3.012 Practice Problems for Recitation 1 (09.13.05) Part I. System
... possible that the gases may carry heat; this is because the walls are semi-permeable. 1. What type of system is a hollow ball made of a thick but flexible rubber? If we can imagine the object above, it is an adiabatic system. Mechanical work may be performed by pressing on the ball, but heat cannot ...
... possible that the gases may carry heat; this is because the walls are semi-permeable. 1. What type of system is a hollow ball made of a thick but flexible rubber? If we can imagine the object above, it is an adiabatic system. Mechanical work may be performed by pressing on the ball, but heat cannot ...
Lecture_1_ Heat and - Arizona State University
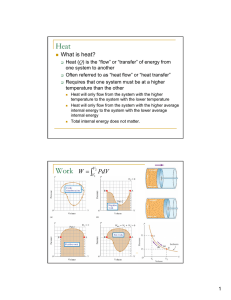
... Sign convention: The work is taken negative if it increases the energy in the system. If the volume of the system is decreased work is done on the system, increasing its energy; hence the positive sign in the equation W pdV . The unusual convention was established to fit the behavior of heat engi ...
... Sign convention: The work is taken negative if it increases the energy in the system. If the volume of the system is decreased work is done on the system, increasing its energy; hence the positive sign in the equation W pdV . The unusual convention was established to fit the behavior of heat engi ...
MODULE 4
... Temperature & Heat • Heat is not the same as temperature • The more thermal energy, the more kinetic energy, the more motion the atoms and molecules will have • The total thermal energy of an object is the sum of all the individual energies • Thermal energy depends on the amount of substance as wel ...
... Temperature & Heat • Heat is not the same as temperature • The more thermal energy, the more kinetic energy, the more motion the atoms and molecules will have • The total thermal energy of an object is the sum of all the individual energies • Thermal energy depends on the amount of substance as wel ...
HEAT- Chapter 9
... Kelvin Scale: 0 = absolute zero Freezing point of water: 273K Boiling point of water: 373K ...
... Kelvin Scale: 0 = absolute zero Freezing point of water: 273K Boiling point of water: 373K ...
Lecture5
... W = -Fex Δx = -p S Δx = -p ΔV Sign convention – from the point of view of the system ...
... W = -Fex Δx = -p S Δx = -p ΔV Sign convention – from the point of view of the system ...
Thermodynamics - StrikerPhysics
... 20°C. They display the warning “Do not dispose of this can in an incinerator”. What is the change in internal energy of such a gas if 500J of heat is added to it, raising the temperature to 2000°F? What is the final pressure of the gas? ...
... 20°C. They display the warning “Do not dispose of this can in an incinerator”. What is the change in internal energy of such a gas if 500J of heat is added to it, raising the temperature to 2000°F? What is the final pressure of the gas? ...
6. Absorption of Heat
... Latent Heat During some phase transitions (i.e. ice - water), heating does not lead to increase of temperature until the transition is completed The thermal energy required for the transition: ...
... Latent Heat During some phase transitions (i.e. ice - water), heating does not lead to increase of temperature until the transition is completed The thermal energy required for the transition: ...
3 - CFD - Anna University
... viewed as a sufficiently slow process that allows the system to adjust itself internally so that properties in one part of the system do not change any faster than those at other parts ...
... viewed as a sufficiently slow process that allows the system to adjust itself internally so that properties in one part of the system do not change any faster than those at other parts ...
Heat Work
... Heat will only flow from the system with the higher temperature to the system with the lower temperature Heat will only flow from the system with the higher average internal energy to the system with the lower average internal energy Total internal energy does not matter. ...
... Heat will only flow from the system with the higher temperature to the system with the lower temperature Heat will only flow from the system with the higher average internal energy to the system with the lower average internal energy Total internal energy does not matter. ...
The First Law of Thermodynamics
... On a microscopic scale, no distinction exists between the result of heat and that of work. The internal energy function is therefore called a state function, whose value is determined by the state of the system. – In general, ...
... On a microscopic scale, no distinction exists between the result of heat and that of work. The internal energy function is therefore called a state function, whose value is determined by the state of the system. – In general, ...
Chapter 15 Notes - Valdosta State University
... Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with the laws that govern the relationships between heat and work. Since heat is a form of energy and work is the mechanism by which energy is transferred, these laws are based on the basic principles that govern the behavior of other types of energ ...
... Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with the laws that govern the relationships between heat and work. Since heat is a form of energy and work is the mechanism by which energy is transferred, these laws are based on the basic principles that govern the behavior of other types of energ ...
New Microsoft Office Word Document
... Depends on the path followed from initial to final state of the system ...
... Depends on the path followed from initial to final state of the system ...
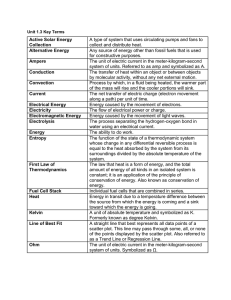
Unit 1.3 Key Terms Active Solar Energy Collection A type of system
... which all parts of the system have attained a uniform temperature which is the same as that of the system’s surroundings. A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties such as temperature, volume, pressure, concentration, surface tension, and viscosity. The study of the e ...
... which all parts of the system have attained a uniform temperature which is the same as that of the system’s surroundings. A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties such as temperature, volume, pressure, concentration, surface tension, and viscosity. The study of the e ...
Heat

In physics, heat is energy in a process of transfer between a system and its surroundings, other than as work or with the transfer of matter. When there is a suitable physical pathway, heat flows from a hotter body to a colder one. The pathway can be direct, as in conduction and radiation, or indirect, as in convective circulation.Because it refers to a process of transfer between two systems, the system of interest, and its surroundings considered as a system, heat is not a state or property of a single system. If heat transfer is slow and continuous, so that the temperature of the system of interest remains well defined, it can sometimes be described by a process function.Kinetic theory explains heat as a macroscopic manifestation of the motions and interactions of microscopic constituents such as molecules and photons.In calorimetry, sensible heat is defined with respect to a specific chosen state variable of the system, such as pressure or volume. Sensible heat transferred into or out of the system under study causes change of temperature while leaving the chosen state variable unchanged. Heat transfer that occurs with the system at constant temperature and that does change that particular state variable is called latent heat with respect to that variable. For infinitesimal changes, the total incremental heat transfer is then the sum of the latent and sensible heat increments. This is a basic paradigm for thermodynamics, and was important in the historical development of the subject.The quantity of energy transferred as heat is a scalar expressed in an energy unit such as the joule (J) (SI), with a sign that is customarily positive when a transfer adds to the energy of a system. It can be measured by calorimetry, or determined by calculations based on other quantities, relying on the first law of thermodynamics.