Document
... Sensory transduction Transforming external physical forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
... Sensory transduction Transforming external physical forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
modality intensity duration location four attributes of a stimulus
... Electrical stimulation of both axons produces the same sensation, although localized to somewhat different places in the skin. Sharp stimuli (A, B) applied to nearby skin regions selectively activate the third ganglion cell, eliciting the sensation of pain. Electrical stimulation of that ganglion ce ...
... Electrical stimulation of both axons produces the same sensation, although localized to somewhat different places in the skin. Sharp stimuli (A, B) applied to nearby skin regions selectively activate the third ganglion cell, eliciting the sensation of pain. Electrical stimulation of that ganglion ce ...
VII. The Nervous System
... a) An action potential arriving at the synaptic terminal at the end of an axon causes Ca+2 to rush through voltage sensitive channels b) The sudden in rush of Ca+2 causes synaptic vesicles which contain neurotransmitters to fuse with the presynaptic membrane releasing neurotransmitters into the syna ...
... a) An action potential arriving at the synaptic terminal at the end of an axon causes Ca+2 to rush through voltage sensitive channels b) The sudden in rush of Ca+2 causes synaptic vesicles which contain neurotransmitters to fuse with the presynaptic membrane releasing neurotransmitters into the syna ...
Ch. 48 - 49
... K+ channels still OPEN K+ still rushes out of the neuron (Hyperpolarizing the inside - - - - - -) ...
... K+ channels still OPEN K+ still rushes out of the neuron (Hyperpolarizing the inside - - - - - -) ...
PRINCIPLES OF SENSORY TRANSDUCTION
... the somatosensory system. Two dorsal root ganglion (DRG) cells (blue) send peripheral axons to be part of a touch receptor, whereas a third cell (red) is a pain receptor. By activating the neurons of touch receptors receptors, direct touching of the skin or electrical stimulation of an appropriate a ...
... the somatosensory system. Two dorsal root ganglion (DRG) cells (blue) send peripheral axons to be part of a touch receptor, whereas a third cell (red) is a pain receptor. By activating the neurons of touch receptors receptors, direct touching of the skin or electrical stimulation of an appropriate a ...
MS Word Version
... autonomic nervous system act indirectly. • Norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and serotonin, another central nervous system neurotransmitter, all produce state changes in the central nervous system. One important example is the change from the sleep state, to wakefulness, to attentive arousal. • Theorie ...
... autonomic nervous system act indirectly. • Norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and serotonin, another central nervous system neurotransmitter, all produce state changes in the central nervous system. One important example is the change from the sleep state, to wakefulness, to attentive arousal. • Theorie ...
31.1 The Neuron Functions of the Nervous System and external
... addictive substances affect brain synapses. Many drugs cause an increase in the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine. The brain reacts to high dopamine levels by reducing the number of receptors. With fewer dopamine receptors available, larger amounts of drugs are required to produce a high. Thi ...
... addictive substances affect brain synapses. Many drugs cause an increase in the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine. The brain reacts to high dopamine levels by reducing the number of receptors. With fewer dopamine receptors available, larger amounts of drugs are required to produce a high. Thi ...
Taste and Smell
... • Specialized to detect chemicals dissolved in a fluid • The fluid may be saliva, mucous, or blood plasma • Rely on receptors that interact with specific molecules to generate an action potential • Receptors are integrated with two or more tissue types making them fit the definition of “organ” ...
... • Specialized to detect chemicals dissolved in a fluid • The fluid may be saliva, mucous, or blood plasma • Rely on receptors that interact with specific molecules to generate an action potential • Receptors are integrated with two or more tissue types making them fit the definition of “organ” ...
Circulatory System Directs blood from the heart to the rest of the
... 1. Action Potentials describe how a nerve impulse is generated and conducted throughout the body 2. The nerve cell is stimulated by an electric current, change in pH, or a pinch, causing an action potential 3. Upon stimulation, Sodium gates in the nerve cell membrane open and sodium rushes into the ...
... 1. Action Potentials describe how a nerve impulse is generated and conducted throughout the body 2. The nerve cell is stimulated by an electric current, change in pH, or a pinch, causing an action potential 3. Upon stimulation, Sodium gates in the nerve cell membrane open and sodium rushes into the ...
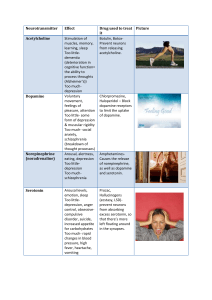
Neurotransmitter - Pamoja Education Blogs
... Stimulation of muscles, memory, learning, sleep Too littledementia (deterioration in cognitive function= the ability to process throughts (Alzheimer’s)) Too muchdepression Voluntary movement, feelings of pleasure, attention Too little- some form of depression & muscular rigidity Too much- social anx ...
... Stimulation of muscles, memory, learning, sleep Too littledementia (deterioration in cognitive function= the ability to process throughts (Alzheimer’s)) Too muchdepression Voluntary movement, feelings of pleasure, attention Too little- some form of depression & muscular rigidity Too much- social anx ...
Describe how action potentials are generated
... and from CNS; most common type of nerve • Ganglia: a collection of neuron cell bodies associated with nerves in the PNS ...
... and from CNS; most common type of nerve • Ganglia: a collection of neuron cell bodies associated with nerves in the PNS ...
