Non-Cell-Autonomous Effect of Human SOD1G37R
... incorporate a-bungarotoxin when cocultured with C2C12 myoblasts, indicating that the cells could form functional neuromuscular junctions (Figures 1I and 1J). Live postmitotic human motor neurons could be visualized after transduction with a lentivirus expressing the green fluorescent protein gene (G ...
... incorporate a-bungarotoxin when cocultured with C2C12 myoblasts, indicating that the cells could form functional neuromuscular junctions (Figures 1I and 1J). Live postmitotic human motor neurons could be visualized after transduction with a lentivirus expressing the green fluorescent protein gene (G ...
Emotion and decision-making explained: A prEcis
... network processes that underlie decision-making, rather than the phenomenological models such as the driftdiffusion model, although these phenomenological models of decision-making are covered in Appendix B. The second is the ultimate level of explanation, the level of adaptive value in evolution, i ...
... network processes that underlie decision-making, rather than the phenomenological models such as the driftdiffusion model, although these phenomenological models of decision-making are covered in Appendix B. The second is the ultimate level of explanation, the level of adaptive value in evolution, i ...
Mirror neurons and the 8 parallel consciousnesses
... present on the left side of their environment, and shaves only on the right, etc.(16) However, it has been shown that such a person is able to unconsciously perceive the images placed on the left(43). This makes neglect an ideal situation for identifying the correlates of cerebral consciousness. Ind ...
... present on the left side of their environment, and shaves only on the right, etc.(16) However, it has been shown that such a person is able to unconsciously perceive the images placed on the left(43). This makes neglect an ideal situation for identifying the correlates of cerebral consciousness. Ind ...
PDF-document - homepage.ruhr-uni
... found a large number of SC units that were specifically activated when the monkeys contacted and pushed a target that had been reached with either hand. These neurons, however, were silent when the monkeys simply looked at or reached for the target but did not touch it. The activity related to inter ...
... found a large number of SC units that were specifically activated when the monkeys contacted and pushed a target that had been reached with either hand. These neurons, however, were silent when the monkeys simply looked at or reached for the target but did not touch it. The activity related to inter ...
PDF file
... The following technical characteristics required by developmental learning make such work challenging: (1) Integrate both bottom-up and top-down attention; (2) Integrate attentionbased recognition and object-based spacial attention interactively; (3) Enable supervised and unsupervised learning in an ...
... The following technical characteristics required by developmental learning make such work challenging: (1) Integrate both bottom-up and top-down attention; (2) Integrate attentionbased recognition and object-based spacial attention interactively; (3) Enable supervised and unsupervised learning in an ...
How Does the Brain Produce Movement?
... In summary, the frontal cortex executes precise movements, as well as planning them and coordinating different body parts to carry them out. The various regions of the frontal cortex that perform these functions are hierarchically related. After the prefrontal cortex has formulated a plan of action, ...
... In summary, the frontal cortex executes precise movements, as well as planning them and coordinating different body parts to carry them out. The various regions of the frontal cortex that perform these functions are hierarchically related. After the prefrontal cortex has formulated a plan of action, ...
Learning Grounded Language through Situated Interactive Instruction
... developing robotic agents that can learn to associate language to various aspects of cognition (perception and spatial, semantic, and procedural knowledge) that may originate outside of the linguistic system. In this paper, we focus on learning three categories of linguistic symbols: adjectives/noun ...
... developing robotic agents that can learn to associate language to various aspects of cognition (perception and spatial, semantic, and procedural knowledge) that may originate outside of the linguistic system. In this paper, we focus on learning three categories of linguistic symbols: adjectives/noun ...
Behavioural Domain Knowledge Transfer for Autonomous Agents
... for choosing certain actions over others under particular conditions. We thus seek to model these local action selection preferences as a form of prior knowledge which can be extended as the agent learns about different tasks in the domain. This then acts as a form of action pruning, which is also e ...
... for choosing certain actions over others under particular conditions. We thus seek to model these local action selection preferences as a form of prior knowledge which can be extended as the agent learns about different tasks in the domain. This then acts as a form of action pruning, which is also e ...
