HUSC 141 - Community College of Baltimore County
... G. Psychotherapeutic drugs, including over-the-counter drugs and dietary supplements H. Performance-enhancing drugs History of psychoactive substances Drug control policies and trends in legislation The nervous system and neurotransmission Neurochemical effects of each major substance category A. Ph ...
... G. Psychotherapeutic drugs, including over-the-counter drugs and dietary supplements H. Performance-enhancing drugs History of psychoactive substances Drug control policies and trends in legislation The nervous system and neurotransmission Neurochemical effects of each major substance category A. Ph ...
MDA Ch 30&37 Study Guide
... A drug is identified by three names • Chemical name: which is the chemical formula of a drug • Generic name: which may be used by any company; acetaminophen is an example of a generic name • Brand name, or trade name: which is controlled by business firm as a registered trademark; such as Tylenol i ...
... A drug is identified by three names • Chemical name: which is the chemical formula of a drug • Generic name: which may be used by any company; acetaminophen is an example of a generic name • Brand name, or trade name: which is controlled by business firm as a registered trademark; such as Tylenol i ...
Forensic Science - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... 1. anxiety 2. convulsions 3. stomach cramps 4. vomiting 76- The use of which drug will NOT lead to physical dependence? 1. alcohol 2.barbiturates 3. cocaine ...
... 1. anxiety 2. convulsions 3. stomach cramps 4. vomiting 76- The use of which drug will NOT lead to physical dependence? 1. alcohol 2.barbiturates 3. cocaine ...
A Brief Overview of Drugs of Abuse (pages 1-17) Read Pages 1
... The addictive process involves use, misuse, abuse and dependence. Regardless of the chemical, the process is the same. After use of a psychoactive chemical, the central nervous system is affected and causes physiological and mental changes to take place. It is the mental changes that produce the des ...
... The addictive process involves use, misuse, abuse and dependence. Regardless of the chemical, the process is the same. After use of a psychoactive chemical, the central nervous system is affected and causes physiological and mental changes to take place. It is the mental changes that produce the des ...
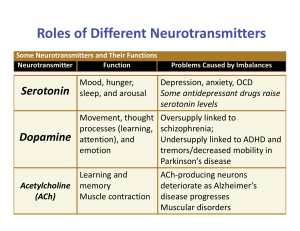
Roles of Different Neurotransmitters
... neurotransmitter; the brain, producing migraines or involved in memory seizures; this is why some people avoid MSG (monosodium glutamate) in food ...
... neurotransmitter; the brain, producing migraines or involved in memory seizures; this is why some people avoid MSG (monosodium glutamate) in food ...
Cultural, Legal, and Ethical Considerations
... Must be kept locked and signed out only by registered personal. On the wards need key or code to gain access to medications – narcotics for pain relief. ...
... Must be kept locked and signed out only by registered personal. On the wards need key or code to gain access to medications – narcotics for pain relief. ...
CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
... self-stim and to have cocaine delivered to them • possibly a final common pathway for positive stimulation and reward; this pathway is dopamine-rich; • most drugs produce changes in this system, but “broccoli” (food) does not produce dramatic changes, presumably because it does not have the intensit ...
... self-stim and to have cocaine delivered to them • possibly a final common pathway for positive stimulation and reward; this pathway is dopamine-rich; • most drugs produce changes in this system, but “broccoli” (food) does not produce dramatic changes, presumably because it does not have the intensit ...
Grade 2008-2010 final exam-B
... 4.Drug resistance is the phenomenon that susceptibility of pathogenic microorganisms to drugs becomes lower or even loses after the microorganisms contact with drugs for many times. As a result, the antimicrobial effect of the drugs will decrease or even disappear. 5. Antimicrobial activity:is the a ...
... 4.Drug resistance is the phenomenon that susceptibility of pathogenic microorganisms to drugs becomes lower or even loses after the microorganisms contact with drugs for many times. As a result, the antimicrobial effect of the drugs will decrease or even disappear. 5. Antimicrobial activity:is the a ...
Antimicrobial Agents (General considerations)
... due to decreased metabolism. (Least with Lome, Levo, ...
... due to decreased metabolism. (Least with Lome, Levo, ...
Supplementary Materials and Methods
... without an approved NDA. We also considered as a new drug approval the first approval of a biologics license application (BLA). We excluded drugs distributed “over the counter” and duplicate records of the same drugs by using the application number as a unique identifier. We used the Anatomical Ther ...
... without an approved NDA. We also considered as a new drug approval the first approval of a biologics license application (BLA). We excluded drugs distributed “over the counter” and duplicate records of the same drugs by using the application number as a unique identifier. We used the Anatomical Ther ...
Final Exam Key spring 2010
... 2 things: exclusivity and profit motive drive innovation. In addition, to get a patent, you have to tell how something is made so it disseminates information (5) 13. What is informed consent? Why is it important? a document that ensures that the subject of a clinical trial is well-informed as to wha ...
... 2 things: exclusivity and profit motive drive innovation. In addition, to get a patent, you have to tell how something is made so it disseminates information (5) 13. What is informed consent? Why is it important? a document that ensures that the subject of a clinical trial is well-informed as to wha ...
The New York Times
... leukemia are now routinely given genetic tests to determine their individual response to a medication. ''We've seen it save lives here,'' she said. ''That's made me a believer.'' When hundreds of patients are given a drug, she continued, ''some will get no benefit, others will have terrible side eff ...
