Slide 1
... Vowel sounds are produced by vocal cords vibrations. The vibrations produce an alternating wave. Any alternating wave has a fundamental frequency and a number of harmonics. These harmonics are the integer multiples of the fundamental frequency. The fundamental frequency of the alternating wave pro ...
... Vowel sounds are produced by vocal cords vibrations. The vibrations produce an alternating wave. Any alternating wave has a fundamental frequency and a number of harmonics. These harmonics are the integer multiples of the fundamental frequency. The fundamental frequency of the alternating wave pro ...
Major Concepts of Anatomy and Physiology
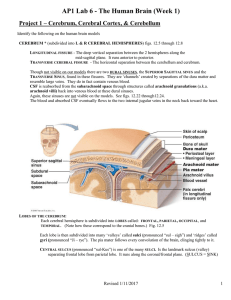
... Choroid Plexuses: Networks of capillaries in the walls of the ventricles where CSF is produced. Arachnoid Villi: Location where CSF is reabsorbed and dumped into the brain's sinus cavities for drainage. Hydrocephalus: Marked by a failure to drain CFS, resulting in increased intracranial pressure. ...
... Choroid Plexuses: Networks of capillaries in the walls of the ventricles where CSF is produced. Arachnoid Villi: Location where CSF is reabsorbed and dumped into the brain's sinus cavities for drainage. Hydrocephalus: Marked by a failure to drain CFS, resulting in increased intracranial pressure. ...
1. What different types of attention exist? Name and describe at least
... Exogenous or bottom-up attention: type of attention associated with sensory stimuli “popping out” of the background withouth cognitive input, e.g., a flash of light in the darkness, a loud sound in quietness, a warm spot in a cold environment etc. Endogenous / selective / top-down attention: attenti ...
... Exogenous or bottom-up attention: type of attention associated with sensory stimuli “popping out” of the background withouth cognitive input, e.g., a flash of light in the darkness, a loud sound in quietness, a warm spot in a cold environment etc. Endogenous / selective / top-down attention: attenti ...
storyboards
... by the motor cortex, however, is regulated by other brain circuits. One of these is called the basal ganglia, a Basal Ganglia group of interconnected structures in the Show signal going from brain to middle of the brain. hand (motor cortex to spinal cord, Specifically, the basal spinal cord to motor ...
... by the motor cortex, however, is regulated by other brain circuits. One of these is called the basal ganglia, a Basal Ganglia group of interconnected structures in the Show signal going from brain to middle of the brain. hand (motor cortex to spinal cord, Specifically, the basal spinal cord to motor ...
Commentary on slides for lecture 15
... muscle itself called the muscle spindle. The muscle spindle is an encapsulated structure that contains very fine muscle fibers, the intrafusal fibers, and the endings of neurons located in the dorsal root ganglia, the Ia afferent fibers. The intrafusal fibers are arranged in parallel with the main ...
... muscle itself called the muscle spindle. The muscle spindle is an encapsulated structure that contains very fine muscle fibers, the intrafusal fibers, and the endings of neurons located in the dorsal root ganglia, the Ia afferent fibers. The intrafusal fibers are arranged in parallel with the main ...
PowerPoint
... • all sentences are defined this way to simplify processing – disjunction of literals with exactly one positive – clause is either atomic or an implication whose antecedent is a conjunction of positive literals and whose consequent is a single positive literal ...
... • all sentences are defined this way to simplify processing – disjunction of literals with exactly one positive – clause is either atomic or an implication whose antecedent is a conjunction of positive literals and whose consequent is a single positive literal ...
Chapter 6 - Sensory - Austin Community College
... Motor neurons are the final common pathway by which various regions of the CNS exert control over skeletal muscle activity The areas of the CNS that influence skeletal muscle activity by acting through the motor neurons are the spinal cord, motor regions of the cortex, basal nuclei, cerebellum, and ...
... Motor neurons are the final common pathway by which various regions of the CNS exert control over skeletal muscle activity The areas of the CNS that influence skeletal muscle activity by acting through the motor neurons are the spinal cord, motor regions of the cortex, basal nuclei, cerebellum, and ...
