Atoms and Molecules - New Age International
... (iv) energy (E). Moreover, a particle occupies a definite position in space. In view of the above facts, it is rather difficult to accept two conflicting ideas, that radiation is a wave which is spread out over space and also a particle which is localised at a point in space. de-Broglies Equation ( ...
... (iv) energy (E). Moreover, a particle occupies a definite position in space. In view of the above facts, it is rather difficult to accept two conflicting ideas, that radiation is a wave which is spread out over space and also a particle which is localised at a point in space. de-Broglies Equation ( ...
Document
... At constant V, the change in E is equal to the heat gained or lost At constant P, the change in H is equal to the heat gained or lost The difference between E and H is the amount of P-V work done by the system when the process occurs at constant P, −PV In many reactions, V is close to ...
... At constant V, the change in E is equal to the heat gained or lost At constant P, the change in H is equal to the heat gained or lost The difference between E and H is the amount of P-V work done by the system when the process occurs at constant P, −PV In many reactions, V is close to ...
슬라이드 1
... ∂c/∂t = D∇2c - v∙∇c: generalized diffusion equation • If a reaction occurs, it has also to be included. For a 1st-order reaction - kc term is included. • This is the key equation in designing a chemical reactor. • Finite element method in carrying out computer calculation. ...
... ∂c/∂t = D∇2c - v∙∇c: generalized diffusion equation • If a reaction occurs, it has also to be included. For a 1st-order reaction - kc term is included. • This is the key equation in designing a chemical reactor. • Finite element method in carrying out computer calculation. ...
SHM1simpleHarm
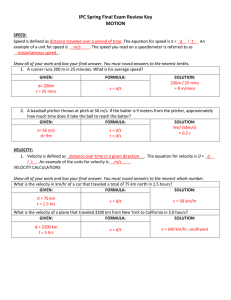
... 6. A block of mass 608 grams is fastened to a spring whose spring constant is 65 N/m. The block is pulled a distance of 11 cm from its equilibrium position and then released. a. What force does the spring exert on the block just before the block is released? b. What are the angular frequency, freque ...
... 6. A block of mass 608 grams is fastened to a spring whose spring constant is 65 N/m. The block is pulled a distance of 11 cm from its equilibrium position and then released. a. What force does the spring exert on the block just before the block is released? b. What are the angular frequency, freque ...
Vijay Ramani, J. M. Fenton Thermodynamics of Fuel Cells
... fundamental to the second law of thermodynamics. A system is said to undergo a reversible change if it remains in equilibrium as it passes from its initial state to its final state. A reversible process is a reversible change in which the system remains in equilibrium with its environment. The visua ...
... fundamental to the second law of thermodynamics. A system is said to undergo a reversible change if it remains in equilibrium as it passes from its initial state to its final state. A reversible process is a reversible change in which the system remains in equilibrium with its environment. The visua ...
Document
... bonded atoms and the other having strongly bonded atoms. With reference to bond– energy curves a material with a high modulus will have a narrow, steep potential energy well; a broad, shallow energy well would be characteristic of a low modulus. Table 1.1 lists values of Young’s moduli for different ...
... bonded atoms and the other having strongly bonded atoms. With reference to bond– energy curves a material with a high modulus will have a narrow, steep potential energy well; a broad, shallow energy well would be characteristic of a low modulus. Table 1.1 lists values of Young’s moduli for different ...
Intro to Optics - RosedaleGrade10Science
... that can travel through empty space. Other forms of electromagnetic radiation include invisible waves such as radio, infrared, ultraviolet and x-rays. Light is produced when electrons in atoms absorb energy and jump to a higher energy level, and then return to their stable ground state, emitting the ...
... that can travel through empty space. Other forms of electromagnetic radiation include invisible waves such as radio, infrared, ultraviolet and x-rays. Light is produced when electrons in atoms absorb energy and jump to a higher energy level, and then return to their stable ground state, emitting the ...
Introduction to Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Define electron, proton, neutron in terms of mass, charge, location in the atom, and the affect they have to the identity of an atom Determine number of protons, electrons, neutrons, valence electrons, mass number, and atomic number for any element using the periodic table Determine the elements and ...
... Define electron, proton, neutron in terms of mass, charge, location in the atom, and the affect they have to the identity of an atom Determine number of protons, electrons, neutrons, valence electrons, mass number, and atomic number for any element using the periodic table Determine the elements and ...
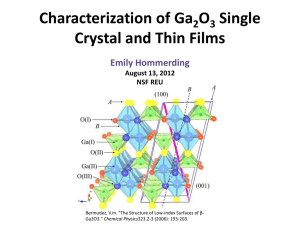
Characterization of Ga 2 0 3 Single Crystal and Thin Films
... sample • A detector lies behind the sample • The percent of light transmitted through the system at a given wavelength is measured and compared with a ...
... sample • A detector lies behind the sample • The percent of light transmitted through the system at a given wavelength is measured and compared with a ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.