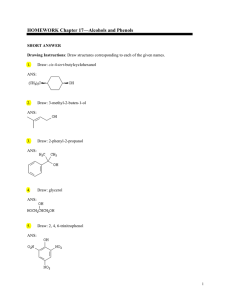
Topic 17 notes - A
... If a carboxylic acid and an alcohol are heated under reflux with concentrated H2SO4, a condensation reaction takes place and an ester is formed: Carboxylic acid + alcohol == ester + H2O R1-COOH + R2OH == R1-COOR2 + H2O This reaction is known as esterification. Esterifcation is an example of condensa ...
... If a carboxylic acid and an alcohol are heated under reflux with concentrated H2SO4, a condensation reaction takes place and an ester is formed: Carboxylic acid + alcohol == ester + H2O R1-COOH + R2OH == R1-COOR2 + H2O This reaction is known as esterification. Esterifcation is an example of condensa ...
Protection (and Deprotection) of Functional Groups in Organic
... Fine chemicals are complex and multifunctional molecules, often characterized by low volatility and limited thermal stability, whose manufacture generally is based on multistep synthesis performed in the liquid phase and frequently involving protectiondeprotection steps. The use of blocking function ...
... Fine chemicals are complex and multifunctional molecules, often characterized by low volatility and limited thermal stability, whose manufacture generally is based on multistep synthesis performed in the liquid phase and frequently involving protectiondeprotection steps. The use of blocking function ...
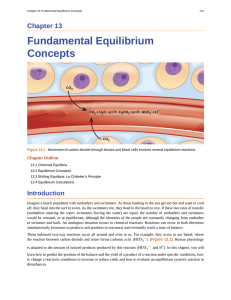
Fundamental Equilibrium Concepts
... value for Kc indicates that equilibrium is attained only after the reactants have been largely converted into products. A small value of Kc—much less than 1—indicates that equilibrium is attained when only a small proportion of the reactants have been converted into products. Once a value of Kc is k ...
... value for Kc indicates that equilibrium is attained only after the reactants have been largely converted into products. A small value of Kc—much less than 1—indicates that equilibrium is attained when only a small proportion of the reactants have been converted into products. Once a value of Kc is k ...
No Slide Title
... • Thermodynamics is the branch of science concerned with the energy changes that accompany chemical and physical changes. • Enthalpy is one of three thermodynamic properties. ...
... • Thermodynamics is the branch of science concerned with the energy changes that accompany chemical and physical changes. • Enthalpy is one of three thermodynamic properties. ...
Chapter 7. Alcohols, Thiols, Phenols, Ethers
... alkyl halide is produced in the SN1 process. But if a nucleophile is absent, then the E1 process is followed to give an alkene. Alcohols are easily dehydrated by the E1 reaction with sulfuric acid. The sulfate formed is too poor to serve as a nucleophile, thus only elimination is observed. But carbo ...
... alkyl halide is produced in the SN1 process. But if a nucleophile is absent, then the E1 process is followed to give an alkene. Alcohols are easily dehydrated by the E1 reaction with sulfuric acid. The sulfate formed is too poor to serve as a nucleophile, thus only elimination is observed. But carbo ...
Study Guide Chapter 4 Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
... The hydroxyl group is trans to the isopropyl group and cis to the methyl group. All three substituents need not always be equatorial; instead, one or two of them may be axial. Since neomenthol is the second most stable stereoisomer, we choose the structure with one axial substituent. Furthermore, we ...
... The hydroxyl group is trans to the isopropyl group and cis to the methyl group. All three substituents need not always be equatorial; instead, one or two of them may be axial. Since neomenthol is the second most stable stereoisomer, we choose the structure with one axial substituent. Furthermore, we ...
PowerPoint ******
... (4) Rearrangements of a-hydroxyaldehydes and a-hydroxyketones (acyloin rearrangement) In acid-catalyzed rearrangements of a-hydroxyaldehydes or ketones, the migrating groups migrate to carbon atoms of protonated carbonyl groups rather than to carbocation ...
... (4) Rearrangements of a-hydroxyaldehydes and a-hydroxyketones (acyloin rearrangement) In acid-catalyzed rearrangements of a-hydroxyaldehydes or ketones, the migrating groups migrate to carbon atoms of protonated carbonyl groups rather than to carbocation ...
2nd Semester Practice Chemistry Final 2009
... Multiple Choice: Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What happens to the volume of a gas during compression? a. The volume increases. b. The volume decreases. c. The volume remains constant. d. It is impossible to tell because all gases are ...
... Multiple Choice: Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What happens to the volume of a gas during compression? a. The volume increases. b. The volume decreases. c. The volume remains constant. d. It is impossible to tell because all gases are ...
Amines
... IUPAC nomenclature retains the common name aniline for C6H5NH2, the simplest aromatic amine use numbers to locate substituents or, alternatively, use the prefixes ortho (o), meta (m), and para (p) common names are still widely used NH2 ...
... IUPAC nomenclature retains the common name aniline for C6H5NH2, the simplest aromatic amine use numbers to locate substituents or, alternatively, use the prefixes ortho (o), meta (m), and para (p) common names are still widely used NH2 ...
HOTS Worksheet
... Ans. The (— CO — NH —) amide bond in nylon gets hydrolysed. Q. 2. Fibres are of crystalline structure. Why ? Ans. Fibres have strong intermolecular forces of attraction which leads to close packing of their chains and impart crystalline structure. Q. 3. Which artificial polymer is present in bubble ...
... Ans. The (— CO — NH —) amide bond in nylon gets hydrolysed. Q. 2. Fibres are of crystalline structure. Why ? Ans. Fibres have strong intermolecular forces of attraction which leads to close packing of their chains and impart crystalline structure. Q. 3. Which artificial polymer is present in bubble ...
Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Oxidative Cyclization Strategies Andreas K. Å. Persson
... already in 1836.3 Under ideal conditions, the catalyst is not consumed during the reaction and theoretically it can be reused in an infinite number of cycles. As a result, catalytic processes have the potential to become environmentally friendly as well as very cost effective. Although there are num ...
... already in 1836.3 Under ideal conditions, the catalyst is not consumed during the reaction and theoretically it can be reused in an infinite number of cycles. As a result, catalytic processes have the potential to become environmentally friendly as well as very cost effective. Although there are num ...
ammines ncert solution
... and aromatic primary amines are heated with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide, carbylamines (or isocyanides) are formed. These carbylamines have very unpleasant odours. Secondary and tertiary amines do not respond to this test. ...
... and aromatic primary amines are heated with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide, carbylamines (or isocyanides) are formed. These carbylamines have very unpleasant odours. Secondary and tertiary amines do not respond to this test. ...