Computational cognitive neuroscience: 10. Prefrontal Cortex (PFC)
... • The lateral PFC areas are interconnected with sensory and motor areas and play a role in controlling the processing in these areas. • The medial PFC areas are more strongly interconnected with subcortical brain areas associated with affective and motivational functions. • Functionally we can chara ...
... • The lateral PFC areas are interconnected with sensory and motor areas and play a role in controlling the processing in these areas. • The medial PFC areas are more strongly interconnected with subcortical brain areas associated with affective and motivational functions. • Functionally we can chara ...
Intention, Action Planning, and Decision Making in Parietal
... review, we will refer to the hand and eye preference for movement planning as effector specificity, and this term is meant to indicate relative, not absolute, specificity. For example, an area may be active for planning a reach or a saccade, but if it is significantly more active for one plan over t ...
... review, we will refer to the hand and eye preference for movement planning as effector specificity, and this term is meant to indicate relative, not absolute, specificity. For example, an area may be active for planning a reach or a saccade, but if it is significantly more active for one plan over t ...
Neurotic Overview
... i. Bilateral loss of pain/temp (spinothalamic) at level of lesion, since decussates at level it enters SC ii. UMN paralysis of upper ˃ lower limbs (corticospinal) d. Anterior cord syndrome (usually due to ischemic injury to ant spinal artery) i. Bilateral loss of pain/temp below lesion (already decu ...
... i. Bilateral loss of pain/temp (spinothalamic) at level of lesion, since decussates at level it enters SC ii. UMN paralysis of upper ˃ lower limbs (corticospinal) d. Anterior cord syndrome (usually due to ischemic injury to ant spinal artery) i. Bilateral loss of pain/temp below lesion (already decu ...
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
... The tiny spaces between neurons and effectors are called synapses or synaptic clefts. Synapses are formed between the end plates of one neuron and the dendrites, axon, or cell body of another neuron. They can also be formed between the endplates of one neuron and an ...
... The tiny spaces between neurons and effectors are called synapses or synaptic clefts. Synapses are formed between the end plates of one neuron and the dendrites, axon, or cell body of another neuron. They can also be formed between the endplates of one neuron and an ...
Where do mirror neurons come from?
... or before, the primary eliciting stimulus (grasping). In this study, a container was always presented in trials involving grasping before placing, and never in trials involving grasping before eating. Therefore, the presence or absence of a container could become a conditional cue differentially act ...
... or before, the primary eliciting stimulus (grasping). In this study, a container was always presented in trials involving grasping before placing, and never in trials involving grasping before eating. Therefore, the presence or absence of a container could become a conditional cue differentially act ...
Testing Promotes Long-Term Learning via Stabilizing Activation
... (BA 45/46), the left precuneus (BA 39) and the bilateral superior parietal lobule (BA 7). These results were considered to be evidence that repeated testing reduces cognitive control demands during future episodic retrieval by making the cue-target link easier to process (Kuhl et al. 2007). Further ...
... (BA 45/46), the left precuneus (BA 39) and the bilateral superior parietal lobule (BA 7). These results were considered to be evidence that repeated testing reduces cognitive control demands during future episodic retrieval by making the cue-target link easier to process (Kuhl et al. 2007). Further ...
A double-dissociation of English past
... argued that clinical double-dissociations could be low-probability stochastic (i.e. non-systematic) phenomena and as such can be simulated in homogeneous networks (Gonnerman et al., 1997; Juola and Plunkett, 1998). A number of investigators turned to brain-mapping techniques in order to gather more ...
... argued that clinical double-dissociations could be low-probability stochastic (i.e. non-systematic) phenomena and as such can be simulated in homogeneous networks (Gonnerman et al., 1997; Juola and Plunkett, 1998). A number of investigators turned to brain-mapping techniques in order to gather more ...
Language repetition and short-term memory: an integrative
... regions of the temporal lobe and involving also the anterior inferior prefrontal and orbito-frontal cortex (Mummery et al., 2000; Good et al., 2002; Desgranges et al., 2007). During language repetition, in both single and multiple word/nonword repetition tasks, patients with semantic dementia presen ...
... regions of the temporal lobe and involving also the anterior inferior prefrontal and orbito-frontal cortex (Mummery et al., 2000; Good et al., 2002; Desgranges et al., 2007). During language repetition, in both single and multiple word/nonword repetition tasks, patients with semantic dementia presen ...
