Syllabus of the International Chemistry Olympiad
... concerning the understanding of chemistry in qualitative and quantitative terms are included as well. While working on the problems students will encounter, for example, the chemistry of lactose, which is the by-product of Dutch cheese making, how whales manage to stay under water for a considerable ...
... concerning the understanding of chemistry in qualitative and quantitative terms are included as well. While working on the problems students will encounter, for example, the chemistry of lactose, which is the by-product of Dutch cheese making, how whales manage to stay under water for a considerable ...
Ch04-04-alkenes-2
... Explained by the intermediates, for example: tert-butyl cation is formed faster and it is more stable ...
... Explained by the intermediates, for example: tert-butyl cation is formed faster and it is more stable ...
Electrophilic Additions: Alkenes Addition of Hydrogen Halides
... Vs. Markovnikov’s rule in product formation (more substituted alcohols) ...
... Vs. Markovnikov’s rule in product formation (more substituted alcohols) ...
MS PowerPoint - Catalysis Eprints database
... The power law model correlates reaction with two basic parameters: the reaction rate constant and the order (participating species) The general expression for the power law model for an elementary reaction AB is written as: -rA = kCAn (where n is 1 ) This expression can be applicable to complex ...
... The power law model correlates reaction with two basic parameters: the reaction rate constant and the order (participating species) The general expression for the power law model for an elementary reaction AB is written as: -rA = kCAn (where n is 1 ) This expression can be applicable to complex ...
Chemistry
... Kinetic theory of gases and derivation of gas law. Non-ideal Behaviour of gases; Van Der Waal equation, the critical temperature and liquefaction of gases. Heat capacities of gases, law of equiparition of energy. Mean free path, collision diameter and collision number. Liquids: Vapor pressure, visco ...
... Kinetic theory of gases and derivation of gas law. Non-ideal Behaviour of gases; Van Der Waal equation, the critical temperature and liquefaction of gases. Heat capacities of gases, law of equiparition of energy. Mean free path, collision diameter and collision number. Liquids: Vapor pressure, visco ...
Chemical Equilibrium II
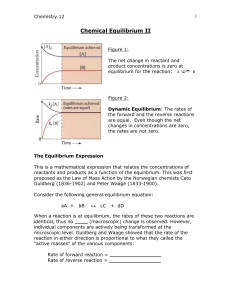
... The Equilibrium Expression This is a mathematical expression that relates the concentrations of reactants and products as a function of the equilibrium. This was first proposed as the Law of Mass Action by the Norwegian chemists Cato Guldberg (1836-1902) and Peter Waage (1833-1900). Consider the fol ...
... The Equilibrium Expression This is a mathematical expression that relates the concentrations of reactants and products as a function of the equilibrium. This was first proposed as the Law of Mass Action by the Norwegian chemists Cato Guldberg (1836-1902) and Peter Waage (1833-1900). Consider the fol ...
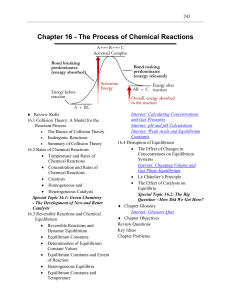
In Class Overview of Chapter
... Consider a lot of molecules. Entropy is a measure of disorder. The more vibrational, rotational, and translational energies populated by a collection of molecules means greater entropy. Consider a group of molecules, without translational, vibrational, or rotational energies and highly ordered. This ...
... Consider a lot of molecules. Entropy is a measure of disorder. The more vibrational, rotational, and translational energies populated by a collection of molecules means greater entropy. Consider a group of molecules, without translational, vibrational, or rotational energies and highly ordered. This ...
Chapter 3: Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Chapter 17: Reaction Energy and Reaction Kinetics Define the following terms: heat, temperature, specific heat, heat of reaction, enthalpy, enthalpy change, molar heat of formation, molar heat of combustion, entropy, free energy, reaction rate, chemical kinetics, rate law, calorimeter, thermochemist ...
... Chapter 17: Reaction Energy and Reaction Kinetics Define the following terms: heat, temperature, specific heat, heat of reaction, enthalpy, enthalpy change, molar heat of formation, molar heat of combustion, entropy, free energy, reaction rate, chemical kinetics, rate law, calorimeter, thermochemist ...
10 bioenergetics 03
... A sharing in driving force is possible by lowering H2 until reaction 1 becomes feasible (exergonic) but not so low that reaction 2 becomes ...
... A sharing in driving force is possible by lowering H2 until reaction 1 becomes feasible (exergonic) but not so low that reaction 2 becomes ...
Document
... Some reactions require more energy than is produced; others produce more energy than is ...
... Some reactions require more energy than is produced; others produce more energy than is ...
Unit 4 test review Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration What is an
... 15. Where does this energy come from (originally)? 16. Fill in the missing parts of the following flowchart: Is produced during ...
... 15. Where does this energy come from (originally)? 16. Fill in the missing parts of the following flowchart: Is produced during ...
Objective Reaction Type Structural Feature How to figure out how reactants react?
... What is the reaction type? (acid-base, addition, elimination, substitution) What is the intermediate formed in each reaction? 2. What are acyl chlorides used for? (see Ch. 19) ...
... What is the reaction type? (acid-base, addition, elimination, substitution) What is the intermediate formed in each reaction? 2. What are acyl chlorides used for? (see Ch. 19) ...