Chemistry 112A Second Midterm Review Sheet Summary of
... Allowing fluorine (lowest priority) to point away from the viewer the rotation is clockwise hence the R-assignment. In the assignment of L-serine highest priority is given to the nitrogen atom (Z = 7) in the amino group (NH2). Both the methylalcohol group (CH2OH ) and the carboxylic acid group (COOH ...
... Allowing fluorine (lowest priority) to point away from the viewer the rotation is clockwise hence the R-assignment. In the assignment of L-serine highest priority is given to the nitrogen atom (Z = 7) in the amino group (NH2). Both the methylalcohol group (CH2OH ) and the carboxylic acid group (COOH ...
Time
... -calculate rate of reactions using: r = Δc/Δt - explain the factors which effect reaction rates; predicting rate of reactions - concentration vs time graphs – instantaneous rate of reaction - use activation energy diagrams and kinetic energy diagrams to show effect of temperature and catalysts on re ...
... -calculate rate of reactions using: r = Δc/Δt - explain the factors which effect reaction rates; predicting rate of reactions - concentration vs time graphs – instantaneous rate of reaction - use activation energy diagrams and kinetic energy diagrams to show effect of temperature and catalysts on re ...
4. Water (2)
... 8.3.3 Any two atoms can not be brought together closer than the sum of their van der Waals radii (repulsion due to electron clouds) ( which are bigger than the covalent radii of the corresponding ...
... 8.3.3 Any two atoms can not be brought together closer than the sum of their van der Waals radii (repulsion due to electron clouds) ( which are bigger than the covalent radii of the corresponding ...
unit_k_reading_notes
... already seen—it’s composition stoichiometry, which is the study of mass relationships of elements in compounds. Examples of this include calculating percentage composition, and determination of empirical and molecular formulas. The second one is reaction stoichiometry, which deals with the mass, mol ...
... already seen—it’s composition stoichiometry, which is the study of mass relationships of elements in compounds. Examples of this include calculating percentage composition, and determination of empirical and molecular formulas. The second one is reaction stoichiometry, which deals with the mass, mol ...
Dissociation energy of the C-H bond in chloroform Cl3C
... degradation of chlorinated molecules in the atmosphere, and the rate of hydrogen abstraction is strongly correlated with the C-H bond strength. Homolytic bond cleavage is a simple process to write: ...
... degradation of chlorinated molecules in the atmosphere, and the rate of hydrogen abstraction is strongly correlated with the C-H bond strength. Homolytic bond cleavage is a simple process to write: ...
Principles of Chemical Thermodynamics and Kinetics
... Living organisms maintain their systems in a dynamic steady state by taking in food. Energy is extracted from food to build complex molecules from simpler ones, and for storage. Collectively, these processes are called metabolism, the enzyme-catalyzed transformation of energy and matter. The metabol ...
... Living organisms maintain their systems in a dynamic steady state by taking in food. Energy is extracted from food to build complex molecules from simpler ones, and for storage. Collectively, these processes are called metabolism, the enzyme-catalyzed transformation of energy and matter. The metabol ...
Aldehydes and ketones
... Aldehydes and ketones with less than 5 carbons are soluble in water. Explain why this is the case using a diagram to illustrate the bonding that can occur between them and water. ...
... Aldehydes and ketones with less than 5 carbons are soluble in water. Explain why this is the case using a diagram to illustrate the bonding that can occur between them and water. ...
RULE
... The TS will have a significant amount of positive charge on a carbon atom The same factors contributing to stabilization of the carbocation intermediate will affect stability of the transition state - because the tert-butyl cation is more stable than the isobutyl cation, the TS leading to its format ...
... The TS will have a significant amount of positive charge on a carbon atom The same factors contributing to stabilization of the carbocation intermediate will affect stability of the transition state - because the tert-butyl cation is more stable than the isobutyl cation, the TS leading to its format ...
Halogenoalkanes
... Light of the right frequency (UV) can split the C-X bond by homolytic fission, creating very reactive radicals. ...
... Light of the right frequency (UV) can split the C-X bond by homolytic fission, creating very reactive radicals. ...
Section 2 Types of Chemical Reactions Chapter 8
... CH4(g) + O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) (partially balanced) • Now consider the number of oxygen atoms. • Increase the number of oxygen atoms on the left side to four by placing the coefficient 2 in front of the molecular formula ...
... CH4(g) + O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) (partially balanced) • Now consider the number of oxygen atoms. • Increase the number of oxygen atoms on the left side to four by placing the coefficient 2 in front of the molecular formula ...
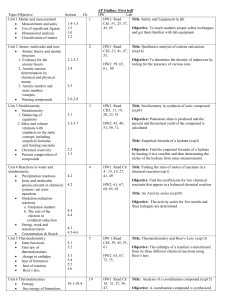
Topic/Objective - cloudfront.net
... Title: Molecular mass of a volatile liquid (exp3) Objective: A small amount of a volatile liquid inside a small test tube and then heated in boiling water until all the liquid vaporizes and fills the tube as excess water escapes. After the gas is cooled, the mass, volume, and pressure is measured to ...
... Title: Molecular mass of a volatile liquid (exp3) Objective: A small amount of a volatile liquid inside a small test tube and then heated in boiling water until all the liquid vaporizes and fills the tube as excess water escapes. After the gas is cooled, the mass, volume, and pressure is measured to ...
HS-PS1-2. Construct and revise an explanation for the outcome of a
... reactions, graphs showing the relative energies of reactants and products, and representations showing energy is conserved.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include calculating the total bond energy changes during a chemical reaction from the bond energies of reactants and products.] ...
... reactions, graphs showing the relative energies of reactants and products, and representations showing energy is conserved.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include calculating the total bond energy changes during a chemical reaction from the bond energies of reactants and products.] ...
Thermodynamics
... Where is the Energy? • Definitions we will use: – System: Reaction (bonds) – Surrounding: solvent, reaction vessel, air, etc. • An everyday example: burning wood – Initially, much energy stored as potential in C-H bonds, little kinetic energy in the air – Finally, lower potential energy in the C=O ...
... Where is the Energy? • Definitions we will use: – System: Reaction (bonds) – Surrounding: solvent, reaction vessel, air, etc. • An everyday example: burning wood – Initially, much energy stored as potential in C-H bonds, little kinetic energy in the air – Finally, lower potential energy in the C=O ...
Structure and Bonding
... The cis and trans isomers of an alkene are configurational isomers (also called geometric isomers) because they have different shapes and cannot interconvert since the double bond of an alkene cannot rotate. Therefore, the substituents are ‘fixed’ in space relative to each other. The methyl groups c ...
... The cis and trans isomers of an alkene are configurational isomers (also called geometric isomers) because they have different shapes and cannot interconvert since the double bond of an alkene cannot rotate. Therefore, the substituents are ‘fixed’ in space relative to each other. The methyl groups c ...