32. Sensory organs. organ of smell and taste
... • Between the papillae are the taste buds, which provide the sense of taste. ...
... • Between the papillae are the taste buds, which provide the sense of taste. ...
The Neuron: The Basic Unit of Communication Neuron: Basic
... How do these drugs affect neural communication and behavior (page 178, 179)? Many drugs, especially those that affect moods or behavior, work by interfering with normal functioning of neurotransmitters in the synapse. How this occurs depends on the drug, such as the following: 1. Drugs can mimic spe ...
... How do these drugs affect neural communication and behavior (page 178, 179)? Many drugs, especially those that affect moods or behavior, work by interfering with normal functioning of neurotransmitters in the synapse. How this occurs depends on the drug, such as the following: 1. Drugs can mimic spe ...
Chapter 6 - Sensory - Austin Community College
... Voltage-regulated calcium channels in the axon termincal open and allow Ca2+ to enter the axon Ca2+ inside the axon terminal causes some of the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the axon membrane and release ACh into the synaptic cleft (exocytosis) The synaptic end bulbs releases acetylcholine from the ...
... Voltage-regulated calcium channels in the axon termincal open and allow Ca2+ to enter the axon Ca2+ inside the axon terminal causes some of the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the axon membrane and release ACh into the synaptic cleft (exocytosis) The synaptic end bulbs releases acetylcholine from the ...
Lewy Body Diseases
... nucleus basalis more severely involved in DLB than in AD its cholinergic neurons innervate cortex and are normally involved in sleep, dreams and attention loss of those neurons produces visual hallucinations, similar to what happens with anesthetics (eg. scopolamine) that block ACh receptors ...
... nucleus basalis more severely involved in DLB than in AD its cholinergic neurons innervate cortex and are normally involved in sleep, dreams and attention loss of those neurons produces visual hallucinations, similar to what happens with anesthetics (eg. scopolamine) that block ACh receptors ...
Myers Module Four
... Each consists of a cell body and branching fibres. The dendrites are the bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body. For the biology students: dendrites are complex microtubules, proof that neurons are specializations from ...
... Each consists of a cell body and branching fibres. The dendrites are the bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body. For the biology students: dendrites are complex microtubules, proof that neurons are specializations from ...
Nervous System notes
... b. functional- based on the direction in which they transmit nerve impulses - sensory (afferent) – transmit form receptors in skin, sensory organs muscles, joints, and viscera to the brain and spinal cord - motor (efferent) – convey impulses from brain and spinal cord to effectors which may be muscl ...
... b. functional- based on the direction in which they transmit nerve impulses - sensory (afferent) – transmit form receptors in skin, sensory organs muscles, joints, and viscera to the brain and spinal cord - motor (efferent) – convey impulses from brain and spinal cord to effectors which may be muscl ...
Nervous System
... world: sights, sounds, smells, feel, etc … • Taking in all the stimuli and reacting to it • The brain is generally (very, very generally) divided into 3 main sections – Cerebrum – Cerebellum – Medulla ...
... world: sights, sounds, smells, feel, etc … • Taking in all the stimuli and reacting to it • The brain is generally (very, very generally) divided into 3 main sections – Cerebrum – Cerebellum – Medulla ...
Nervous & Endocrine Systems
... 2. Receptors in your ear pick the sound of a ringing phone 5. Receptors trigger nerve impulses in sensory neurons 1. The nerve impulses pass to interneurons in the brain. 6. Your brain interprets the impulses from many interneurons and you realize the phone is ringing. Your brain also decides that y ...
... 2. Receptors in your ear pick the sound of a ringing phone 5. Receptors trigger nerve impulses in sensory neurons 1. The nerve impulses pass to interneurons in the brain. 6. Your brain interprets the impulses from many interneurons and you realize the phone is ringing. Your brain also decides that y ...
PNS Study Guide
... 6. What are the two functional classifications of the PNS? Describe the function of each (flow chart). 7. What are the 2 types of motor nerves? How are they different? 8. What are the 2 types of autonomic nerves? Make sure you know when they are used. 9. Be able to draw and describe a reflex arc. 10 ...
... 6. What are the two functional classifications of the PNS? Describe the function of each (flow chart). 7. What are the 2 types of motor nerves? How are they different? 8. What are the 2 types of autonomic nerves? Make sure you know when they are used. 9. Be able to draw and describe a reflex arc. 10 ...
Antihistamines
... Histamine Signal involved in local immune response, also a neurotransmitter synthesized by the decarboxylation of histidine Either stored or quickly inactivated by histamine-Nmethyltransferase and diamine oxidase Release of histamine from mast cells is stimulated by IgE antibodies which res ...
... Histamine Signal involved in local immune response, also a neurotransmitter synthesized by the decarboxylation of histidine Either stored or quickly inactivated by histamine-Nmethyltransferase and diamine oxidase Release of histamine from mast cells is stimulated by IgE antibodies which res ...
Nervous Systems
... • Have gated ion channels that allow cell to change its membrane potential in response to stimuli ...
... • Have gated ion channels that allow cell to change its membrane potential in response to stimuli ...
