Work & Energy
... Key Ideas • Gravitational Potential Energy is the energy that an object has due to its vertical position relative to the Earth’s surface. • Elastic Potential Energy is the energy stored in a spring or other elastic material. • Hooke’s Law: The displacement of a spring from its unstretched position ...
... Key Ideas • Gravitational Potential Energy is the energy that an object has due to its vertical position relative to the Earth’s surface. • Elastic Potential Energy is the energy stored in a spring or other elastic material. • Hooke’s Law: The displacement of a spring from its unstretched position ...
Lecture01 - Lcgui.net
... 1. Provide definitions for the following measureable flow properties: angular momentum, entropy, thermal conductivity, molecular diffusivity, and surface tension. 2. List the established names for the SI units of force, pressure, energy, and power and their relationships to primary units. Also list ...
... 1. Provide definitions for the following measureable flow properties: angular momentum, entropy, thermal conductivity, molecular diffusivity, and surface tension. 2. List the established names for the SI units of force, pressure, energy, and power and their relationships to primary units. Also list ...
6.Utilization of photon equation of motion to
... Introduction Light and electromagnetic waves, (E.M.W) play an important role in our daily life [1]. Light is the oldest known form of( E.M.W) Theories about the nature of light can be traced from the writing of ancient authors like Newton, who proposed that light behaves like the smallest of tiny pa ...
... Introduction Light and electromagnetic waves, (E.M.W) play an important role in our daily life [1]. Light is the oldest known form of( E.M.W) Theories about the nature of light can be traced from the writing of ancient authors like Newton, who proposed that light behaves like the smallest of tiny pa ...
Fundamentals of chemical thermodynamics and bioenergetics
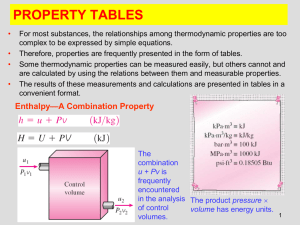
... air and water vapor at about 20 atm. Because of the large difference in pressure between the tank and the outside atmosphere, when the mixture is sprayed into the atmosphere it expands so rapidly that, as a good approximation, no heat exchange occurs between the system (air and water) and its surrou ...
... air and water vapor at about 20 atm. Because of the large difference in pressure between the tank and the outside atmosphere, when the mixture is sprayed into the atmosphere it expands so rapidly that, as a good approximation, no heat exchange occurs between the system (air and water) and its surrou ...
ENGINEERING_THERMODYNAMICS
... 1.1 What is Thermodynamics? The science, which deals the analysis of various machines by quantity, which involves the transfer of energy into useful work, is called thermodynamics. Many energy conversion devices require the transfer of energy into work. Thermodynamics is applied in various thermal e ...
... 1.1 What is Thermodynamics? The science, which deals the analysis of various machines by quantity, which involves the transfer of energy into useful work, is called thermodynamics. Many energy conversion devices require the transfer of energy into work. Thermodynamics is applied in various thermal e ...
Changes TO - Spring Branch ISD
... Elements and symbols vocabulary below make flashcards for +5 ...
... Elements and symbols vocabulary below make flashcards for +5 ...
Lecture01 - Lcgui.net
... 1. Provide definitions for the following measureable flow properties: angular momentum, entropy, thermal conductivity, molecular diffusivity, and surface tension. 2. List the established names for the SI units of force, pressure, energy, and power and their relationships to primary units. Also list ...
... 1. Provide definitions for the following measureable flow properties: angular momentum, entropy, thermal conductivity, molecular diffusivity, and surface tension. 2. List the established names for the SI units of force, pressure, energy, and power and their relationships to primary units. Also list ...
June 2011 review
... Explain, in terms of electronegativity difference, why the bond between hydrogen and oxygen in a water molecule is more polar than the bond between hydrogen and nitrogen in an ammonia molecule. [1] 9. Base your answer on the information below. In 1864, the Solvay process was developed to make soda ...
... Explain, in terms of electronegativity difference, why the bond between hydrogen and oxygen in a water molecule is more polar than the bond between hydrogen and nitrogen in an ammonia molecule. [1] 9. Base your answer on the information below. In 1864, the Solvay process was developed to make soda ...
W - Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics
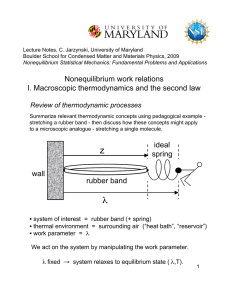
... Nonequilibrium work relations I. Macroscopic thermodynamics and the second law Review of thermodynamic processes Summarize relevant thermodynamic concepts using pedagogical example stretching a rubber band - then discuss how these concepts might apply to a microscopic analogue - stretching a single ...
... Nonequilibrium work relations I. Macroscopic thermodynamics and the second law Review of thermodynamic processes Summarize relevant thermodynamic concepts using pedagogical example stretching a rubber band - then discuss how these concepts might apply to a microscopic analogue - stretching a single ...
2. Laws of thermodynamics
... b. Analyze what happens to the size and shape of an object when it is heated. c. Analyze qualitatively the effects of conduction, radiation, and convection in thermal processes. C. Kinetic theory and thermodynamics 1. Ideal gases a. Students should understand the kinetic theory model of an ideal gas ...
... b. Analyze what happens to the size and shape of an object when it is heated. c. Analyze qualitatively the effects of conduction, radiation, and convection in thermal processes. C. Kinetic theory and thermodynamics 1. Ideal gases a. Students should understand the kinetic theory model of an ideal gas ...
Slide 1
... • For objects in motion, we have kinetic energy Ke which is always a scalar quantity and not a vector. • The potential energy of a mass m at a height h in a gravitational field with constant g is given in the next table. Only differences in potential energy are meaningful. For mechanical systems wit ...
... • For objects in motion, we have kinetic energy Ke which is always a scalar quantity and not a vector. • The potential energy of a mass m at a height h in a gravitational field with constant g is given in the next table. Only differences in potential energy are meaningful. For mechanical systems wit ...
Thermodynamics
... leave or enter the system. Q= 0 by definition U= Q + W U = W only W = - since gas expands hence U < 0 (tem drops) gas loses temp as expands since don’t provide heat to offset work done by gas ...
... leave or enter the system. Q= 0 by definition U= Q + W U = W only W = - since gas expands hence U < 0 (tem drops) gas loses temp as expands since don’t provide heat to offset work done by gas ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.