Chapter 17
... since near the spine, most axons are short generally innervate organs above the diaphragm. ...
... since near the spine, most axons are short generally innervate organs above the diaphragm. ...
Sensorimotor Neural Plasticity following Hand Transplantation
... hypothesized pathways between the areas in the DMN along with how purported increases in activity in one region results in a decrease in activity in another. In summary, we sought to determine how a hand transplant would alter brain connectivity in a large-scale cortical network (i.e. DMN) that incl ...
... hypothesized pathways between the areas in the DMN along with how purported increases in activity in one region results in a decrease in activity in another. In summary, we sought to determine how a hand transplant would alter brain connectivity in a large-scale cortical network (i.e. DMN) that incl ...
Chapter 13 - Los Angeles City College
... Prefrontal lobes involve retrieval of parts of memories from different areas of the brain to use as a whole. ...
... Prefrontal lobes involve retrieval of parts of memories from different areas of the brain to use as a whole. ...
Nervous System
... • The system that constantly monitors and responds the stimuli (stimulus) around you … • Stimuli your body can respond to … (Internal or External) ...
... • The system that constantly monitors and responds the stimuli (stimulus) around you … • Stimuli your body can respond to … (Internal or External) ...
Dependency-Based Hybrid Model of Syntactic Analysis for
... them from being involved in other dependencies — they do not necessarily have to be placed together. For instance, the parser also accepts constructions like liels koka galds ‘big wooden table’. ...
... them from being involved in other dependencies — they do not necessarily have to be placed together. For instance, the parser also accepts constructions like liels koka galds ‘big wooden table’. ...
Lec 7 Lab Demo Handout
... thermoeffector response giving increased contractile activity of skeletal muscles to increase metabolic heat production. It is referred to as shivering thermogenesis and has an electromyographically distinct pattern of motor unit discharges that is quantified as the integrated voltage (V) deflection ...
... thermoeffector response giving increased contractile activity of skeletal muscles to increase metabolic heat production. It is referred to as shivering thermogenesis and has an electromyographically distinct pattern of motor unit discharges that is quantified as the integrated voltage (V) deflection ...
Chapter 2 - Safford Unified School
... A) The cerebral cortex is divided into four parts, with the occipital and parietal lobes in the right hemisphere and the frontal and temporal lobes in the left hemisphere. B) In general, each of the cerebral hemispheres controls feeling and movement on the opposite side of the body. C) The cerebral ...
... A) The cerebral cortex is divided into four parts, with the occipital and parietal lobes in the right hemisphere and the frontal and temporal lobes in the left hemisphere. B) In general, each of the cerebral hemispheres controls feeling and movement on the opposite side of the body. C) The cerebral ...
Vertebrate Nervous System
... May be visceral/somatic, sensory/motor, general/special Terminal (0) – sensory (olfactory) zeroth nerve cause it’s the first nerve, not present in all vertebrates, prominent in fishes appearance is controversial in mammals, serves as sensory function, particularly for olfactory signals Olfactory (I) ...
... May be visceral/somatic, sensory/motor, general/special Terminal (0) – sensory (olfactory) zeroth nerve cause it’s the first nerve, not present in all vertebrates, prominent in fishes appearance is controversial in mammals, serves as sensory function, particularly for olfactory signals Olfactory (I) ...
NervousSystem3
... The motor cortex is the area of the cerebral cortex at which initiation of voluntary motor activity takes place. In all the species that we study, and in humans, the motor cortex is located immediately anterior to the somatosensory cortex. Voluntary, deliberate, motor activity is the result of proc ...
... The motor cortex is the area of the cerebral cortex at which initiation of voluntary motor activity takes place. In all the species that we study, and in humans, the motor cortex is located immediately anterior to the somatosensory cortex. Voluntary, deliberate, motor activity is the result of proc ...
Research paper : Why the Mirror Neurons Cannot Support
... action explicitly (in his/her behavior) with agility and finesse. This happens due to associative learning processes [17]. The more frequently a synaptic connection is activated, the stronger it becomes. There are data confirming that observation of another individual learning a new action can impro ...