Optogenetics
... neuromodulation therapies Parkinson's disease. Deep brain stimulation devices have been efficacious in correcting movement disorders in patients with advanced stage Parkinson's disease. High frequency stimulation is thought to suppress firing of neurons in the subthalamic nucleus (STN). Optical neur ...
... neuromodulation therapies Parkinson's disease. Deep brain stimulation devices have been efficacious in correcting movement disorders in patients with advanced stage Parkinson's disease. High frequency stimulation is thought to suppress firing of neurons in the subthalamic nucleus (STN). Optical neur ...
11/5/2014 Cannabinoids Activate CB Receptors
... CB1 and CB2 subtypes identified to‐date; potentially additional receptors exist Involved in appetite, mood, pain sensation and memory Present on cells in brain that repress neurotransmitter release, as well as peripheral cells ...
... CB1 and CB2 subtypes identified to‐date; potentially additional receptors exist Involved in appetite, mood, pain sensation and memory Present on cells in brain that repress neurotransmitter release, as well as peripheral cells ...
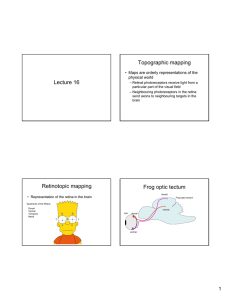
Lecture 16 Topographic mapping Retinotopic mapping Frog optic
... posterior • Nasal axons project more anterior! ...
... posterior • Nasal axons project more anterior! ...
This Week in The Journal - The Journal of Neuroscience
... The glutamatergic subthalamic nucleus (STN) exerts control over motor output through nuclei of the basal ganglia. High-frequency electrical stimuli in the STN effectively alleviate motor symptoms in movement disorders, and cholinergic stimulation boosts this effect. To gain knowledge about the mecha ...
... The glutamatergic subthalamic nucleus (STN) exerts control over motor output through nuclei of the basal ganglia. High-frequency electrical stimuli in the STN effectively alleviate motor symptoms in movement disorders, and cholinergic stimulation boosts this effect. To gain knowledge about the mecha ...
Feeding Pathways
... • The ob/ob mouse: do not have circulating leptin levels, but this does not mean that they are insensitive to leptin – In fact, they are hypersensitized to exogenously administered leptin. WHY? ...
... • The ob/ob mouse: do not have circulating leptin levels, but this does not mean that they are insensitive to leptin – In fact, they are hypersensitized to exogenously administered leptin. WHY? ...
Notes – Neurons and the nervous system
... strong the signal was. No matter how excitatory a signal is, the neuron will always fire with the same intensity. ...
... strong the signal was. No matter how excitatory a signal is, the neuron will always fire with the same intensity. ...
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
... Room temperature does not stay at set point, it oscillates around the set point; this is the same for homeostatic control The body is said to be in homeostasis when its cellular needs are adequate ...
... Room temperature does not stay at set point, it oscillates around the set point; this is the same for homeostatic control The body is said to be in homeostasis when its cellular needs are adequate ...
BIO 132
... of motor responses by environmental stimuli. The VTA seems to be involved in “rewarding” behavior. Note this is not the same as feeling pleasure. The VTA pairs behavior or sensation with ...
... of motor responses by environmental stimuli. The VTA seems to be involved in “rewarding” behavior. Note this is not the same as feeling pleasure. The VTA pairs behavior or sensation with ...
The Nervous System
... synapse. This junction can be with another neuron, muscles or glands. All receiving cells have receptors. Chemicals, called neurotransmitters, are released into the synapse to transmit the impulse from one neuron to the next, or to the receptor tissue. ...
... synapse. This junction can be with another neuron, muscles or glands. All receiving cells have receptors. Chemicals, called neurotransmitters, are released into the synapse to transmit the impulse from one neuron to the next, or to the receptor tissue. ...
BHS 150.1 – Biochemistry II Date: 2/8/2013, 2sndhalf Notetaker: Kim
... 7. In the retina, glutamate release onto the bipolar on cells will result in a: cGMP sensitive-Na+ channel closing 8. Chloinergic agonists lower IOP by contracting the ciliary body muscle, which stretches the TM causing channels to: Open and increase outflow 9. What is the function of connexins in t ...
... 7. In the retina, glutamate release onto the bipolar on cells will result in a: cGMP sensitive-Na+ channel closing 8. Chloinergic agonists lower IOP by contracting the ciliary body muscle, which stretches the TM causing channels to: Open and increase outflow 9. What is the function of connexins in t ...
Tactile and Body Senses
... tremendous psychological ramifications in areas like child development, persuasion, healing, and reducing anxiety and tension. ...
... tremendous psychological ramifications in areas like child development, persuasion, healing, and reducing anxiety and tension. ...
Nerve Impulses - manorlakesscience
... change in the charge across the axon membrane. A nerve impulse is a wave of electrical change (an action potential) that passes rapidly along an axon. After the nerve impulse has been transmitted – the distribution of ions across the cell membrane is restored. ...
... change in the charge across the axon membrane. A nerve impulse is a wave of electrical change (an action potential) that passes rapidly along an axon. After the nerve impulse has been transmitted – the distribution of ions across the cell membrane is restored. ...