GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL ENERGY
... Let’s assume that the particle of mass m moves from A to B along the indicated trajectory. As we know, the particle will pick up some kinetic energy, and some potential energy along the way. Question: What does an external agent will have to do in order to move the particle from A to B, along the sa ...
... Let’s assume that the particle of mass m moves from A to B along the indicated trajectory. As we know, the particle will pick up some kinetic energy, and some potential energy along the way. Question: What does an external agent will have to do in order to move the particle from A to B, along the sa ...
Chemistry: The Study of Change
... Mechanical energy is sum of kinetic (energy of motion) & potential (energy of position) of macroscopic objects. Trebuchet converting potential energy to kinetic energy to perform work (moving matter). ...
... Mechanical energy is sum of kinetic (energy of motion) & potential (energy of position) of macroscopic objects. Trebuchet converting potential energy to kinetic energy to perform work (moving matter). ...
lecture 6
... Due to shorter range of d orbitals, bonding will favour smaller lattice constants to maximize wavefunction overlap. Around the middle of the TM series, have strong cohesion and decreasing lattice constants. As filling continues s-electron density becomes higher than the optimum for metallic bonding ...
... Due to shorter range of d orbitals, bonding will favour smaller lattice constants to maximize wavefunction overlap. Around the middle of the TM series, have strong cohesion and decreasing lattice constants. As filling continues s-electron density becomes higher than the optimum for metallic bonding ...
Proposal for nano science and technology project on nitride based
... The strain built up from lattice-mismatch during growth usually leads to the formation of crystal defects and/or self-assembled nano clusters. Aside from lattice-mismatch, the InGaN/InN compound can also spontaneously form nano dots or clusters due to its phase segregation property. These nano-scale ...
... The strain built up from lattice-mismatch during growth usually leads to the formation of crystal defects and/or self-assembled nano clusters. Aside from lattice-mismatch, the InGaN/InN compound can also spontaneously form nano dots or clusters due to its phase segregation property. These nano-scale ...
Physics 141 Mechanics Yongli Gao Lecture 4 Motion in 3-D
... The simplest oscillation is a particle of mass m attached to a massless spring of spring constant k on a horizontal frictionless plane. From Hooke's law, F=-kx d2x From Newton's 2nd law, F ma m 2 kx dt The solution is the simple harmonic oscillation x(t) Acos(wt f ) (SHO) where A is the a ...
... The simplest oscillation is a particle of mass m attached to a massless spring of spring constant k on a horizontal frictionless plane. From Hooke's law, F=-kx d2x From Newton's 2nd law, F ma m 2 kx dt The solution is the simple harmonic oscillation x(t) Acos(wt f ) (SHO) where A is the a ...
LEWIS DOT STRUCTURES , MOLECULAR SHAPES, AND
... LEWIS DOT STRUCTURES and VSEPR MOLECULAR SHAPES Valence electrons— electrons occupying the last s & p sublevels used. The number of valence electrons is easily determined for Representative elements. You simply need to look at the group number. Examples: Group 1A elements like sodium have 1 valence ...
... LEWIS DOT STRUCTURES and VSEPR MOLECULAR SHAPES Valence electrons— electrons occupying the last s & p sublevels used. The number of valence electrons is easily determined for Representative elements. You simply need to look at the group number. Examples: Group 1A elements like sodium have 1 valence ...
Lecture 8
... - The rate of reaction generally depends on the concentration of reactants. Rate =k[A]n[B]m - where k is the rate constant and n and m are the orders of reaction with respect to reactants A and B. - Orders of reaction depend on the mechanism and are not necessarily equal to the stoichiometric coeffi ...
... - The rate of reaction generally depends on the concentration of reactants. Rate =k[A]n[B]m - where k is the rate constant and n and m are the orders of reaction with respect to reactants A and B. - Orders of reaction depend on the mechanism and are not necessarily equal to the stoichiometric coeffi ...
Ballistic Pendulum
... 1. Determine the mass of the bullet and the pendulum. 2. Prepare the ballistic pendulum for firing and measure the height of the pendulum from its center of mass (CM). Let this height be the reference height (h = 0). If your pendulum can be measured in degrees of swing, then record the starting angl ...
