The Nervous System - Marblehead High School
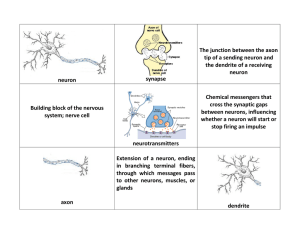
... Dendrites - branched extensions that carry impulses to the cell body Axon - long fiber ending at the terminals that carries impulses away from the cell body Myelin sheath - protective membrane surrounding the axon ...
... Dendrites - branched extensions that carry impulses to the cell body Axon - long fiber ending at the terminals that carries impulses away from the cell body Myelin sheath - protective membrane surrounding the axon ...
Central Nervous System
... • Primary motor cortex – Paralyzes voluntary muscles; reflexes intact – Contralateral effects ...
... • Primary motor cortex – Paralyzes voluntary muscles; reflexes intact – Contralateral effects ...
Brainfunction - Oakton Community College
... our brain PET Scans: measure amount of glucose being metabolized in different areas of the brain EEG: measure electric charges coming from surface of the brain ...
... our brain PET Scans: measure amount of glucose being metabolized in different areas of the brain EEG: measure electric charges coming from surface of the brain ...
Singularity
... • Only about 20 megabytes of compressed design information about the brain in the genome – A brain has ~ billion times more information than the genome that describes its design ...
... • Only about 20 megabytes of compressed design information about the brain in the genome – A brain has ~ billion times more information than the genome that describes its design ...
Neurotransmission
... 5 factors that influence teens choices about drugs? 4 classifications of drugs? ...
... 5 factors that influence teens choices about drugs? 4 classifications of drugs? ...
CNS=Central Nervous System
... The brain is not only responsible for language and movement but it is also responsible for determining one’s emotions and personality 8) What are the different lobes of the cerebral cortex and what are their functions? – Frontal: movement, thinking, problem-solving – Parietal: touch, pain and pressu ...
... The brain is not only responsible for language and movement but it is also responsible for determining one’s emotions and personality 8) What are the different lobes of the cerebral cortex and what are their functions? – Frontal: movement, thinking, problem-solving – Parietal: touch, pain and pressu ...
PsychSim5: Neural Messages 1 PsychSim 5: NEURAL MESSAGES
... In this activity you will take a tour of the human brain and explore the major brain regions to discover the functions of each region or area. Functional Specialization In terms of brain function, what is functional specialization? ...
... In this activity you will take a tour of the human brain and explore the major brain regions to discover the functions of each region or area. Functional Specialization In terms of brain function, what is functional specialization? ...
HW CH 5 PSY 2513 Submit your answers on canvas
... In a highly plastic cerebral cortex, a. the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than langua ...
... In a highly plastic cerebral cortex, a. the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than langua ...
Myers Module Four
... The autonomic nervous system controls our glands and the muscles of our internal organs, influencing such functions as glandular activity, heartbeat, and digestion. It may be consciously overridden. The sympathetic nervous system arouses and expends energy. Heartrate, blood pressure, digestion, bloo ...
... The autonomic nervous system controls our glands and the muscles of our internal organs, influencing such functions as glandular activity, heartbeat, and digestion. It may be consciously overridden. The sympathetic nervous system arouses and expends energy. Heartrate, blood pressure, digestion, bloo ...
Notes_2-4_bcsd Biologic basis of behavior
... -branch out from soma -receive input from other neurons through receptors on their surface -fatty coating surrounding the axon -insulation for the electrical impulses carried down the axon and speeds up the rate at which electrical information travels down the axon -small gaps between myelin -help s ...
... -branch out from soma -receive input from other neurons through receptors on their surface -fatty coating surrounding the axon -insulation for the electrical impulses carried down the axon and speeds up the rate at which electrical information travels down the axon -small gaps between myelin -help s ...
Nervous System
... PET scan on the left shows two areas of the brain (red and yellow) that become particularly active when volunteers read words on a video screen: the primary visual cortex and an additional part of the visual system, both in the back of the left hemisphere. Other brain regions become especially activ ...
... PET scan on the left shows two areas of the brain (red and yellow) that become particularly active when volunteers read words on a video screen: the primary visual cortex and an additional part of the visual system, both in the back of the left hemisphere. Other brain regions become especially activ ...
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending
... Large band of neural fibers connecting the two hemispheres of the brain and carrying messages between them. Plasticity ...
... Large band of neural fibers connecting the two hemispheres of the brain and carrying messages between them. Plasticity ...
Introduction to the brain and behaviour
... Cortical areas 1. Sensory cortex areas – receive and process information from the senses. 2. Motor cortex area – receives, processes and sends information about voluntary bodily movements. 3. Association cortex areas – integrate sensory, motor and other information and are involved in complex menta ...
... Cortical areas 1. Sensory cortex areas – receive and process information from the senses. 2. Motor cortex area – receives, processes and sends information about voluntary bodily movements. 3. Association cortex areas – integrate sensory, motor and other information and are involved in complex menta ...
Nervous System
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior
... carry information between other neurons only found in the brain and spinal cord ...
... carry information between other neurons only found in the brain and spinal cord ...
The Nervous System
... Complex beyond comprehension Although, human brains are more complex our nervous systems and those of animals operate in a similar fashion – advantage of this is experimentation ...
... Complex beyond comprehension Although, human brains are more complex our nervous systems and those of animals operate in a similar fashion – advantage of this is experimentation ...
Unit 3 - Mayfield City Schools
... -transmits a neural message down its length and then passes its information on to other cells -branch out from soma -receive input from other neurons through receptors on their surface -fatty coating surrounding the axon -insulation for the electrical impulses carried down the axon and speeds up the ...
... -transmits a neural message down its length and then passes its information on to other cells -branch out from soma -receive input from other neurons through receptors on their surface -fatty coating surrounding the axon -insulation for the electrical impulses carried down the axon and speeds up the ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint Notes
... People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...
... People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...
Document
... Complex beyond comprehension Although, human brains are more complex our nervous systems and those of animals operate in a similar fashion – advantage of this is experimentation ...
... Complex beyond comprehension Although, human brains are more complex our nervous systems and those of animals operate in a similar fashion – advantage of this is experimentation ...
Chapter 28- Nervous System
... ions that start new action potential or stops one • Neurotransmitter is then broken down or taken back into signaling cell ...
... ions that start new action potential or stops one • Neurotransmitter is then broken down or taken back into signaling cell ...
Nervous System
... Control center of the body that relays messages, and processes and analyzes information ...
... Control center of the body that relays messages, and processes and analyzes information ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... – include the visual areas, which receive visual information from the opposite visual field ...
... – include the visual areas, which receive visual information from the opposite visual field ...
NOTE
... • Amygdala –two almondshaped neural clusters that are components of the limbic system and are linked to emotion and fear ...
... • Amygdala –two almondshaped neural clusters that are components of the limbic system and are linked to emotion and fear ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.