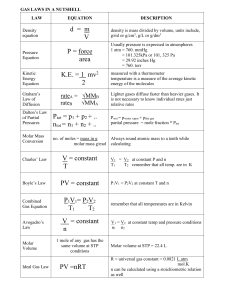
SPS8. Students will determine relationships among
... c. Demonstrate that solubility is related to temperature by constructing a solubility curve. SPS7. Students will relate transformations and flow of energy within a system. b. Investigate molecular motion as it relates to thermal energy changes in terms of conduction, convection, and radiation. c. De ...
... c. Demonstrate that solubility is related to temperature by constructing a solubility curve. SPS7. Students will relate transformations and flow of energy within a system. b. Investigate molecular motion as it relates to thermal energy changes in terms of conduction, convection, and radiation. c. De ...
Test Review CBA 2B
... 9. Examples: Decide whether each is Conduction, Convection or Radiation. a. Heat from a light bulb Radiation b. A hot air balloon rising Convection c. Cooking eggs in a pan Conduction d. Burning your tongue on soup Conduction e. Walking on hot sand Conduction f. Boiling water Convection g. Heating ...
... 9. Examples: Decide whether each is Conduction, Convection or Radiation. a. Heat from a light bulb Radiation b. A hot air balloon rising Convection c. Cooking eggs in a pan Conduction d. Burning your tongue on soup Conduction e. Walking on hot sand Conduction f. Boiling water Convection g. Heating ...
Lecture 3
... What is light • Light is both a wave and a particle • It can be broken up into particles (or pieces) called photons • Each photon carries energy – The higher the frequency (or smaller the wavelength), the higher the energy ...
... What is light • Light is both a wave and a particle • It can be broken up into particles (or pieces) called photons • Each photon carries energy – The higher the frequency (or smaller the wavelength), the higher the energy ...
Slide 1
... A person is pulling a crate of mass M along the floor with a constant force F over a distance d. The coefficient of friction is . (a) Find the work done by the force F on the crate. (b) Same if F changes as F0(1+x2/d2). (c) Find the work done by the force of friction on the crate. (d) Find the net ...
... A person is pulling a crate of mass M along the floor with a constant force F over a distance d. The coefficient of friction is . (a) Find the work done by the force F on the crate. (b) Same if F changes as F0(1+x2/d2). (c) Find the work done by the force of friction on the crate. (d) Find the net ...
Review Guide
... 49. A system that has 20 units of heat entering the system and 40 units of work are done on the system, what is the internal energy? 50. A system that has 10 units of heat entering the system and the system does 40 units of work, what is the internal energy? 51. A system that has 30 units of heat le ...
... 49. A system that has 20 units of heat entering the system and 40 units of work are done on the system, what is the internal energy? 50. A system that has 10 units of heat entering the system and the system does 40 units of work, what is the internal energy? 51. A system that has 30 units of heat le ...
Some useful Statistical Thermodynamics 1 Introduction
... The second law states that the number of accessible micro-states of an isolated system, Ω, never decreases. If we consider subsystem A to contain and ideal atomic gas, then the number of accessible micro-states of A is simply the number of places in space that may be occupied by the gas atoms. Thus, ...
... The second law states that the number of accessible micro-states of an isolated system, Ω, never decreases. If we consider subsystem A to contain and ideal atomic gas, then the number of accessible micro-states of A is simply the number of places in space that may be occupied by the gas atoms. Thus, ...
Section 10.2 The Flow of Energy
... • How much energy is there in a substance? 2. To understand how heat is measured • What are the units of energy? 3. To understand how the flow of heat changes temperature • How does an amount of heat gained or lost relate to a change in temperature? ...
... • How much energy is there in a substance? 2. To understand how heat is measured • What are the units of energy? 3. To understand how the flow of heat changes temperature • How does an amount of heat gained or lost relate to a change in temperature? ...
Week 3 - Help-A-Bull
... See assumptions in text …. ..molecules in constant motion .. collision time negligible compared to free motion .. collisions are elastic .. no effect from external forces etc. ...
... See assumptions in text …. ..molecules in constant motion .. collision time negligible compared to free motion .. collisions are elastic .. no effect from external forces etc. ...
Lectures 22
... A particle moves along the x-axis while acted on by a single conservative force parallel to the xaxis. The force corresponds to the potentialenergy function graphed in the Figure. The particle is released from rest at point A. a)What is the direction of the force on the particle when it is at point ...
... A particle moves along the x-axis while acted on by a single conservative force parallel to the xaxis. The force corresponds to the potentialenergy function graphed in the Figure. The particle is released from rest at point A. a)What is the direction of the force on the particle when it is at point ...
Chem 2 AP Ch 7 MC Review
... 2. Is it possible for a fluorescent material to emit radiation in the ultraviolet region after absorbing visible light? Explain your answer. A) No, ultraviolet light has higher energy than visible light. B) No, fluorescent materials only emit purple and green visible light. C) Yes, fluorescent mater ...
... 2. Is it possible for a fluorescent material to emit radiation in the ultraviolet region after absorbing visible light? Explain your answer. A) No, ultraviolet light has higher energy than visible light. B) No, fluorescent materials only emit purple and green visible light. C) Yes, fluorescent mater ...
Name
... following best explains why the 2p peak for S is further to the left than the 2p peak for P, but the 3p peak for S is further to the right than the 3p peak for P? Circle your answer. I. S has a greater effective nuclear charge than P, and the 3p sublevel in S has greater electron repulsions than in ...
... following best explains why the 2p peak for S is further to the left than the 2p peak for P, but the 3p peak for S is further to the right than the 3p peak for P? Circle your answer. I. S has a greater effective nuclear charge than P, and the 3p sublevel in S has greater electron repulsions than in ...
Modern Atomic Theory (aka the electron chapter!)
... We need a new theory — now called QUANTUM or WAVE MECHANICS. e- can only exist in certain discrete orbits e- is restricted to QUANTIZED energy state (quanta = bundles of energy) ...
... We need a new theory — now called QUANTUM or WAVE MECHANICS. e- can only exist in certain discrete orbits e- is restricted to QUANTIZED energy state (quanta = bundles of energy) ...
Chem 2 AP Ch 7 MC Review Key
... B) No, fluorescent materials only emit purple and green visible light. C) Yes, fluorescent materials emit a broad spectrum of light. D) Yes, after storing enough visible light energy, the fluorescent material can emit ultraviolet light. ...
... B) No, fluorescent materials only emit purple and green visible light. C) Yes, fluorescent materials emit a broad spectrum of light. D) Yes, after storing enough visible light energy, the fluorescent material can emit ultraviolet light. ...
May 2002
... Show that the circular motion is stable. If Ω is the frequency of small oscillations about the unperturbed motion, show that the ratio Ω/ω depends only on α. Determine this dependence. ...
... Show that the circular motion is stable. If Ω is the frequency of small oscillations about the unperturbed motion, show that the ratio Ω/ω depends only on α. Determine this dependence. ...
EC210Course_File_Summary
... EC 210- Solid State Electronics Required Syllabus COURSE DESCRIPTION: Elementary materials science concepts: Atomic structure, Bonding and types of solids, The crystalline state. Lattice vibrations. The hall effect and hall devices. Quantum mechanics: photons, particles and waves, the electron as a ...
... EC 210- Solid State Electronics Required Syllabus COURSE DESCRIPTION: Elementary materials science concepts: Atomic structure, Bonding and types of solids, The crystalline state. Lattice vibrations. The hall effect and hall devices. Quantum mechanics: photons, particles and waves, the electron as a ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.