Module Two
... The neurotransmitters are released from the vesicles and then attach to receptors located on the postsynaptic neuron. ...
... The neurotransmitters are released from the vesicles and then attach to receptors located on the postsynaptic neuron. ...
Describe how action potentials are generated and
... and from CNS; most common type of nerve • Ganglia: a collection of neuron cell bodies associated with nerves in the PNS ...
... and from CNS; most common type of nerve • Ganglia: a collection of neuron cell bodies associated with nerves in the PNS ...
Physio study guide unit 2
... What two types of receptors can ACh bind to? What actions result from the binding of ACh at these two different receptors? How many ACh bind to an ACh receptor? What ion will flow through? What type of event would this trigger on a post-synaptic cell? What are Ionotropic receptors? That is, how do t ...
... What two types of receptors can ACh bind to? What actions result from the binding of ACh at these two different receptors? How many ACh bind to an ACh receptor? What ion will flow through? What type of event would this trigger on a post-synaptic cell? What are Ionotropic receptors? That is, how do t ...
Nervous Systems
... The right and left halves of the brain are connected by the corpus callosum. The left side of the brain is associated with language, mathematical abilities, and learning. The right side of the brain is associated with spatial, intuitive, musical, and artistic abilities. ...
... The right and left halves of the brain are connected by the corpus callosum. The left side of the brain is associated with language, mathematical abilities, and learning. The right side of the brain is associated with spatial, intuitive, musical, and artistic abilities. ...
The Nervous System
... transfer messages (impulses)around the body by electrical energy • sensory neurons –collect information and send to CNS • motor neurons – respond to information sent from CNS ...
... transfer messages (impulses)around the body by electrical energy • sensory neurons –collect information and send to CNS • motor neurons – respond to information sent from CNS ...
CONTENTS by guest on September 24, 2016 Downloaded from
... (10:1 I -6997/88/4004-Oiii$02.00/0 I’IIARMACOL.oCICAL Copyright c’ 1988 ...
... (10:1 I -6997/88/4004-Oiii$02.00/0 I’IIARMACOL.oCICAL Copyright c’ 1988 ...
Biology 201-Worksheet on Autonomic Nervous System
... 17. List 3 groups of ANS fibers that are cholinergic. ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ __________________________________________________ 18. Fibers that release NE at their synapses are called: ______________________________________. 19. Whic ...
... 17. List 3 groups of ANS fibers that are cholinergic. ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ __________________________________________________ 18. Fibers that release NE at their synapses are called: ______________________________________. 19. Whic ...
Module 3
... contributes to motor control, vision, and many other cortical functions. It also regulates anxiety. Some drugs that increase the level of GABA in the brain are used to treat epilepsy and to calm the trembling of people ...
... contributes to motor control, vision, and many other cortical functions. It also regulates anxiety. Some drugs that increase the level of GABA in the brain are used to treat epilepsy and to calm the trembling of people ...
Chapter 16A
... • Many types of inputs can activate the RAS -- pain, light, noise, muscle activity, touch • When the RAS is activated, the cerebral cortex is also activated and arousal occurs • The result is a state of wakefulness called consciousness ...
... • Many types of inputs can activate the RAS -- pain, light, noise, muscle activity, touch • When the RAS is activated, the cerebral cortex is also activated and arousal occurs • The result is a state of wakefulness called consciousness ...
chapter the nervous system and the effects of drugs
... The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps between them, called synapses, which an electri ...
... The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps between them, called synapses, which an electri ...
A17 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... - no matter where particular sensory pathway is stimulated along its course to cortex, conscious sensation location is referred to location of receptor. e.g. neurosurgical procedures on conscious patients - when cortical receiving area for impulses from left hand is stimulated, patient reports sensa ...
... - no matter where particular sensory pathway is stimulated along its course to cortex, conscious sensation location is referred to location of receptor. e.g. neurosurgical procedures on conscious patients - when cortical receiving area for impulses from left hand is stimulated, patient reports sensa ...
Nervous System 1
... an impulse in the next neuron . • Only one end of a neuron can make this chemical. So synapses make sure an impulse can only travel in one direction. • Synapses have two other functions: A Resistor- it may take a number of impulses before enough chemical is made to start the impulse in the next ne ...
... an impulse in the next neuron . • Only one end of a neuron can make this chemical. So synapses make sure an impulse can only travel in one direction. • Synapses have two other functions: A Resistor- it may take a number of impulses before enough chemical is made to start the impulse in the next ne ...
APP Ch_3 Outline
... 1. Neurons – Individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information. a. They are basic links that allow communication within the Nervous System. b. Soma – Cell Body of the neuron that contains the nucleus and much of cells normal organs. c. Dendrite – Parts of a Neu ...
... 1. Neurons – Individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information. a. They are basic links that allow communication within the Nervous System. b. Soma – Cell Body of the neuron that contains the nucleus and much of cells normal organs. c. Dendrite – Parts of a Neu ...
The Nervous System
... The Synaptic Knob • Is expanded area of axon • Contains synaptic vesicles of neurotransmitters – Chemical messengers – Released at presynaptic membrane – Affect receptors of postsynaptic membrane ...
... The Synaptic Knob • Is expanded area of axon • Contains synaptic vesicles of neurotransmitters – Chemical messengers – Released at presynaptic membrane – Affect receptors of postsynaptic membrane ...