SPHS 4050, Neurological bases, PP 03a
... SYSTEM which includes the hippocampus and amygdala, interconneted with parts of the diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus) and olfactory (smell) system. The limbic system is strongly associated with memory and emotion ...
... SYSTEM which includes the hippocampus and amygdala, interconneted with parts of the diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus) and olfactory (smell) system. The limbic system is strongly associated with memory and emotion ...
ch. 48 Nervous System notes
... – Carried out by Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – Conduction of signals to muscle or gland cells – Carry out body’s responses to stimuli ...
... – Carried out by Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – Conduction of signals to muscle or gland cells – Carry out body’s responses to stimuli ...
Injury and brain development
... • The brain has the capacity to correct minor abnormalities that may occur during development (brain plasticity). • The plastic properties of the brain continue into adulthood and allow us to cope with the neuronal loss that occurs during aging. ...
... • The brain has the capacity to correct minor abnormalities that may occur during development (brain plasticity). • The plastic properties of the brain continue into adulthood and allow us to cope with the neuronal loss that occurs during aging. ...
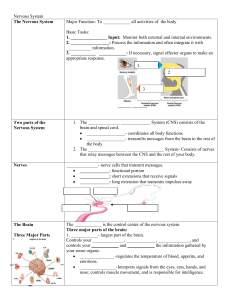
Nervous system
... Medulla Oblongata lies within the midbrain between the pons and spinal cord,it forms the brainstem. The medulla controls heart rate, breathing swallowing, coughing and vomiting. The midbrain and the pons relay messages between the medulla oblongata and the cerebrum. ...
... Medulla Oblongata lies within the midbrain between the pons and spinal cord,it forms the brainstem. The medulla controls heart rate, breathing swallowing, coughing and vomiting. The midbrain and the pons relay messages between the medulla oblongata and the cerebrum. ...
Brain and Cranial Nerves
... – Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity – Control center for many of body’s functions ...
... – Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity – Control center for many of body’s functions ...
sensationandperception_PP_Vision_Mods 18 and 19
... Despite the way the world appears, color does not exist outside the brain, because color is a perception that the brain creates based on the wavelength of light striking our eyes. ◦ Color is created when the wavelength in a beam of light is recorded by the photoreceptors in the form of neural impuls ...
... Despite the way the world appears, color does not exist outside the brain, because color is a perception that the brain creates based on the wavelength of light striking our eyes. ◦ Color is created when the wavelength in a beam of light is recorded by the photoreceptors in the form of neural impuls ...
Brain
... 2. Foramen of Monro to 3rd Ventricle(center of diencephalon) 3. Cerebral Aqueduct to 4. Fourth ventricle(between cerebellum and brainstem) 5 to central canal and subarachnoid space of SC 6. To cranial subarachnoid space passing out of arachnoid villi and into the Superior Sagittal Sinus(a large vei ...
... 2. Foramen of Monro to 3rd Ventricle(center of diencephalon) 3. Cerebral Aqueduct to 4. Fourth ventricle(between cerebellum and brainstem) 5 to central canal and subarachnoid space of SC 6. To cranial subarachnoid space passing out of arachnoid villi and into the Superior Sagittal Sinus(a large vei ...
Unit: Regulation Notes
... receptor (recognizes the stimulus), goes to the 2) sensory neuron (sends signal to brain), to the 3) interneuron (routes the impulse to the correct part of the brain), to the 4) motor neuron (alerts the muscle), and then to the 5) effector (the muscle or gland) Ex. Touching hot stove ...
... receptor (recognizes the stimulus), goes to the 2) sensory neuron (sends signal to brain), to the 3) interneuron (routes the impulse to the correct part of the brain), to the 4) motor neuron (alerts the muscle), and then to the 5) effector (the muscle or gland) Ex. Touching hot stove ...
Inside the Human Brain
... system and is the most complex organ in any creature on earth. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over five times as large as the "average brain" of a mammal with the same body size. ...
... system and is the most complex organ in any creature on earth. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over five times as large as the "average brain" of a mammal with the same body size. ...
Topic 8
... which produces a three-dimensional image or picture of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide (tracer), which is introduced into the body on a biologically active molecule. ...
... which produces a three-dimensional image or picture of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide (tracer), which is introduced into the body on a biologically active molecule. ...
PSC - University of Pittsburgh
... datasets within high performance parallel computing environments using both CPU and GPGPU processing. We are also interested in the image warping and other processes required for neural circuit reconstruction. The Filesystem in User Space mechanism (FUSE) provides a convenient implementation basis t ...
