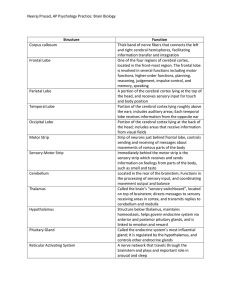
Brain Anatomy and Function p. 95
... areas. It affects sensory, motor, and visceral functions.The RAS allows screening/filtering of stimuli so the brain does not have to react to all stimuli. RAS controls the sleepwake cycle. ...
... areas. It affects sensory, motor, and visceral functions.The RAS allows screening/filtering of stimuli so the brain does not have to react to all stimuli. RAS controls the sleepwake cycle. ...
session1vocabulary
... This half of the brain goes more towards creativity and artistic ability. Left Half of the Brain This half of the brain is more for mathematical skills, speech, writing, and logical thinking. Frontal Lobe Located at the front of the brain. Associated with reasoning. Parietal Lobe Located in the midd ...
... This half of the brain goes more towards creativity and artistic ability. Left Half of the Brain This half of the brain is more for mathematical skills, speech, writing, and logical thinking. Frontal Lobe Located at the front of the brain. Associated with reasoning. Parietal Lobe Located in the midd ...
Chapter 4
... and right ears simultaneously – Most people will report hearing the words presented in the right ear – Indicates the left side of the brain ...
... and right ears simultaneously – Most people will report hearing the words presented in the right ear – Indicates the left side of the brain ...
Cognition and Perception as Interactive Activation
... three words to make a compound word: Pine, crab, tree ...
... three words to make a compound word: Pine, crab, tree ...
Neeraj Prasad, AP Psychology Practice: Brain Biology Structure
... homeostasis, helps govern endocrine system via anterior and posterior pituitary glands, and is linked to emotion and reward Called the endocrine system’s most influential gland; It is regulated by the hypothalamus, and controls other endrocrine glands A nerve network that travels through the brainst ...
... homeostasis, helps govern endocrine system via anterior and posterior pituitary glands, and is linked to emotion and reward Called the endocrine system’s most influential gland; It is regulated by the hypothalamus, and controls other endrocrine glands A nerve network that travels through the brainst ...
Significant Mirrorings in the Process of Teaching and Learning
... knowledge, attributing it to the presence of a neural mechanism of mirroring that involves the motor area of the brain were presented. The mirroring mechanism, mapping our intentional relations with things and others, would acquire a fundamental role in our understanding of the world and in the way ...
... knowledge, attributing it to the presence of a neural mechanism of mirroring that involves the motor area of the brain were presented. The mirroring mechanism, mapping our intentional relations with things and others, would acquire a fundamental role in our understanding of the world and in the way ...
Dec9
... than when holding it with lips; even funnier if holding it with teeth. (But note that the effect goes away when it pertains specifically to “objective” funniness, as opposed to the subjective feeling of ...
... than when holding it with lips; even funnier if holding it with teeth. (But note that the effect goes away when it pertains specifically to “objective” funniness, as opposed to the subjective feeling of ...
04 Physiology of large hemispheres, cerebellum
... In the skin, free nerve endings and hair follicle receptors remain largely unchanged with age. Meissner’s corpuscles and pacinian corpuscles, however, decrease in number. The capsules of those that remain become thicker and structurally distorted and, therefore, exhibit reduced function. As a result ...
... In the skin, free nerve endings and hair follicle receptors remain largely unchanged with age. Meissner’s corpuscles and pacinian corpuscles, however, decrease in number. The capsules of those that remain become thicker and structurally distorted and, therefore, exhibit reduced function. As a result ...
Bioenergetics - Eastern Michigan University
... – Provide CNS with information about body position and joint angle • Free nerve endings ...
... – Provide CNS with information about body position and joint angle • Free nerve endings ...
Electrophysiological Methods for Mapping Brain Motor and Sensory
... • Activation of muscles in isolation is difficult • Motor fields: all movements that engage a neuron • Functional (type of movement) • Structural (target muscles) • Neuroantomic labeling • TMS ...
... • Activation of muscles in isolation is difficult • Motor fields: all movements that engage a neuron • Functional (type of movement) • Structural (target muscles) • Neuroantomic labeling • TMS ...
Control of Motor Movement
... Spinal neurons remain intact and muscles are stimulated irregularly There is no voluntary control of muscles Exaggerated reflexes ...
... Spinal neurons remain intact and muscles are stimulated irregularly There is no voluntary control of muscles Exaggerated reflexes ...
RECOGNIZING WORD ELEMENTS
... Sixty percent of English words have been adapted from Latin and Greek. The Latin and Greek languages use a system of word parts, or word elements, that can be used alone or in combination in order to form words. As the combinations of the word parts change, so does the meaning of the words. Many med ...
... Sixty percent of English words have been adapted from Latin and Greek. The Latin and Greek languages use a system of word parts, or word elements, that can be used alone or in combination in order to form words. As the combinations of the word parts change, so does the meaning of the words. Many med ...
