Motor “Binding:” Do Functional Assemblies in Primary Motor Cortex
... to the brain stem and spinal cord to express neural computations related to sensation, perception, and thought for voluntary action. Functional and anatomical features of M1 make it a particularly likely neocortical candidate site for implementation of motor binding. The intrinsic organization of M1 ...
... to the brain stem and spinal cord to express neural computations related to sensation, perception, and thought for voluntary action. Functional and anatomical features of M1 make it a particularly likely neocortical candidate site for implementation of motor binding. The intrinsic organization of M1 ...
Chapter 48 Worksheet
... b. The concentration of sodium is much higher inside the cell than outside. c. The sodium-potassium pump plays a role in maintaining the resting potential. d. Inside the cell, the concentration of potassium is much higher than the concentration of sodium. e. All of these are true statements. 3. Whic ...
... b. The concentration of sodium is much higher inside the cell than outside. c. The sodium-potassium pump plays a role in maintaining the resting potential. d. Inside the cell, the concentration of potassium is much higher than the concentration of sodium. e. All of these are true statements. 3. Whic ...
The Nervous System
... emotion reflects its activity. Its cells communicate by electrical and chemical signals, which are rapid and specific, and usually cause almost immediate responses. ...
... emotion reflects its activity. Its cells communicate by electrical and chemical signals, which are rapid and specific, and usually cause almost immediate responses. ...
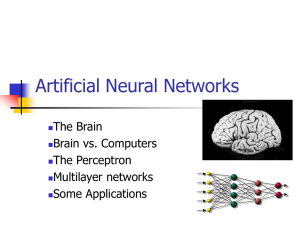
Part 7.2 Neural Networks
... • Each hidden or output neuron has weighted input connections from each of the units in the preceding layer. • The unit performs a weighted sum of its inputs, and subtracts its threshold value, to give its activation level. • Activation level is passed through a sigmoid activation function to determ ...
... • Each hidden or output neuron has weighted input connections from each of the units in the preceding layer. • The unit performs a weighted sum of its inputs, and subtracts its threshold value, to give its activation level. • Activation level is passed through a sigmoid activation function to determ ...
nerve
... over a 2cm rat sciatic nerve gap. o In vivo the graft was penetrated by Schwann cells fibroblasts, perineural and endothelial cells, axon regenerated within 3 weeks. Vein grafts to bridge sensory nerve lesions in the hand but inferior to muscle. Small intestinal mucosa, stripped of its mucosal a ...
... over a 2cm rat sciatic nerve gap. o In vivo the graft was penetrated by Schwann cells fibroblasts, perineural and endothelial cells, axon regenerated within 3 weeks. Vein grafts to bridge sensory nerve lesions in the hand but inferior to muscle. Small intestinal mucosa, stripped of its mucosal a ...
Nervous System - Science
... • Somatic NS – Sensory nerves – Motor nerves – Messages between brain and body – CONTROLS VOLUNTARY MUSCLES ...
... • Somatic NS – Sensory nerves – Motor nerves – Messages between brain and body – CONTROLS VOLUNTARY MUSCLES ...
ANATOMY NEURO REVALIDA QUESTIONS
... Arrange the following structures from top to bottom (or outermost to innermost): cerebral cortex, medulla, skull, dura mater, midbrain What are the structures included in the brain stem? What are their functions? You have learned a couple of prefixes/suffixes that will help you understand nursing te ...
... Arrange the following structures from top to bottom (or outermost to innermost): cerebral cortex, medulla, skull, dura mater, midbrain What are the structures included in the brain stem? What are their functions? You have learned a couple of prefixes/suffixes that will help you understand nursing te ...
Chapter 6 Notes
... 1. Shows the absence or presence state of activity in an area of the brain through radioactive dye iii. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) 1. Ability to study both activity and brain structure 2. Uses both CAT and PET scanning capabilities iv. fMRI (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging) 1. New, can ...
... 1. Shows the absence or presence state of activity in an area of the brain through radioactive dye iii. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) 1. Ability to study both activity and brain structure 2. Uses both CAT and PET scanning capabilities iv. fMRI (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging) 1. New, can ...
Unit 3 Neuroscience and Behavior CHAPTER PREVIEW Our
... the autonomic nervous system, which controls the glands and muscles of our internal organs. Hormones released by endocrine glands affect other tissues, including the brain. The most influential endocrine gland, the pituitary gland, releases hormones that influence growth, and its secretions also inf ...
... the autonomic nervous system, which controls the glands and muscles of our internal organs. Hormones released by endocrine glands affect other tissues, including the brain. The most influential endocrine gland, the pituitary gland, releases hormones that influence growth, and its secretions also inf ...