Huffman PowerPoint Slides
... rates between identical and fraternal twins – Adoption studies: compare the similarity between adopted children and their biological/adopted parents – Mutations: examine behaviors in genetically abnormal subjects or in animals in which a specific gene has been “knocked out” ...
... rates between identical and fraternal twins – Adoption studies: compare the similarity between adopted children and their biological/adopted parents – Mutations: examine behaviors in genetically abnormal subjects or in animals in which a specific gene has been “knocked out” ...
Eye movement control by the cerebral cortex
... function with eye movements. In this paradigm, the participant has to memorize the location of a target flashed in the peripheral visual field while fixating a central point, and then, after a delay of several seconds or more, make a memory-guided saccade to the remembered position of the flash. The amp ...
... function with eye movements. In this paradigm, the participant has to memorize the location of a target flashed in the peripheral visual field while fixating a central point, and then, after a delay of several seconds or more, make a memory-guided saccade to the remembered position of the flash. The amp ...
Measuring the degree of Synonymy between Words using
... by a group of 38 human subjects. However, most previous work have used only 28 pairs for evaluation because one word was not registered in WordNet 3.0. Consequently, we follow those previous work and use only 28 word pairs such that we can directly compare our results with previous work [1]. In addi ...
... by a group of 38 human subjects. However, most previous work have used only 28 pairs for evaluation because one word was not registered in WordNet 3.0. Consequently, we follow those previous work and use only 28 word pairs such that we can directly compare our results with previous work [1]. In addi ...
Role of the Human Anterior Cingulate Cortex in the Control of
... demands and/ or “response selection” processes may underlie significant changes in rCBF in the ACC obtained during the performance of the Stroop test (Pardo et al. 1990) and voluntary generation of motor responses (Frith et al. 199 1). In the present study, we set out to test a somewhat different vi ...
... demands and/ or “response selection” processes may underlie significant changes in rCBF in the ACC obtained during the performance of the Stroop test (Pardo et al. 1990) and voluntary generation of motor responses (Frith et al. 199 1). In the present study, we set out to test a somewhat different vi ...
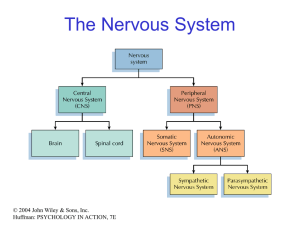
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous
... efferent divisions of the nervous system, and explain what is meant by the somatic nervous system. • 15-2 Explain why receptors respond to specific stimuli, and how the organization of a receptor affects its sensitivity. • 15-3 Identify the receptors for the general senses, and describe how they fun ...
... efferent divisions of the nervous system, and explain what is meant by the somatic nervous system. • 15-2 Explain why receptors respond to specific stimuli, and how the organization of a receptor affects its sensitivity. • 15-3 Identify the receptors for the general senses, and describe how they fun ...
JEB Classics - Journal of Experimental Biology
... Leksell to be derived in mammals from a special group of small myelinated axons in the spinal ventral roots and referred to as ␥-efferent (Leksell, 1945). Stimulation of these axons caused no detectable contraction but excited an afferent discharge from the spindles. This was seen as a means by whic ...
... Leksell to be derived in mammals from a special group of small myelinated axons in the spinal ventral roots and referred to as ␥-efferent (Leksell, 1945). Stimulation of these axons caused no detectable contraction but excited an afferent discharge from the spindles. This was seen as a means by whic ...
Short frontal lobe connections of the human brain
... middle frontal gyri (13 and 14). D) Regions of interest for the fronto-orbitopolar (FOP) (15 and 16) and fronto-marginal tracts (FMT) (17 and 18). E) Regions of interest for the fronto-insular tracts (FIT) connecting the posterior insula with the subcentral gyrus (19 and 21) and the anterior insula ...
... middle frontal gyri (13 and 14). D) Regions of interest for the fronto-orbitopolar (FOP) (15 and 16) and fronto-marginal tracts (FMT) (17 and 18). E) Regions of interest for the fronto-insular tracts (FIT) connecting the posterior insula with the subcentral gyrus (19 and 21) and the anterior insula ...
