3 layers
... after a period of high-frequency stimulation – role for glutamate = binds NMDA glutamate receptors on post-synaptic neurons • different categories of memory – 1. immediate: ability to recall ongoing experiences, provides perspective to the present time so we know where we are and what we are doing – ...
... after a period of high-frequency stimulation – role for glutamate = binds NMDA glutamate receptors on post-synaptic neurons • different categories of memory – 1. immediate: ability to recall ongoing experiences, provides perspective to the present time so we know where we are and what we are doing – ...
Optic Nerves * Jack Baesman
... Sensory Nerves associated with sense of smell Contains only axons of sensory, bipolar neurons. Located in upper nasal cavity Olfactory receptor cells carry impulses to neurons in olfactory bulbs Sensory impulses travel from bulbs along olfactory tracts to the cerebral centers where they are interpre ...
... Sensory Nerves associated with sense of smell Contains only axons of sensory, bipolar neurons. Located in upper nasal cavity Olfactory receptor cells carry impulses to neurons in olfactory bulbs Sensory impulses travel from bulbs along olfactory tracts to the cerebral centers where they are interpre ...
Psychology-Parts-of-the-Brain-and-Their
... The limbic system contains glands which help relay emotions. Many hormonal responses that the body generates are initiated in this area. The limbic system includes the amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus and thalamus. Amygdala:The amygdala helps the body responds to emotions, memories and fear. It i ...
... The limbic system contains glands which help relay emotions. Many hormonal responses that the body generates are initiated in this area. The limbic system includes the amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus and thalamus. Amygdala:The amygdala helps the body responds to emotions, memories and fear. It i ...
Behavioral Neuroscience
... stem, inside the temporal lobes • Integrates visceral information with perceptions from external environment by using input from multiple modalities (visual, auditory cues etc). • Relates this information with previous experience • Emotional significance or meaning of our perceptions and experiences ...
... stem, inside the temporal lobes • Integrates visceral information with perceptions from external environment by using input from multiple modalities (visual, auditory cues etc). • Relates this information with previous experience • Emotional significance or meaning of our perceptions and experiences ...
The Nervous System - riverridge210.org
... 4. Most important feature is there are small nodes or gaps in thy myelin allowing the impulse to jump from note to node instead of moving along the membrane. Jumping greatly increases the speed of the impulse. 5. The minimum level of a stimulus that is required to activate a neuron is called a thre ...
... 4. Most important feature is there are small nodes or gaps in thy myelin allowing the impulse to jump from note to node instead of moving along the membrane. Jumping greatly increases the speed of the impulse. 5. The minimum level of a stimulus that is required to activate a neuron is called a thre ...
Basic principles of attention and decision
... • Do not mistake with the ‘where’ (old) pathway: SC and pulvinar • Parietal cortex represents potential targets to reach with respect to body, and is involved in motor control (see Ramachandran, Balint’s syndrom) • Lateral Intraparietal cortex (LIP): highest-order area in the visual hierarchy of t ...
... • Do not mistake with the ‘where’ (old) pathway: SC and pulvinar • Parietal cortex represents potential targets to reach with respect to body, and is involved in motor control (see Ramachandran, Balint’s syndrom) • Lateral Intraparietal cortex (LIP): highest-order area in the visual hierarchy of t ...
Slide 1
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
ling411-21 - Rice University
... syntactic processing were distinguished, one dealing with building a local phrase (i.e. a noun phrase consisting of a determiner and a noun ‘the boy’) and one dealing with building complex, hierarchically structured sequences (like embedded sentences ‘This is the girl who kissed the president’). DTI ...
... syntactic processing were distinguished, one dealing with building a local phrase (i.e. a noun phrase consisting of a determiner and a noun ‘the boy’) and one dealing with building complex, hierarchically structured sequences (like embedded sentences ‘This is the girl who kissed the president’). DTI ...