... datasets within high performance parallel computing environments using both CPU and GPGPU processing. We are also interested in the image warping and other processes required for neural circuit reconstruction. The Filesystem in User Space mechanism (FUSE) provides a convenient implementation basis t ...
lecture-4-post
... Axon: Extension that sends information to other cells Action Potential: electric impulse based on balance of ions in the cell, all or none Myelin Sheath: contains electrical signal (prevents crossover & facilitates transmission Dendrites: receives information from other cells, multiple signals are t ...
... Axon: Extension that sends information to other cells Action Potential: electric impulse based on balance of ions in the cell, all or none Myelin Sheath: contains electrical signal (prevents crossover & facilitates transmission Dendrites: receives information from other cells, multiple signals are t ...
Neuron encyclopaedia fires up to reveal brain secrets
... or the tens of billions in the human one. “There are too many neurons in the brain, and we have only sampled a very, very small set,” says the Allen Institute’s Hanchuan Peng, who is leading the BigNeuron project. A major bottleneck in cataloguing more neurons has been extracting the three-dimension ...
... or the tens of billions in the human one. “There are too many neurons in the brain, and we have only sampled a very, very small set,” says the Allen Institute’s Hanchuan Peng, who is leading the BigNeuron project. A major bottleneck in cataloguing more neurons has been extracting the three-dimension ...
ElectroEncephaloGram (EEG) - MIT Biology
... activity of the brain. In this laboratory class you will record electroencephalograms from a volunteer, look at interfering signals, and examine the effects of visual activity on alpha waves. The EEG or electroencephalogram has long been used to record and study the electrical activity of the outerm ...
... activity of the brain. In this laboratory class you will record electroencephalograms from a volunteer, look at interfering signals, and examine the effects of visual activity on alpha waves. The EEG or electroencephalogram has long been used to record and study the electrical activity of the outerm ...
EEG - mitbrain
... activity of the brain. In this laboratory class you will record electroencephalograms from a volunteer, look at interfering signals, and examine the effects of visual activity on alpha waves. The EEG or electroencephalogram has long been used to record and study the electrical activity of the outerm ...
... activity of the brain. In this laboratory class you will record electroencephalograms from a volunteer, look at interfering signals, and examine the effects of visual activity on alpha waves. The EEG or electroencephalogram has long been used to record and study the electrical activity of the outerm ...
Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... A. Natural decline in functioning neurons, including sensory neurons. (balance loss, coordination, blood pressure, bladder) B. By the age of 60 up to 50% loss of lower motor neurons in lumbar ...
... A. Natural decline in functioning neurons, including sensory neurons. (balance loss, coordination, blood pressure, bladder) B. By the age of 60 up to 50% loss of lower motor neurons in lumbar ...
nervous quiz RG
... What is negative feedback? When a neuron is at rest where are the sodium and potassium ions located in relationship to the membrane? Why are impulses able to travel from one neuron to another? Mylinated sheaths allow impulses to travel faster along a neuron by jumping from ______ to node. ...
... What is negative feedback? When a neuron is at rest where are the sodium and potassium ions located in relationship to the membrane? Why are impulses able to travel from one neuron to another? Mylinated sheaths allow impulses to travel faster along a neuron by jumping from ______ to node. ...
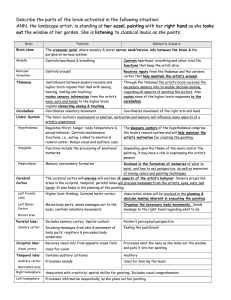
Temporal Lobe
... contains the nucleus, which in turn contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes. o Neurons have a large number of extensions called dendrites. It is primarily the surfaces of the dendrites that receive chemical messages from other neurons. o One extension is different from all the other ...
... contains the nucleus, which in turn contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes. o Neurons have a large number of extensions called dendrites. It is primarily the surfaces of the dendrites that receive chemical messages from other neurons. o One extension is different from all the other ...
Chapter 2 Review Notes
... Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. A neuron consists of a cell body and branching fibers: The dendrite fibers receive information from sensory receptors or other neurons, and the axon fibers pass that information along to other neurons. A layer of fatty tissu ...
... Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. A neuron consists of a cell body and branching fibers: The dendrite fibers receive information from sensory receptors or other neurons, and the axon fibers pass that information along to other neurons. A layer of fatty tissu ...
Describe the parts of the brain activated in the following situation
... higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting and touching; routes sensory information from the artist’s eyes, ears and hands to the higher brain regions connecting seeing & touching. Coordinates voluntary movement ...
... higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting and touching; routes sensory information from the artist’s eyes, ears and hands to the higher brain regions connecting seeing & touching. Coordinates voluntary movement ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.