Reading - 1st Law of Thermodynamics
... Heading up the do-not camp was Stuart Nelson Jr., head veterinarian for the famous Iditarod dogsled race currently under way in Alaska. This 1,100-mile event lasts two weeks and features several dozen dog teams and their mushers racing from Anchorage to Nome in some of the most grueling conditions i ...
... Heading up the do-not camp was Stuart Nelson Jr., head veterinarian for the famous Iditarod dogsled race currently under way in Alaska. This 1,100-mile event lasts two weeks and features several dozen dog teams and their mushers racing from Anchorage to Nome in some of the most grueling conditions i ...
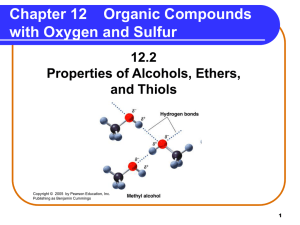
Chapter 12 Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
... Methane is fully reduced and gives off more energy during combustion than methanol. 2nd, the number of oxygen molecules required to react with a fuel molecule can give an estimate of how much energy is available. ...
... Methane is fully reduced and gives off more energy during combustion than methanol. 2nd, the number of oxygen molecules required to react with a fuel molecule can give an estimate of how much energy is available. ...
Physical Science Day Starters
... a. It will go to the upper right, straight, and will slow down b. It will curl to the right and “up”, at the same speed c. It will go to the upper right at a constant speed d. It will go to the upper left and up at a decreasing speed ...
... a. It will go to the upper right, straight, and will slow down b. It will curl to the right and “up”, at the same speed c. It will go to the upper right at a constant speed d. It will go to the upper left and up at a decreasing speed ...
Chapter 4 Energy and Stability
... The damping causes dissipation of energy. When the potential energy is proportional to the mass of the particle, as is the case for instance in vertical motion under gravity where V (z) = mgz + const., it is sometimes useful to consider the potential energy per unit mass, which would here be just Vu ...
... The damping causes dissipation of energy. When the potential energy is proportional to the mass of the particle, as is the case for instance in vertical motion under gravity where V (z) = mgz + const., it is sometimes useful to consider the potential energy per unit mass, which would here be just Vu ...
Classical thermodynamics of particles in harmonic traps
... ger confinement of the gas, increased density, and positive work on the gas. The form of the first law in Eq. 共4兲 runs counter to the intuition that we develop in studying ideal gases in rigid containers. It might seem more natural to express the term describing mechanical work as −b⌬A instead of A⌬ ...
... ger confinement of the gas, increased density, and positive work on the gas. The form of the first law in Eq. 共4兲 runs counter to the intuition that we develop in studying ideal gases in rigid containers. It might seem more natural to express the term describing mechanical work as −b⌬A instead of A⌬ ...
toolkit - The Open University
... given element consists of matter entirely composed of atoms with the same number of protons in their nuclei. elementary particle A piece of matter that is of sub-nuclear size. Such particles include protons and neutrons, as well as electrons and quarks. They may or may not ...
... given element consists of matter entirely composed of atoms with the same number of protons in their nuclei. elementary particle A piece of matter that is of sub-nuclear size. Such particles include protons and neutrons, as well as electrons and quarks. They may or may not ...
Chapter 2
... 12. The chemical characteristics or reactivity of an element depend mostly on the _____. (Concept 2.2 ) a) number of electrons in its outermost shell b) number of electron shells present in the atoms c) mean energy level of its electrons d) degree to which it has more or fewer electrons than protons ...
... 12. The chemical characteristics or reactivity of an element depend mostly on the _____. (Concept 2.2 ) a) number of electrons in its outermost shell b) number of electron shells present in the atoms c) mean energy level of its electrons d) degree to which it has more or fewer electrons than protons ...
8 Elementary statistical thermodynamics
... The differences between energy levels of electron motion and nucleus motion are big enough to keep the electrons and nuclei stay at their ground states. Both degree of degeneracy, ge,0, for electron motion at ground state and degree of degeneracy, gn,0, for nucleus motion at ground state are differe ...
... The differences between energy levels of electron motion and nucleus motion are big enough to keep the electrons and nuclei stay at their ground states. Both degree of degeneracy, ge,0, for electron motion at ground state and degree of degeneracy, gn,0, for nucleus motion at ground state are differe ...
Process
... ions of а substance is two different oxidation states. Thus, for the ferric - ferrous ion electrode functioning as а cathode, ...
... ions of а substance is two different oxidation states. Thus, for the ferric - ferrous ion electrode functioning as а cathode, ...
Experiment 1 - 8. Form of Energy
... although they passed different courses. It corresponds to the transfer of water in a dam, in which the amount of water is changed not only by the in-and-out process on the gate but also by the rain or evaporation. But the water from different sources can't be distinguished. ...
... although they passed different courses. It corresponds to the transfer of water in a dam, in which the amount of water is changed not only by the in-and-out process on the gate but also by the rain or evaporation. But the water from different sources can't be distinguished. ...
Manual(Exp.1)
... corresponds to the transfer of water in a dam, in which the amount of water is changed not only by the in-and-out process on the gate but also by the rain or evaporation. But the water from different sources can't be distinguished. Since the heat and the work have been using different units even tho ...
... corresponds to the transfer of water in a dam, in which the amount of water is changed not only by the in-and-out process on the gate but also by the rain or evaporation. But the water from different sources can't be distinguished. Since the heat and the work have been using different units even tho ...
What are the 3 primary phases of matter?
... Ex: a sprinting runner, a moving wheel or fast moving particles that are too small to see ...
... Ex: a sprinting runner, a moving wheel or fast moving particles that are too small to see ...
IB Physics
... State the first law of thermodynamics. We can add energy to a gas by heating Q (temperature gradient) Or by working (mechanical energy) = W ...
... State the first law of thermodynamics. We can add energy to a gas by heating Q (temperature gradient) Or by working (mechanical energy) = W ...
Chapter 2: You must understand chemistry to understand life (and to
... 4. the radiation emitted upon decay (alpha, beta, and/or gamma) can be used as a tool for experiments; can also be used medically; has other uses and dangers (nuclear power, nuclear bombs, radiation poisoning, etc.) 5. radiation can cause mutations in DNA, can interfere with cell division E. electro ...
... 4. the radiation emitted upon decay (alpha, beta, and/or gamma) can be used as a tool for experiments; can also be used medically; has other uses and dangers (nuclear power, nuclear bombs, radiation poisoning, etc.) 5. radiation can cause mutations in DNA, can interfere with cell division E. electro ...
Worksheet on Ionic and Atomic Size Trends
... Both of these electron configurations contain the same number of energy levels. The size of these atoms decreases because the number of protons increases from left to right, resulting in an increasing nuclear charge. This greater charge pulls the energy levels closer to the nucleus as the nuclear ch ...
... Both of these electron configurations contain the same number of energy levels. The size of these atoms decreases because the number of protons increases from left to right, resulting in an increasing nuclear charge. This greater charge pulls the energy levels closer to the nucleus as the nuclear ch ...
High School Physics - Scituate Public Schools
... related to why some objects move in certain ways, why objects change their motion, and why some materials are attracted to each other while others are not. This core idea helps students answer the question, “How can one explain and predict interactions between objects and within systems of objects?” ...
... related to why some objects move in certain ways, why objects change their motion, and why some materials are attracted to each other while others are not. This core idea helps students answer the question, “How can one explain and predict interactions between objects and within systems of objects?” ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.