35-3 Divisions of the Nervous System
... • 3. The cerebellum is the 2nd largest region of the brain located in the back of the skull. ...
... • 3. The cerebellum is the 2nd largest region of the brain located in the back of the skull. ...
A1984TV50600001
... this report may be that it was the first description of a sensitive, specific, and relatively simple method for measuring catecholamines in brain tissue. The overarching strategies involved in the assay—use3 of a partially purified methyltransferase, [ HJ-Sadenosyl-L-methionine, and differential org ...
... this report may be that it was the first description of a sensitive, specific, and relatively simple method for measuring catecholamines in brain tissue. The overarching strategies involved in the assay—use3 of a partially purified methyltransferase, [ HJ-Sadenosyl-L-methionine, and differential org ...
Reflex action, reflex Arc, Human Brain
... The organ in the body that has aesthetic sense to appreciate poetry etc. is _____ The part of the brain that helps in analyzing a problem is _____. Brain has more than _____ neurons. Brain Consumes about _____ % of total oxygen consume by the human body. Withdrawing the hand when we touch fire is __ ...
... The organ in the body that has aesthetic sense to appreciate poetry etc. is _____ The part of the brain that helps in analyzing a problem is _____. Brain has more than _____ neurons. Brain Consumes about _____ % of total oxygen consume by the human body. Withdrawing the hand when we touch fire is __ ...
Bio 17 – Nervous & Endocrine Systems
... low levels; important for sleep and low levels assoc with depression Runner’s High = DECREASED GABA ...
... low levels; important for sleep and low levels assoc with depression Runner’s High = DECREASED GABA ...
Right Brain/Left Brain: Different Qualities and an Uneasy Alliance?
... -consciousness resides only in this part of the brain -intellect, learning, memory, sensations are formed and stored here -has two halves connected by corpus callosum ...
... -consciousness resides only in this part of the brain -intellect, learning, memory, sensations are formed and stored here -has two halves connected by corpus callosum ...
File
... and the hindbrain gives rise to regions of the brainstem and the cerebellum. The cerebral cortex is greatly enlarged in human brains, and is considered the seat of complex thought. Visual processing takes place in the occipital lobe, near the back of the skull. The temporal lobe processes sound and ...
... and the hindbrain gives rise to regions of the brainstem and the cerebellum. The cerebral cortex is greatly enlarged in human brains, and is considered the seat of complex thought. Visual processing takes place in the occipital lobe, near the back of the skull. The temporal lobe processes sound and ...
C2 - The Biological Perspective
... hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal ...
... hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal ...
PSY110 Psychology
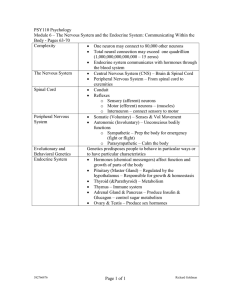
... Complexity One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Periphe ...
... Complexity One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Periphe ...
E4 Neurotransmitters and Synapses (and drugs!)
... function and respiratory function for a long time without the patient responding to signals fMRI may be used to determine brain activity When it is presumed that there is no longer any form of consciousness, doctors are allowed to declare the patient dead and turn off life support equipment ...
... function and respiratory function for a long time without the patient responding to signals fMRI may be used to determine brain activity When it is presumed that there is no longer any form of consciousness, doctors are allowed to declare the patient dead and turn off life support equipment ...
The Human Body Systems
... d) When the impulse reaches the tip of the axon, packets of neurotransmitters (acetylcholine) are released into the synapse and are received by the receptors on the adjacent dendrite which starts a new impulse traveling. C. Divisions of the Nervous System – Central Nervous System & Peripheral Nervou ...
... d) When the impulse reaches the tip of the axon, packets of neurotransmitters (acetylcholine) are released into the synapse and are received by the receptors on the adjacent dendrite which starts a new impulse traveling. C. Divisions of the Nervous System – Central Nervous System & Peripheral Nervou ...
PPT File - Newark Central Schools
... a. Located outside of the CNS. b. Made up of all of the neurons and nerve fibers outside the brain and spinal cord. ...
... a. Located outside of the CNS. b. Made up of all of the neurons and nerve fibers outside the brain and spinal cord. ...
Nervous System
... Impulses jump from the axon Across the synapse To the dendrite of the next neuron ...
... Impulses jump from the axon Across the synapse To the dendrite of the next neuron ...
Topology - UCSB Physics
... The topology of the central nervous system has been, and remains today a topic of considerable study. It is known that for humans, the central nervous system starts in the embryo as a plate, eventually deforming into a tube, one end of which thickens to become the brain (the remainder being the spin ...
... The topology of the central nervous system has been, and remains today a topic of considerable study. It is known that for humans, the central nervous system starts in the embryo as a plate, eventually deforming into a tube, one end of which thickens to become the brain (the remainder being the spin ...
Neuron Structure
... this was cacao beans from the tree Cacao theobroma • Chocolate causes brain to produce natural opiates • Opiates produce feelings of euphoria, dull pain • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC bi ...
... this was cacao beans from the tree Cacao theobroma • Chocolate causes brain to produce natural opiates • Opiates produce feelings of euphoria, dull pain • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC bi ...
Nervous - Lamont High
... this was cacao beans from the tree Cacao theobroma • Chocolate causes brain to produce natural opiates • Opiates produce feelings of euphoria, dull pain • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC bi ...
... this was cacao beans from the tree Cacao theobroma • Chocolate causes brain to produce natural opiates • Opiates produce feelings of euphoria, dull pain • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC bi ...
APP Ch_3 Outline
... 1. Neurons – Individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information. a. They are basic links that allow communication within the Nervous System. b. Soma – Cell Body of the neuron that contains the nucleus and much of cells normal organs. c. Dendrite – Parts of a Neu ...
... 1. Neurons – Individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information. a. They are basic links that allow communication within the Nervous System. b. Soma – Cell Body of the neuron that contains the nucleus and much of cells normal organs. c. Dendrite – Parts of a Neu ...
Chapter 2 Notes Packet (Part 1)
... ________________: Single long fiber extending from the cell body; carries outgoing messages to other neurons, muscles or glands All neurons only have one axon but at the end they branch off into many terminal branches o Nerves: group of axons bundled together like wires o ___________________: wh ...
... ________________: Single long fiber extending from the cell body; carries outgoing messages to other neurons, muscles or glands All neurons only have one axon but at the end they branch off into many terminal branches o Nerves: group of axons bundled together like wires o ___________________: wh ...
The nervous system
... be here. It is the true center for command and control in your body. The Frontal lobe is responsible for functions such as reasoning, problem solving, judgement, impulse control. This coupled with the fact that it's the last to develop when we are young adults, probably answers a lot of questions fo ...
... be here. It is the true center for command and control in your body. The Frontal lobe is responsible for functions such as reasoning, problem solving, judgement, impulse control. This coupled with the fact that it's the last to develop when we are young adults, probably answers a lot of questions fo ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind
... Each brain hemisphere is divided into four lobes that are separated by prominent fissures. These lobes are the frontal lobe (forehead), parietal lobe (top to rear head), occipital lobe (back head) and temporal lobe (side of head). ...
... Each brain hemisphere is divided into four lobes that are separated by prominent fissures. These lobes are the frontal lobe (forehead), parietal lobe (top to rear head), occipital lobe (back head) and temporal lobe (side of head). ...
neural migration - proffittscience
... The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary processes in the body using centers located in the medulla oblongata. The medulla oblongata ...
... The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary processes in the body using centers located in the medulla oblongata. The medulla oblongata ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.