Nerve cells (Neurons)
... The CNS is constantly kept aware of muscle condition through stimuli produced from sensory receptors located in the muscles, _____________, _______________ and _______________. Sensory (afferent) neurons transfer messages to the central nervous system where they are analyzed and responded to by mot ...
... The CNS is constantly kept aware of muscle condition through stimuli produced from sensory receptors located in the muscles, _____________, _______________ and _______________. Sensory (afferent) neurons transfer messages to the central nervous system where they are analyzed and responded to by mot ...
Slides Ch 2 - Department of Linguistics and English Language
... movements When monkeys moved mouth and hands the electrons fired ...
... movements When monkeys moved mouth and hands the electrons fired ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-31
... o Descending motor axons from cortex and red nucleus (in midbrain) o Ascending sensory axons from body AND face Cranial nerves – V, VI, VII, VIII Cerebellar Peduncles axons linking the cerebellum & brainstem Inferior Input (ICP) – unconscious proprioception info (what you are doing) o Info fro ...
... o Descending motor axons from cortex and red nucleus (in midbrain) o Ascending sensory axons from body AND face Cranial nerves – V, VI, VII, VIII Cerebellar Peduncles axons linking the cerebellum & brainstem Inferior Input (ICP) – unconscious proprioception info (what you are doing) o Info fro ...
romistalk - Marieke Rohde
... The modern would-be materialist thus finds himself in a curious position, for, while he may with a certain degree of success reduce the activities of the mind to those of the body, he cannot explain away the fact that the body itself is merely a convenient concept invented by the mind. We find ourse ...
... The modern would-be materialist thus finds himself in a curious position, for, while he may with a certain degree of success reduce the activities of the mind to those of the body, he cannot explain away the fact that the body itself is merely a convenient concept invented by the mind. We find ourse ...
Document
... Autonomic Nervous System. • it controls hunger, body temperature, aggression and other aspects of behaviour and metabolism. • the hypothalamus controls the endocrine hormone system because attached to it is the pituitary gland. • the pituitary gland produces hormones that control many of the endocri ...
... Autonomic Nervous System. • it controls hunger, body temperature, aggression and other aspects of behaviour and metabolism. • the hypothalamus controls the endocrine hormone system because attached to it is the pituitary gland. • the pituitary gland produces hormones that control many of the endocri ...
CNS
... Autonomic Nervous System. • it controls hunger, body temperature, aggression and other aspects of behaviour and metabolism. • the hypothalamus controls the endocrine hormone system because attached to it is the pituitary gland. • the pituitary gland produces hormones that control many of the endocri ...
... Autonomic Nervous System. • it controls hunger, body temperature, aggression and other aspects of behaviour and metabolism. • the hypothalamus controls the endocrine hormone system because attached to it is the pituitary gland. • the pituitary gland produces hormones that control many of the endocri ...
Embodied Verbal Semantics: Evidence from a lexical matching task
... This second, embodied perspective makes a strong claim that the logical perspective does not; namely, that linguistic semantics is grounded in the perceptual and motor systems, and therefore reflects characteristics of these systems. We present some evidence that supports this prediction, and sugges ...
... This second, embodied perspective makes a strong claim that the logical perspective does not; namely, that linguistic semantics is grounded in the perceptual and motor systems, and therefore reflects characteristics of these systems. We present some evidence that supports this prediction, and sugges ...
Fig 1
... • Activity of F5 mirror neurons is part of the code for Declarative: Grasp-A(Agent, Object) The full neural representation of the “Cognitive Form” (CF): Grasp-A(Agent, Object) requires not only the regions AIP, STS, 7a, 7b and F5miirror shown in the MNS diagram, but also inferotemporal cortex (IT) w ...
... • Activity of F5 mirror neurons is part of the code for Declarative: Grasp-A(Agent, Object) The full neural representation of the “Cognitive Form” (CF): Grasp-A(Agent, Object) requires not only the regions AIP, STS, 7a, 7b and F5miirror shown in the MNS diagram, but also inferotemporal cortex (IT) w ...
Lecture ppt 1 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... • Two regions with additional gray called “cortex” ________________________________ – Cerebrum: “cerebral cortex” – Cerebellum: “cerebellar cortex” ...
... • Two regions with additional gray called “cortex” ________________________________ – Cerebrum: “cerebral cortex” – Cerebellum: “cerebellar cortex” ...
Brain Parts Matching Review - District 196 e
... _______ 11. pathway for neural fibers traveling to and from brain; controls simple reflexes. _______ 12. a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. _______ 13. axon fibers connecting two cerebral hemispheres _______ 14. two almond-shaped neural clusters that are linked to emotion ...
... _______ 11. pathway for neural fibers traveling to and from brain; controls simple reflexes. _______ 12. a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. _______ 13. axon fibers connecting two cerebral hemispheres _______ 14. two almond-shaped neural clusters that are linked to emotion ...
Invitation to the Life Span by Kathleen Stassen Berger
... restructured to include, or accommodate, new experiences. • object permanence – The realization that objects (including people) still exist when they can no longer be seen, touched, or hear. ...
... restructured to include, or accommodate, new experiences. • object permanence – The realization that objects (including people) still exist when they can no longer be seen, touched, or hear. ...