Changing Channels
... (IPD) is tethered to an independently functioning ligand-binding domain (LBD). Scientists had previously engineered “chimeric” ion channels by genetically splicing the LBD from one type of channel to the IPD from another. Such hybrid channels transport ions specified by the IPD but in response to th ...
... (IPD) is tethered to an independently functioning ligand-binding domain (LBD). Scientists had previously engineered “chimeric” ion channels by genetically splicing the LBD from one type of channel to the IPD from another. Such hybrid channels transport ions specified by the IPD but in response to th ...
File
... Figure 6.13 Intermittent reinforcement schedules Skinner’s laboratory pigeons produced these response patterns to each of four reinforcement schedules. (Reinforcers are indicated by diagonal marks.) For people, as for pigeons, reinforcement linked to number of responses (a ratio schedule) produces ...
... Figure 6.13 Intermittent reinforcement schedules Skinner’s laboratory pigeons produced these response patterns to each of four reinforcement schedules. (Reinforcers are indicated by diagonal marks.) For people, as for pigeons, reinforcement linked to number of responses (a ratio schedule) produces ...
Discoveries from the Black Box - Boulder Institute for Psychotherapy
... conceptual bridge among biology, attachment research, development psychology, brain science, and systems theory. "But we survived as a species not so much because of our physical brawn, but due to our interpersonal capacity. More and more, we're realizing that evolution has designed our brains to be ...
... conceptual bridge among biology, attachment research, development psychology, brain science, and systems theory. "But we survived as a species not so much because of our physical brawn, but due to our interpersonal capacity. More and more, we're realizing that evolution has designed our brains to be ...
Addictive Drug Use - Dayton Independent Schools
... • Treat the urges directly, if possible • Establish why the person uses the drug • What needs are being fulfilled by that drug? • Find methods to fulfil those needs without the drug ...
... • Treat the urges directly, if possible • Establish why the person uses the drug • What needs are being fulfilled by that drug? • Find methods to fulfil those needs without the drug ...
The ventral striatum in goal-directed behavior and - UvA-DARE
... theories is the ‘standard’ theory of declarative memory consolidation. This theory posits that the hippocampus, together with other areas of the medial temporal lobe, is crucial for all forms of declarative memory for a limited period of time (Squire, 1986; Squire et al., 2004). Ultimately, all memo ...
... theories is the ‘standard’ theory of declarative memory consolidation. This theory posits that the hippocampus, together with other areas of the medial temporal lobe, is crucial for all forms of declarative memory for a limited period of time (Squire, 1986; Squire et al., 2004). Ultimately, all memo ...
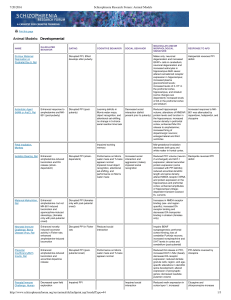
Developmental - Schizophrenia Research Forum
... Increased expression of D2like and NMDA receptors in the frontal cortex and hippocampus; prolonged corticosterone stress response and decreased expression of central corticosteroid receptors (sensitive to cross-fostering); increased basal dopamine and decreased noradrenaline output in the nucleus ac ...
... Increased expression of D2like and NMDA receptors in the frontal cortex and hippocampus; prolonged corticosterone stress response and decreased expression of central corticosteroid receptors (sensitive to cross-fostering); increased basal dopamine and decreased noradrenaline output in the nucleus ac ...
Phobias SD AS
... 1) A marked and persistent fear of one or more social or performance situations in which the person is exposed to unfamiliar people or to possible scrutiny by others. The individual fears that he or she will act in a way (or show anxiety symptoms) that will be humiliating or embarrassing. Note: In c ...
... 1) A marked and persistent fear of one or more social or performance situations in which the person is exposed to unfamiliar people or to possible scrutiny by others. The individual fears that he or she will act in a way (or show anxiety symptoms) that will be humiliating or embarrassing. Note: In c ...
Cortical inputs to the CA1 field of the monkey hippocampus originate
... injections were available for analysis. In three additional experiments, discrete injections of the retrograde tracers FB, DY or W G A - H R P were placed into different rostrocaudal levels of the medial portion of the CAi field of the hippocampus. After a survival period of two weeks (or 2 days in ...