... action explicitly (in his/her behavior) with agility and finesse. This happens due to associative learning processes [17]. The more frequently a synaptic connection is activated, the stronger it becomes. There are data confirming that observation of another individual learning a new action can impro ...
Unit 3-2 Nervous System Pt 2 Notes File
... 1.Neurotransmitter binds to G protein-linked receptor 1.G protein is activated and GTP is hydrolyzed (hydrolysis) to GDP 2.The activated G protein complex activates adenylate cyclase 3.Adenylate cyclase catalyzes the formation of cAMP from ATP 4.cAMP, a second messenger, brings about various cellula ...
... 1.Neurotransmitter binds to G protein-linked receptor 1.G protein is activated and GTP is hydrolyzed (hydrolysis) to GDP 2.The activated G protein complex activates adenylate cyclase 3.Adenylate cyclase catalyzes the formation of cAMP from ATP 4.cAMP, a second messenger, brings about various cellula ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... 21. Action Potential is another name for a (an) impulse 22. A(n) reflex is an automatic response to a stimulus. 23 Subdivision of the PNS that regulates the activity of the heart and smooth muscle and of glands; also called the involuntary nervous system… autonomic 24.Sensory neurons carry impulses ...
... 21. Action Potential is another name for a (an) impulse 22. A(n) reflex is an automatic response to a stimulus. 23 Subdivision of the PNS that regulates the activity of the heart and smooth muscle and of glands; also called the involuntary nervous system… autonomic 24.Sensory neurons carry impulses ...
chapter 8 movement
... – Progressive disease that produces involuntary, jerky movements and cognitive symptoms – Caused by abnormality on gene on chromosome 4 – No cure or effective treatments ...
... – Progressive disease that produces involuntary, jerky movements and cognitive symptoms – Caused by abnormality on gene on chromosome 4 – No cure or effective treatments ...
Evolution and analysis of minimal neural circuits for klinotaxis in
... Recently, Iino and colleagues have described a complementary strategy, called klinotaxis. This work combines neural network modeling and evolutionary algorithms to identify simple circuit motifs for klinotaxis. It then uses dynamical systems analysis to understand how they function. ...
... Recently, Iino and colleagues have described a complementary strategy, called klinotaxis. This work combines neural network modeling and evolutionary algorithms to identify simple circuit motifs for klinotaxis. It then uses dynamical systems analysis to understand how they function. ...
Neurocase - McGill University
... cerebral blood flow were observed across all three languages (French, Spanish and English), when synonym generation was compared with a silent resting baseline. In particular, several regions in the right inferior frontal cortex were activated. These foci are in locations corresponding to those obser ...
... cerebral blood flow were observed across all three languages (French, Spanish and English), when synonym generation was compared with a silent resting baseline. In particular, several regions in the right inferior frontal cortex were activated. These foci are in locations corresponding to those obser ...
Lab Activity Sheets
... bulbs receive messages for the sense of smell from bipolar neurons in your nasal cavity. Axons from these neurons travel in the olfactory tracts to the appropriate portion of the cerebral cortex. PITUITARY GLAND – (Fig. 12.11) the bulb-like structure just under the hypothalamus. Because it releases ...
... bulbs receive messages for the sense of smell from bipolar neurons in your nasal cavity. Axons from these neurons travel in the olfactory tracts to the appropriate portion of the cerebral cortex. PITUITARY GLAND – (Fig. 12.11) the bulb-like structure just under the hypothalamus. Because it releases ...
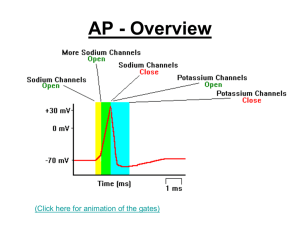
AP – All or nothing
... • There is a time after depolarisation where no new AP can start – called the refractory period. – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one ...
... • There is a time after depolarisation where no new AP can start – called the refractory period. – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one ...