Energy
... o Mechanical energy - the KE of an object is calculated from mass and velocity o Thermal energy – temperature it a measure of the average KE of particles o Electrical energy – motion of electrons PE – potential energy o Gravitational energy - as a result of height, PE = mgh o Electrostatic energy - ...
... o Mechanical energy - the KE of an object is calculated from mass and velocity o Thermal energy – temperature it a measure of the average KE of particles o Electrical energy – motion of electrons PE – potential energy o Gravitational energy - as a result of height, PE = mgh o Electrostatic energy - ...
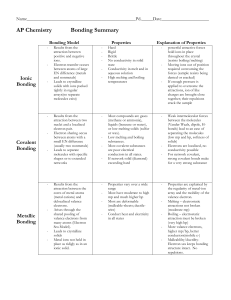
Types of Bonding Summary
... small EN difference (usually two nonmetals) Leads to separate molecules with specific shapes or to extended networks ...
... small EN difference (usually two nonmetals) Leads to separate molecules with specific shapes or to extended networks ...
Mechanics 1: The Pendulum
... from which it follows, after differentiating with respect to time, that the component of acceleration in the θ 1 direction is given by: ℓθ̈θ 1 . The gravitational force is given by −mgk. The component of this force in the θ 1 direction is given by: ...
... from which it follows, after differentiating with respect to time, that the component of acceleration in the θ 1 direction is given by: ℓθ̈θ 1 . The gravitational force is given by −mgk. The component of this force in the θ 1 direction is given by: ...
Energy and Radiation Reading: p. 25
... specific heating). It’s the amount of energy (not heat, as your book says), needed to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius. See Table 2.1 (p.28) for a comparison of many substances. Latent heating—This tends to be a bit confusing, yet is hugely important in meteorol ...
... specific heating). It’s the amount of energy (not heat, as your book says), needed to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius. See Table 2.1 (p.28) for a comparison of many substances. Latent heating—This tends to be a bit confusing, yet is hugely important in meteorol ...
Energy and Work Section 10.1
... – KE = ½ (m)(v²) – Kinetic energy equals one half mass times velocity squared. ...
... – KE = ½ (m)(v²) – Kinetic energy equals one half mass times velocity squared. ...
Conservation of Energy Worksheet
... a) What is its potential energy when it is 1000-m above the ground? b) What is its kinetic energy when it is 1000-m above the ground? c) The boulder begins to fall. What is its potential energy when it is 500-m above the ground? Where did the “lost” potential energy go? d) What is the kinetic energy ...
... a) What is its potential energy when it is 1000-m above the ground? b) What is its kinetic energy when it is 1000-m above the ground? c) The boulder begins to fall. What is its potential energy when it is 500-m above the ground? Where did the “lost” potential energy go? d) What is the kinetic energy ...
PERIODICITY AND ATOMIC STRUCTURE CHAPTER 5
... finding the electron anywhere but a greater probability of finding it near the nucleus. In terms of the volume of space the probability reaches a maximum at the distance of the orbits (H, K, L, M). In order to solve the wave equation various constants must be defined. These are called quantum number ...
... finding the electron anywhere but a greater probability of finding it near the nucleus. In terms of the volume of space the probability reaches a maximum at the distance of the orbits (H, K, L, M). In order to solve the wave equation various constants must be defined. These are called quantum number ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.