... injections were available for analysis. In three additional experiments, discrete injections of the retrograde tracers FB, DY or W G A - H R P were placed into different rostrocaudal levels of the medial portion of the CAi field of the hippocampus. After a survival period of two weeks (or 2 days in ...
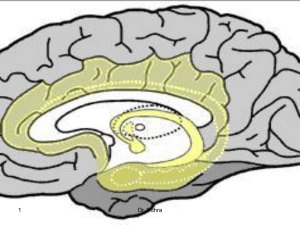
20-Limbic
... important role on the mediation and control of major affective activities like friendship, love and affection, on the expression of mood and, mainly, on fear, anger and violent behavior. The amygdala, being the center for identification of danger. When triggered, it gives rise to fear and anxiety wh ...
... important role on the mediation and control of major affective activities like friendship, love and affection, on the expression of mood and, mainly, on fear, anger and violent behavior. The amygdala, being the center for identification of danger. When triggered, it gives rise to fear and anxiety wh ...
Review Unit 13 Treatment 2015-2016
... Catastrophizing (Illogical, Maladaptive) beliefs: •Client’s told to test their thoughts for accuracy •Example: I never have a good time •Client may come up with times that were actually good. --An unassertive person may be asked to cut in line or ask someone for a favor ...
... Catastrophizing (Illogical, Maladaptive) beliefs: •Client’s told to test their thoughts for accuracy •Example: I never have a good time •Client may come up with times that were actually good. --An unassertive person may be asked to cut in line or ask someone for a favor ...
Mayberg HS, Lozano AM. (2009). Targeted electrode
... in animal models of depression and associated emotional behaviors (30–34), supporting the hypothesis that even subtle disruption of pathways linking these regions in humans can result in disturbances in emotion regulation typical of MDD, namely negative mood coupled with sustained changes in motivat ...
... in animal models of depression and associated emotional behaviors (30–34), supporting the hypothesis that even subtle disruption of pathways linking these regions in humans can result in disturbances in emotion regulation typical of MDD, namely negative mood coupled with sustained changes in motivat ...
Phys Chapter 59 [4-20
... So a grand mall attack involves abnormal activation of the thalamus, cerebral cortex, and subthalamic brainstem parts of the brain activating system o Most people who have grand mal attacks have a hereditary predisposition to epilepsy In these people, things that can increase the excitability enou ...
... So a grand mall attack involves abnormal activation of the thalamus, cerebral cortex, and subthalamic brainstem parts of the brain activating system o Most people who have grand mal attacks have a hereditary predisposition to epilepsy In these people, things that can increase the excitability enou ...
Understanding Psychology Charles G. Morris Albert A. Maisto Tenth
... such as standing on one foot. This action had nothing to do with getting the food, of course. But still the bird repeated it over and over again. Skinner called the bird’s behavior superstitious, because it was learned in a way that is similar to how some human superstitions are learned. If you happ ...
... such as standing on one foot. This action had nothing to do with getting the food, of course. But still the bird repeated it over and over again. Skinner called the bird’s behavior superstitious, because it was learned in a way that is similar to how some human superstitions are learned. If you happ ...
6. Using artificial agents to understand
... ten tokens in market two, whereas all the other players invest in market one, player i will receive 2.05 tokens, considerably more than what market one yielded. However, when all players invest ten tokens in market two, the yields are – 0.2 tokens, thus implying a loss. In the case when the players ...
... ten tokens in market two, whereas all the other players invest in market one, player i will receive 2.05 tokens, considerably more than what market one yielded. However, when all players invest ten tokens in market two, the yields are – 0.2 tokens, thus implying a loss. In the case when the players ...
A Multidisciplinary-economic Framework of Analysis
... economics analyzes economic motivation in interaction with scarce natural resources. It assumes that perfect rationality and non-sociality create a so-called economic world and analyzes the economic mechanism of allocation of scarce resources. Neoclassical economists use this world as a theoretical ...
... economics analyzes economic motivation in interaction with scarce natural resources. It assumes that perfect rationality and non-sociality create a so-called economic world and analyzes the economic mechanism of allocation of scarce resources. Neoclassical economists use this world as a theoretical ...
