Ursa Minor) around in circles, i.e. keeps them at the North pole ...
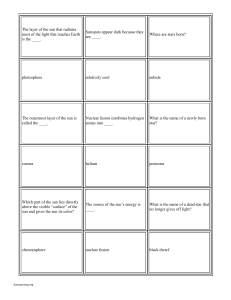
Star Game Cards
... Before being engulfed, matter that is pulled into a black hole should become very hot and emit ____. ...
... Before being engulfed, matter that is pulled into a black hole should become very hot and emit ____. ...
1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light... limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of...
... 1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer p ...
... 1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer p ...
Study Guide Astronomy
... 7. Why must astronomers wait 6 months to measure the parallax of a star? ...
... 7. Why must astronomers wait 6 months to measure the parallax of a star? ...
On my webpage, find the link Star Life Cycle and use it to answer the
... 6. How many solar masses are brown dwarfs on average? ...
... 6. How many solar masses are brown dwarfs on average? ...
Space
... •The distance from Mars to the Sun is 141,620,000 miles. •The core of Mars is solid. •The sky of Mars looks if it’s pink because the clouds are red. ...
... •The distance from Mars to the Sun is 141,620,000 miles. •The core of Mars is solid. •The sky of Mars looks if it’s pink because the clouds are red. ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 9
... 39. What marks the transition of a protostar to star? 40. Name 3 types of stars not on the main sequence. 41. What is a black dwarf? 42. What type of star may become a pulsar? 43. List the steps in the life cycle of a sun-like star. 44. Why might an old main-sequence star have a greater percentage o ...
... 39. What marks the transition of a protostar to star? 40. Name 3 types of stars not on the main sequence. 41. What is a black dwarf? 42. What type of star may become a pulsar? 43. List the steps in the life cycle of a sun-like star. 44. Why might an old main-sequence star have a greater percentage o ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.