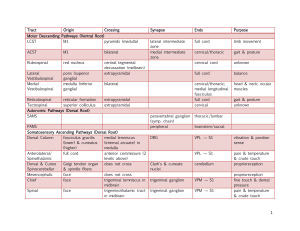
Tract Origin Crossing Synapse Ends Purpose Motor Descending
... peduncle/pontine lesions; hydrocephalus; prefrontal cortex; spinal cord disorder; contralateral ataxia-hemiparesis ...
... peduncle/pontine lesions; hydrocephalus; prefrontal cortex; spinal cord disorder; contralateral ataxia-hemiparesis ...
So it is the number of action potentials per second
... 2. As this occurs, there is a greater and greater negative charge within the cell due to the loss of K+ and the anions left inside. 3. This buildup of negative charge creates a charge gradient for cations (potassium) to flow back in. 4. Eventually potassium would be entering the neuron at the same r ...
... 2. As this occurs, there is a greater and greater negative charge within the cell due to the loss of K+ and the anions left inside. 3. This buildup of negative charge creates a charge gradient for cations (potassium) to flow back in. 4. Eventually potassium would be entering the neuron at the same r ...
Nervous System - ocw@unimas - Universiti Malaysia Sarawak
... At the end of the unit, you should be able to: 1. Discuss the coordina8on process in nervous system. 2. Compare the invertebrate and vertebrate nervous organiza8ons. 3. Describe the soma8c and autonomic ...
... At the end of the unit, you should be able to: 1. Discuss the coordina8on process in nervous system. 2. Compare the invertebrate and vertebrate nervous organiza8ons. 3. Describe the soma8c and autonomic ...
Functional Framework for Cognition
... The verbal part --- such as rehearsing words or numbers silently --involves the speech areas of the cortex (especially the dominant hemisphere). E.g., Broca and Wernicke's areas. The visual part --- such as visual imagery to think about how to walk from one place to another --- seems to involve visu ...
... The verbal part --- such as rehearsing words or numbers silently --involves the speech areas of the cortex (especially the dominant hemisphere). E.g., Broca and Wernicke's areas. The visual part --- such as visual imagery to think about how to walk from one place to another --- seems to involve visu ...
Outline14 Efferent NS
... nicotinic cholinergic receptors at the motor end plate binding of ACh open cation channels → strong EPSP → exceeds threshold → muscle AP B. Autonomic Division (ANS) - involuntary control of autonomic effectors (visceral organs, blood vessels, etc.) - activated by the hypothalamus, pons & medulla, an ...
... nicotinic cholinergic receptors at the motor end plate binding of ACh open cation channels → strong EPSP → exceeds threshold → muscle AP B. Autonomic Division (ANS) - involuntary control of autonomic effectors (visceral organs, blood vessels, etc.) - activated by the hypothalamus, pons & medulla, an ...
PET Imaging of Differential Cortical Activation to
... Abstract. PET imaging was used to investigate the brain activation patterns of listeners presented monaurally (right-ear) with speech and nonspeech stimuli. The major objectives were to identify regions involved with speech and nonspeech processing, and to develop a stimulus paradigm suitable for st ...
... Abstract. PET imaging was used to investigate the brain activation patterns of listeners presented monaurally (right-ear) with speech and nonspeech stimuli. The major objectives were to identify regions involved with speech and nonspeech processing, and to develop a stimulus paradigm suitable for st ...
Lecture 15
... Leaky integrate and fire neurons Encode each individual spike Time is represented exactly Each spike has an associated time The timing of recent incoming spikes determines whether a neuron will fire • Computationally expensive • Can we do almost as well without encoding every single spike? ...
... Leaky integrate and fire neurons Encode each individual spike Time is represented exactly Each spike has an associated time The timing of recent incoming spikes determines whether a neuron will fire • Computationally expensive • Can we do almost as well without encoding every single spike? ...
motor unit
... the cytosolic concentration of Ca2+ remains high The prolonged availability of Ca2+ in the cytosol permits more of the cross bridges to continue participating in the cycling process for a longer time With an increase in the frequency of action potentials, duration of elevated cytosolic Ca2+ concentr ...