BIOLOGICAL AND CULTURAL SHAPING OF MIND AND BEHAVIOUR
... Foundations of Psychology (a) Cerebral Cortex The uppermost layer of the brain is called cerebral cortex (see Figure 3.5). The brain is divided into two halves: the left hemisphere and right hemisphere. They resemble the halves of a walnut. It is interesting to note that each hemisphere processes in ...
... Foundations of Psychology (a) Cerebral Cortex The uppermost layer of the brain is called cerebral cortex (see Figure 3.5). The brain is divided into two halves: the left hemisphere and right hemisphere. They resemble the halves of a walnut. It is interesting to note that each hemisphere processes in ...
Module 24 Operant Conditioning Module Preview While in classical
... 24-5. Explain the importance of cognitive processes and biological predispositions in operant conditioning. Rats exploring a maze seem to develop a mental representation (a cognitive map) of the maze even in the absence of reward. Their latent learning becomes evident only when there is some incenti ...
... 24-5. Explain the importance of cognitive processes and biological predispositions in operant conditioning. Rats exploring a maze seem to develop a mental representation (a cognitive map) of the maze even in the absence of reward. Their latent learning becomes evident only when there is some incenti ...
Larry M. Jordan, Urszula Sławińska
... motoneurons. The L-DOPA treatment produced locomotion in the spinal cat preparation, and the half-center model was proposed as a plausible organization to explain these findings. (B) A computational model of spinal locomotor circuitry with a two-level CPG.31 Rhythm generator (RG) and pattern formati ...
... motoneurons. The L-DOPA treatment produced locomotion in the spinal cat preparation, and the half-center model was proposed as a plausible organization to explain these findings. (B) A computational model of spinal locomotor circuitry with a two-level CPG.31 Rhythm generator (RG) and pattern formati ...
Food for Thought: Essential Fatty Acid Protects
... The significance of this paper lies in the discovery that the neurobiological substrate for the visuospatial constructive impairment in Williams syndrome is localized to a small region in parietal cortex. This finding is consistent with everything we know about the organization of the visual system ...
... The significance of this paper lies in the discovery that the neurobiological substrate for the visuospatial constructive impairment in Williams syndrome is localized to a small region in parietal cortex. This finding is consistent with everything we know about the organization of the visual system ...
Presentation1
... • Research used DTI to map the UF tract in children with conduct disorder and controls. • The authors found that there was a significant difference, with the clinical group having greater diffusion (counter to the hypothesis) through the UF. • Unclear why or what effect this has on conduct disorder. ...
... • Research used DTI to map the UF tract in children with conduct disorder and controls. • The authors found that there was a significant difference, with the clinical group having greater diffusion (counter to the hypothesis) through the UF. • Unclear why or what effect this has on conduct disorder. ...
14/15 April 2008
... – Fitness evaluated on the controller not the network – Requires sophisticated genome ...
... – Fitness evaluated on the controller not the network – Requires sophisticated genome ...
neural mechanisms of animal behavior
... neuromuscular events can be ruled out for the same reasons. This leaves only the junctions between ascending giant fibers and motor neurons in the thoracic ganglia. Attempts to study this synaptic interaction between giants and motor neurons (Roeder, 1948; 1958) indeed showed that this process is so ...
... neuromuscular events can be ruled out for the same reasons. This leaves only the junctions between ascending giant fibers and motor neurons in the thoracic ganglia. Attempts to study this synaptic interaction between giants and motor neurons (Roeder, 1948; 1958) indeed showed that this process is so ...
Investigating - The Biotechnology Institute
... a mild electrical current to a part of the brain that generates a pleasurable sensation. ...
... a mild electrical current to a part of the brain that generates a pleasurable sensation. ...
The Brain Doesn`t Work That Way: From Microgenesis to Cognition
... • The interactive model is clearly a dynamic, process model • Dynamic approaches, however, are often anti-representational – E.g., Van Gelder, Thelen ...
... • The interactive model is clearly a dynamic, process model • Dynamic approaches, however, are often anti-representational – E.g., Van Gelder, Thelen ...