4-nmes
... Electrical stimulation of the muscle causes increase venous and lymphatic return, alter cell membrane permeability, these causes reduction of edema. The treatment is most effective if the current is applied by the method, termed faradism under pressure Faradism under pressure is stimulation of the m ...
... Electrical stimulation of the muscle causes increase venous and lymphatic return, alter cell membrane permeability, these causes reduction of edema. The treatment is most effective if the current is applied by the method, termed faradism under pressure Faradism under pressure is stimulation of the m ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... 1. The hypothalamus controls and integrates the autonomic nervous system. It is connected to both the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions. 2. Control of the ANS by the cerebral cortex occurs primarily during emotional stress. VII. FOCUS ON HOMEOSTASIS: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM A. This section de ...
... 1. The hypothalamus controls and integrates the autonomic nervous system. It is connected to both the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions. 2. Control of the ANS by the cerebral cortex occurs primarily during emotional stress. VII. FOCUS ON HOMEOSTASIS: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM A. This section de ...
Voluntary Movement: The Primary Motor Cortex
... presence of the object provides only the opportunity for acting. Voluntary actions involve choices between alternatives, including the choice not to act. Furthermore, they are organized to achieve some goal in the near or distant future. Voluntary movements often have a labile, context-dependent ass ...
... presence of the object provides only the opportunity for acting. Voluntary actions involve choices between alternatives, including the choice not to act. Furthermore, they are organized to achieve some goal in the near or distant future. Voluntary movements often have a labile, context-dependent ass ...
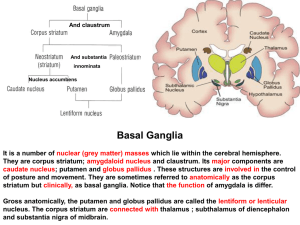
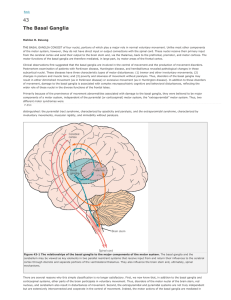
17-Basal ganglion
... They are corpus striatum; amygdaloid nucleus and claustrum. Its major components are caudate nucleus; putamen and globus pallidus . These structures are involved in the control of posture and movement. They are sometimes referred to anatomically as the corpus striatum but clinically, as basal gangli ...
... They are corpus striatum; amygdaloid nucleus and claustrum. Its major components are caudate nucleus; putamen and globus pallidus . These structures are involved in the control of posture and movement. They are sometimes referred to anatomically as the corpus striatum but clinically, as basal gangli ...
Principles of Neural Science
... the skeletomotor circuit originates in the cerebral cortex in precentral motor fields and postcentral somatosensory areas and projects largely to the putamen. The putamen is thus an important site for integration of movement related and sensory feedback information related to movement. The putamen r ...
... the skeletomotor circuit originates in the cerebral cortex in precentral motor fields and postcentral somatosensory areas and projects largely to the putamen. The putamen is thus an important site for integration of movement related and sensory feedback information related to movement. The putamen r ...
Ppt - Michigan`s Mission: Literacy
... prefrontal cortex to do. (…communicate in a way that couples “liking” something to “wanting” it, in turn to go after it.) In paragraph l2, find and highlight how the brain adapts. (…makes the sought-after substance or activity less pleasurable.) In paragraph 14, find and highlight what happens when ...
... prefrontal cortex to do. (…communicate in a way that couples “liking” something to “wanting” it, in turn to go after it.) In paragraph l2, find and highlight how the brain adapts. (…makes the sought-after substance or activity less pleasurable.) In paragraph 14, find and highlight what happens when ...
Cavazza, MO, Charles, F. and Mead, SJ (2002
... The system implements characters’ behaviours using AI planning techniques. In this context, Plans can be seen as a generic formalism for an actor’s behaviour and as a resource for story generation. They represent the storyline acted from a given character’s perspective, i.e. the character’s role. Th ...
... The system implements characters’ behaviours using AI planning techniques. In this context, Plans can be seen as a generic formalism for an actor’s behaviour and as a resource for story generation. They represent the storyline acted from a given character’s perspective, i.e. the character’s role. Th ...
Two Views of Cortex
... Subjects with larger cortical magnification factors have better vernier acuity. ...
... Subjects with larger cortical magnification factors have better vernier acuity. ...
Simulation of Action Theories and an Application to General
... Abstract. We consider the problem of verifying whether one action theory can simulate a second one. Action theories provide modular descriptions of state machines, and simulation means that all possible sequences of actions in one transition system can be matched by the other. We show how Answer Set ...