Topic Option A Neurobio
... 12. Application: Events such as strokes may 3. Neurons are initially produced by differentiation promote reorganization of brain function. in the neural tube. 13. Skill: Annotation of a diagram of embryonic 4. Immature neurons migrate to a final location. tissues in Xenopus, used as an animal model, ...
... 12. Application: Events such as strokes may 3. Neurons are initially produced by differentiation promote reorganization of brain function. in the neural tube. 13. Skill: Annotation of a diagram of embryonic 4. Immature neurons migrate to a final location. tissues in Xenopus, used as an animal model, ...
Biology 30 NERVOUS SYSTEM - Salisbury Composite High School
... 1. Sensory receptor 2. Sensory neuron ...
... 1. Sensory receptor 2. Sensory neuron ...
To allow an immediate response to stimuli in the
... Structures associated with Vision: The photoreceptors: two types – Rods which detect low intensity light in degrees of “black and white”, and Cones which detect color, but only in high intensity light The Retina: The back wall of the eyeball, which contains all the photoreceptors The fovea centralis ...
... Structures associated with Vision: The photoreceptors: two types – Rods which detect low intensity light in degrees of “black and white”, and Cones which detect color, but only in high intensity light The Retina: The back wall of the eyeball, which contains all the photoreceptors The fovea centralis ...
The Nervous System
... Cells of the Nervous System Neurons/nerve cells: receive stimuli and transmit action potentials (send and receive information) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and two extensions Dendrites: shorter, more numerous, and receives information (Action Potentials) Axons: single, long “fiber” whic ...
... Cells of the Nervous System Neurons/nerve cells: receive stimuli and transmit action potentials (send and receive information) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and two extensions Dendrites: shorter, more numerous, and receives information (Action Potentials) Axons: single, long “fiber” whic ...
Neural Pathways
... • where the axon of one neuron meets the dendrites of another (empty space) 1. when an impulse reaches the synaptic -of the knob, neurotransmitters are released ...
... • where the axon of one neuron meets the dendrites of another (empty space) 1. when an impulse reaches the synaptic -of the knob, neurotransmitters are released ...
Development of the spinal cord
... hemispheres of the brain. Still others—those of the internal capsule—will connect the cortical white matter to the brain stem, generally by way of the thalamus. • For example, the axons arising from the motor cortex will pass through the internal capsule to connect to the motor neurons in the spinal ...
... hemispheres of the brain. Still others—those of the internal capsule—will connect the cortical white matter to the brain stem, generally by way of the thalamus. • For example, the axons arising from the motor cortex will pass through the internal capsule to connect to the motor neurons in the spinal ...
Copy of Development of the spinal cord
... hemispheres of the brain. Still others—those of the internal capsule—will connect the cortical white matter to the brain stem, generally by way of the thalamus. • For example, the axons arising from the motor cortex will pass through the internal capsule to connect to the motor neurons in the spinal ...
... hemispheres of the brain. Still others—those of the internal capsule—will connect the cortical white matter to the brain stem, generally by way of the thalamus. • For example, the axons arising from the motor cortex will pass through the internal capsule to connect to the motor neurons in the spinal ...
Neurons and the General Layout of the Nervous System - U
... • the medulla; composed of major ascending and descending tracts and a network of small nuclei involved in sleep, attention, muscle tone, cardiac function, and respiration • the core network of nuclei is the reticular formation; it also composes the core of the hindbrain and midbrain; it is thought ...
... • the medulla; composed of major ascending and descending tracts and a network of small nuclei involved in sleep, attention, muscle tone, cardiac function, and respiration • the core network of nuclei is the reticular formation; it also composes the core of the hindbrain and midbrain; it is thought ...
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body - Nicole
... Take a moment on your computer to research one part of the brain and the role it plays in controlling your body or thought processes. ...
... Take a moment on your computer to research one part of the brain and the role it plays in controlling your body or thought processes. ...
Science - edl.io
... messages to the brain and generally connect to the brain through the spinal cord inside your backbone. Motor nerves carry messages back from the brain to all the muscles and glands in your body. So how do they pass along messages? Through the marvels of chemistry and a kind of electricity! Neurons a ...
... messages to the brain and generally connect to the brain through the spinal cord inside your backbone. Motor nerves carry messages back from the brain to all the muscles and glands in your body. So how do they pass along messages? Through the marvels of chemistry and a kind of electricity! Neurons a ...
GTC Flyer - Graduate Training Centre of Neuroscience
... research-oriented training in a wide spectrum of computational neuroscience topics, such as coding principles in sensory periphery and their clinical application; population coding in the early sensory cortex; perceptual inference mechanisms; and multi-sensory integration processes. Other fields of ...
... research-oriented training in a wide spectrum of computational neuroscience topics, such as coding principles in sensory periphery and their clinical application; population coding in the early sensory cortex; perceptual inference mechanisms; and multi-sensory integration processes. Other fields of ...