... 1. Determine the mass of the bullet and the pendulum. 2. Prepare the ballistic pendulum for firing and measure the height of the pendulum from its center of mass (CM). Let this height be the reference height (h = 0). If your pendulum can be measured in degrees of swing, then record the starting angl ...
Physical Science Day Starters
... a. It will go to the upper right, straight, and will slow down b. It will curl to the right and “up”, at the same speed c. It will go to the upper right at a constant speed d. It will go to the upper left and up at a decreasing speed ...
... a. It will go to the upper right, straight, and will slow down b. It will curl to the right and “up”, at the same speed c. It will go to the upper right at a constant speed d. It will go to the upper left and up at a decreasing speed ...
Syllabus - www.asetmax.com
... Kinetic Theory of Gases: Equation of state of a perfect gas, work done on compressing a gas. Kinetic theory of gases assumptions, concept of pressure. Kinetic energy and temperature: rms speed of gas molecules; Degrees of freedom, Law of equipartition of energy, applications to specific heat capacit ...
... Kinetic Theory of Gases: Equation of state of a perfect gas, work done on compressing a gas. Kinetic theory of gases assumptions, concept of pressure. Kinetic energy and temperature: rms speed of gas molecules; Degrees of freedom, Law of equipartition of energy, applications to specific heat capacit ...
syllabus for aset 2017
... Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations: Complex numbers as ordered pairs of reals, Representation of complex numbers in the form a+ib and their representation in a plane, Argand diagram, algebra of complex numbers, modulus and argument (or amplitude) of a complex number, square root of a complex nu ...
... Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations: Complex numbers as ordered pairs of reals, Representation of complex numbers in the form a+ib and their representation in a plane, Argand diagram, algebra of complex numbers, modulus and argument (or amplitude) of a complex number, square root of a complex nu ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy
... A pulse of electromagnetic radiation covering the entire spectrum under scrutiny (NMR, UV, IR) is used to obtain the whole spectrum instantly. The pulse may be applied multiple times and the results accumulated and averaged, which provides for very high sensitivity. The signal measured is actually t ...
... A pulse of electromagnetic radiation covering the entire spectrum under scrutiny (NMR, UV, IR) is used to obtain the whole spectrum instantly. The pulse may be applied multiple times and the results accumulated and averaged, which provides for very high sensitivity. The signal measured is actually t ...
free energy
... compounds, e.g. sugars, fats, amino acids, can be used to drive the synthesis of other molecules, e.g .structural components of cells, or compounds such as polysaccharides that store energy for future needs. ...
... compounds, e.g. sugars, fats, amino acids, can be used to drive the synthesis of other molecules, e.g .structural components of cells, or compounds such as polysaccharides that store energy for future needs. ...
Lecture 01 units w
... • Unfortunately, in Hydrology our clients are mostly civilians, who expect answers in English units. We must learn to use both. ...
... • Unfortunately, in Hydrology our clients are mostly civilians, who expect answers in English units. We must learn to use both. ...
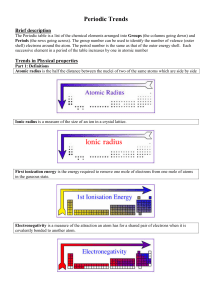
Chem 11 Study Guide SCH3U Unit 1 Definitions: SATP: Standard
... ➢ IUPAC: Intn’l Union of Pure and Applied Chem (approves, makes chem names symbols, etc. ➢ Representative Elements: an element in any of groups 1,2,13-18 ➢ Transition Metal: element of groups 3-12 ➢ Energy level: a space with definite and fixed energy in which an electron is allowed to move ➢ Orbit: ...
... ➢ IUPAC: Intn’l Union of Pure and Applied Chem (approves, makes chem names symbols, etc. ➢ Representative Elements: an element in any of groups 1,2,13-18 ➢ Transition Metal: element of groups 3-12 ➢ Energy level: a space with definite and fixed energy in which an electron is allowed to move ➢ Orbit: ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.