... Abstract. We consider the problem of verifying whether one action theory can simulate a second one. Action theories provide modular descriptions of state machines, and simulation means that all possible sequences of actions in one transition system can be matched by the other. We show how Answer Set ...
Neural-Body Coupling for Emergent Locomotion: A Musculoskeletal
... bipedal musculoskeletal robot that had a walk-driven antagonistic mechanism. Although these robots were driven by an antagonistic mechanism with mono-articular pneumatic muscles, various kinds of animals very commonly have biarticular muscles, which are two cross joints that add torque to both joint ...
... bipedal musculoskeletal robot that had a walk-driven antagonistic mechanism. Although these robots were driven by an antagonistic mechanism with mono-articular pneumatic muscles, various kinds of animals very commonly have biarticular muscles, which are two cross joints that add torque to both joint ...
Internal structure of spinal cord
... – VII. largest region of the spinal gray matter • many interneurons with collaterals within their segment and long axons that go out into the white matter & travel up/down to other segments’ gray matter • VII also contains a few other cell columns (not part of the Lamina system) ...
... – VII. largest region of the spinal gray matter • many interneurons with collaterals within their segment and long axons that go out into the white matter & travel up/down to other segments’ gray matter • VII also contains a few other cell columns (not part of the Lamina system) ...
Movement
... – Ex: cat washing face, gymnast with complex movements, yawn – automatic patterns may be disrupted when thinking about them, e.g., typing or playing piano – evolutionary holdover: chicken still flaps wings when dropped even though can’t fly ...
... – Ex: cat washing face, gymnast with complex movements, yawn – automatic patterns may be disrupted when thinking about them, e.g., typing or playing piano – evolutionary holdover: chicken still flaps wings when dropped even though can’t fly ...
REVIEWS - Institute for Applied Psychometrics
... Figure 3 | The pacemaker–accumulator model and dopaminergic and cholinergic synapses. a | Shows an information-processing (IP) model of time perception8 implementing the scalar expectancy theory43. In the model, a dopaminergic pacemaker sends ‘pulses’ to an accumulator during the training period, an ...
... Figure 3 | The pacemaker–accumulator model and dopaminergic and cholinergic synapses. a | Shows an information-processing (IP) model of time perception8 implementing the scalar expectancy theory43. In the model, a dopaminergic pacemaker sends ‘pulses’ to an accumulator during the training period, an ...
The Nervous System
... readers. Images made after intensive language treatment show how the brain changes as the children gain language proficiency. • Men and women use their brains differently, according to fMRI studies from the University of Alberta. “Sometimes males and females would perform the same tasks and show dif ...
... readers. Images made after intensive language treatment show how the brain changes as the children gain language proficiency. • Men and women use their brains differently, according to fMRI studies from the University of Alberta. “Sometimes males and females would perform the same tasks and show dif ...
Activity Regulates the Incidence of Heteronymous Sensory
... synaptic refinement represents one possible mechanism for the changes in connectivity observed after activity blockade. Our findings therefore reveal that sensory activity does have a limited and selective role in the establishment of patterned monosynaptic sensory-motor connections. INTRODUCTION Th ...
... synaptic refinement represents one possible mechanism for the changes in connectivity observed after activity blockade. Our findings therefore reveal that sensory activity does have a limited and selective role in the establishment of patterned monosynaptic sensory-motor connections. INTRODUCTION Th ...
Neuroanatomical characteristics of deep and superficial needling
... believed to exert its effects through sensory afferent stimulation. Although we are unable to assess, based on the present results, whether acupuncture works via stimulation of motor nerves, as the study was neuroanatomical rather than neurofunctional in nature, it is clear that tracer can be transp ...
... believed to exert its effects through sensory afferent stimulation. Although we are unable to assess, based on the present results, whether acupuncture works via stimulation of motor nerves, as the study was neuroanatomical rather than neurofunctional in nature, it is clear that tracer can be transp ...
PSYB1 Biopsychology Short Qs JM09 December
... 18. Diane is at a pop concert with her friend Robbie. She has been longing to see her favourite band play live. When the band appears on stage, she says to Robbie, “I’m so excited. I can feel my heart pounding.” After the concert, Diane says to Robbie, “That was fantastic, but I’m so hungry, my tumm ...
... 18. Diane is at a pop concert with her friend Robbie. She has been longing to see her favourite band play live. When the band appears on stage, she says to Robbie, “I’m so excited. I can feel my heart pounding.” After the concert, Diane says to Robbie, “That was fantastic, but I’m so hungry, my tumm ...