... the cytosolic concentration of Ca2+ remains high The prolonged availability of Ca2+ in the cytosol permits more of the cross bridges to continue participating in the cycling process for a longer time With an increase in the frequency of action potentials, duration of elevated cytosolic Ca2+ concentr ...
Module 1:Human Nervous System Lecture 5:Spinal cord The
... bundle of axons covering full length of the body. Its primary function is to facilitate reflex movements. The animation given below demonstrates the mechanism of reflex action. ...
... bundle of axons covering full length of the body. Its primary function is to facilitate reflex movements. The animation given below demonstrates the mechanism of reflex action. ...
Nervous System: Reflexes and Peripheral Nervous System
... automatic responses to specific stimuli ...
... automatic responses to specific stimuli ...
Learning to Recover Meaning from Unannotated
... approaches. Additionally, there has been significant recent work on learning to do other, related, natural language semantic analysis tasks from context-dependent database queries [16, 26], grounded event streams [13, 5, 2], environment interactions [3, 4, 20], and even unannotated text [17, 18]. In ...
... approaches. Additionally, there has been significant recent work on learning to do other, related, natural language semantic analysis tasks from context-dependent database queries [16, 26], grounded event streams [13, 5, 2], environment interactions [3, 4, 20], and even unannotated text [17, 18]. In ...
Nervous - Anoka-Hennepin School District
... parietal- recieves and evaluates most sensory information like touch and taste from the skin and muscles of body with large areas for the lips, face. occipital- receives and interprets visual input. temporal- evaluates olfactory and auditory input and plays a role in memory. ...
... parietal- recieves and evaluates most sensory information like touch and taste from the skin and muscles of body with large areas for the lips, face. occipital- receives and interprets visual input. temporal- evaluates olfactory and auditory input and plays a role in memory. ...
The Brain and The Nervous System
... • Her autonomic NS controls involuntary actions of internal organs. At the start of the race her sympathetic NS would be activated, resulting in an increase in Renees’ adrenaline, heart rate, respiration and sweating. After the race her parasympathetic NS would slow her heart rate and respiration ra ...
... • Her autonomic NS controls involuntary actions of internal organs. At the start of the race her sympathetic NS would be activated, resulting in an increase in Renees’ adrenaline, heart rate, respiration and sweating. After the race her parasympathetic NS would slow her heart rate and respiration ra ...
Document
... 3. Match the term.(choose the best answer) cerebrum, The sensorimotor cortex is located here. medulla oblongata thalamus ...
... 3. Match the term.(choose the best answer) cerebrum, The sensorimotor cortex is located here. medulla oblongata thalamus ...
NAlab08_DescMotor
... gyrus. This area is important in the execution of movments. Area 4 lesions produce weakness. Area 6 is a premotor region that includes several somatotopically organized components. One of these is the supplementary motor area (SMA) located in the most dorsomedial part of area 6. This area is thought ...
... gyrus. This area is important in the execution of movments. Area 4 lesions produce weakness. Area 6 is a premotor region that includes several somatotopically organized components. One of these is the supplementary motor area (SMA) located in the most dorsomedial part of area 6. This area is thought ...
Descending Motor Pathways Objective • To learn the functional
... gyrus. This area is important in the execution of movments. Area 4 lesions produce weakness. Area 6 is a premotor region that includes several somatotopically organized components. One of these is the supplementary motor area (SMA) located in the most dorsomedial part of area 6. This area is thought ...
... gyrus. This area is important in the execution of movments. Area 4 lesions produce weakness. Area 6 is a premotor region that includes several somatotopically organized components. One of these is the supplementary motor area (SMA) located in the most dorsomedial part of area 6. This area is thought ...
Notes on Learning to Compute and Computing to Learn
... a statistically significant difference between the neuron’s response to a stimulus combination compared to its response to the individual component stimulus [21]. There is some evidence, based on experiments on cats, that certain areas of the cats’ nervous system comprise unimodal neurons, at least ...
... a statistically significant difference between the neuron’s response to a stimulus combination compared to its response to the individual component stimulus [21]. There is some evidence, based on experiments on cats, that certain areas of the cats’ nervous system comprise unimodal neurons, at least ...