Basal Ganglia: Mechanisms for Action Selection
... loops, termed channels here to distinguish them from the macroscopic-scale loops. For example, the somatotopic map found within the striatal motor domain is maintained throughout the basal ganglia’s intrinsic circuitry, such that there are separate channels for arm, leg, and face representations (Al ...
... loops, termed channels here to distinguish them from the macroscopic-scale loops. For example, the somatotopic map found within the striatal motor domain is maintained throughout the basal ganglia’s intrinsic circuitry, such that there are separate channels for arm, leg, and face representations (Al ...
Dissociable Functions in the Medial and Lateral Orbitofrontal Cortex
... of feedback (positive and negative feedback combined and compared with the no feedback condition). In the guessing task, but not the planning task, the presence of feedback was associated with increased rCBF in the ventromedial OFC. One reason why the medial OFC might be especially concerned with pr ...
... of feedback (positive and negative feedback combined and compared with the no feedback condition). In the guessing task, but not the planning task, the presence of feedback was associated with increased rCBF in the ventromedial OFC. One reason why the medial OFC might be especially concerned with pr ...
Learning, Reward and Decision-Making
... contingencies (Dayan and Berridge, 2014). Despite the fact that there is evidence for the existence of these two distinct strategies within Pavlovian learning, the majority of the research in this domain has been performed using instrumental conditioning, and we focus on this theme in the remainder ...
... contingencies (Dayan and Berridge, 2014). Despite the fact that there is evidence for the existence of these two distinct strategies within Pavlovian learning, the majority of the research in this domain has been performed using instrumental conditioning, and we focus on this theme in the remainder ...
Habit formation
... arises in medium spiny projection neurons as animals acquire the T-maze task is one in which the activity accentuates the boundaries of the maze runs. The majority of task-responsive neurons exhibit a burst of firing activity as the run is initiated, or as the run is completed, or both, resulting i ...
... arises in medium spiny projection neurons as animals acquire the T-maze task is one in which the activity accentuates the boundaries of the maze runs. The majority of task-responsive neurons exhibit a burst of firing activity as the run is initiated, or as the run is completed, or both, resulting i ...
Neural Basis of Psychological Growth following Adverse
... derived from distress or adversity has been discussed, currently no consensus has been reached regarding the relationship between adversity and positive outcomes [7]. Furthermore, studies on PTG tend to focus on the psychological phenomena rather than on the neurological mechanisms, thus the neural ...
... derived from distress or adversity has been discussed, currently no consensus has been reached regarding the relationship between adversity and positive outcomes [7]. Furthermore, studies on PTG tend to focus on the psychological phenomena rather than on the neurological mechanisms, thus the neural ...
Negative BOLD in Sensory Cortices During
... mental imagery, especially in the visual modality (Ishai and Sagi 1995; Kosslyn et al. 1999; Ishai et al. 2000; Kreiman et al. 2000; O’Craven and Kanwisher 2000; Mechelli et al. 2004). For instance, one can predict whether an imagined object during an fMRI scan is a face or a house based on the magn ...
... mental imagery, especially in the visual modality (Ishai and Sagi 1995; Kosslyn et al. 1999; Ishai et al. 2000; Kreiman et al. 2000; O’Craven and Kanwisher 2000; Mechelli et al. 2004). For instance, one can predict whether an imagined object during an fMRI scan is a face or a house based on the magn ...
Brain-Like Learning Directly from Dynamic Cluttered Natural Video
... Abstract—It is mysterious how the brain of a baby figures out which part of a cluttered scene to attend to in the dynamic world. On one hand, the various backgrounds, where object may appear at different locations, make it difficult to find the object of interest. On the other hand, with the numbers ...
... Abstract—It is mysterious how the brain of a baby figures out which part of a cluttered scene to attend to in the dynamic world. On one hand, the various backgrounds, where object may appear at different locations, make it difficult to find the object of interest. On the other hand, with the numbers ...
muscle stretch reflex
... are pulled with the muscle fibers. When this happens, the central region of the intrafusal fiber is stretched and the frequency of action potentials in the sensory fibers increases in frequency. As ...
... are pulled with the muscle fibers. When this happens, the central region of the intrafusal fiber is stretched and the frequency of action potentials in the sensory fibers increases in frequency. As ...