... leukemia are now routinely given genetic tests to determine their individual response to a medication. ''We've seen it save lives here,'' she said. ''That's made me a believer.'' When hundreds of patients are given a drug, she continued, ''some will get no benefit, others will have terrible side eff ...
biochem mcq - Pass the FracP
... poor oral absorption, high protein binding good oral absorption, high first pass metabolism, with renal excretion of metabolites good oral absorption, low first-pass metabolism with high tissue distribution poor oral absorption, high first-pass metabolism, with renal excretion ...
... poor oral absorption, high protein binding good oral absorption, high first pass metabolism, with renal excretion of metabolites good oral absorption, low first-pass metabolism with high tissue distribution poor oral absorption, high first-pass metabolism, with renal excretion ...
N204
... as response physiologically to med. Culturally competent care involves knowledge not only of pt’s beliefs and values about health care and illness, but also of their responses to treatment ...
... as response physiologically to med. Culturally competent care involves knowledge not only of pt’s beliefs and values about health care and illness, but also of their responses to treatment ...
8th Grade Illegal Drugs
... Codeine: Pain killer produced from Morphine. Used in some cough syrups and pain ...
... Codeine: Pain killer produced from Morphine. Used in some cough syrups and pain ...
H. Sodium Channel Blockers
... A. Absorption 1. Time the drug enters the body until it gets into the bloodstream 2. Affected by dosage form, route, GI motility B. Distribution 1. Drug distributed to site of action 2. Protein binding 3. Blood brain barrier C. Metabolism 1. Liver 2. Hepatic First Pass Effect 3. Infants and Elderly ...
... A. Absorption 1. Time the drug enters the body until it gets into the bloodstream 2. Affected by dosage form, route, GI motility B. Distribution 1. Drug distributed to site of action 2. Protein binding 3. Blood brain barrier C. Metabolism 1. Liver 2. Hepatic First Pass Effect 3. Infants and Elderly ...
Drug therapy - Beauchamp Psychology
... replaced with a placebo relapsed, compared to 19% of those who remained on the drug. • This therefore shows the therapeutic effect of traditional antipsychotics, although…. ...
... replaced with a placebo relapsed, compared to 19% of those who remained on the drug. • This therefore shows the therapeutic effect of traditional antipsychotics, although…. ...
Title goes in here - Beauchamp Psychology
... replaced with a placebo relapsed, compared to 19% of those who remained on the drug. • This therefore shows the therapeutic effect of traditional antipsychotics, although…. ...
... replaced with a placebo relapsed, compared to 19% of those who remained on the drug. • This therefore shows the therapeutic effect of traditional antipsychotics, although…. ...
Unit XIII: Treatment of Abnormal Behavior
... Antianxiety Drugs • Antianxiety drugs depress the central nervous system, and reduce anxiety and tension by elevating the levels of neurotransmitters like ...
... Antianxiety Drugs • Antianxiety drugs depress the central nervous system, and reduce anxiety and tension by elevating the levels of neurotransmitters like ...
Significant Drug Interactions with Tuberculosis Medications
... Isoniazid-Case Presentation › CN is a 75yo WF who is taking Coumadin. She is started on Isoniazid at the local health department. When she started therapy, she was told that she needs to have her INR checked regularly. She calls the TB clinic to report that her check up showed her INR had increased ...
... Isoniazid-Case Presentation › CN is a 75yo WF who is taking Coumadin. She is started on Isoniazid at the local health department. When she started therapy, she was told that she needs to have her INR checked regularly. She calls the TB clinic to report that her check up showed her INR had increased ...
04 GENERAL PHARMACOLOGY
... Parenteral administration is the suitable route to provide rapid effect IV is used in emergency and provide high ...
... Parenteral administration is the suitable route to provide rapid effect IV is used in emergency and provide high ...
study on identification and assessment of drug interactions in
... function, such as cirrhosis or congestive heart failure ,are likely to decrease the rate of drug metabolism.CytochromeP450 enzymes are polymorphic, there exist ethnic differences in hepatic enzymes that influence the pharmacokinetics of drugs and also due to lack of knowledge about the active ingred ...
... function, such as cirrhosis or congestive heart failure ,are likely to decrease the rate of drug metabolism.CytochromeP450 enzymes are polymorphic, there exist ethnic differences in hepatic enzymes that influence the pharmacokinetics of drugs and also due to lack of knowledge about the active ingred ...
Drug interaction

A drug interaction is a situation in which a substance (usually another drug) affects the activity of a drug when both are administered together. This action can be synergistic (when the drug's effect is increased) or antagonistic (when the drug's effect is decreased) or a new effect can be produced that neither produces on its own. Typically, interactions between drugs come to mind (drug-drug interaction). However, interactions may also exist between drugs and foods (drug-food interactions), as well as drugs and medicinal plants or herbs (drug-plant interactions). People taking antidepressant drugs such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors should not take food containing tyramine as hypertensive crisis may occur (an example of a drug-food interaction). These interactions may occur out of accidental misuse or due to lack of knowledge about the active ingredients involved in the relevant substances.It is therefore easy to see the importance of these pharmacological interactions in the practice of medicine. If a patient is taking two drugs and one of them increases the effect of the other it is possible that an overdose may occur. The interaction of the two drugs may also increase the risk that side effects will occur. On the other hand, if the action of a drug is reduced it may cease to have any therapeutic use because of under dosage. Notwithstanding the above, on occasion these interactions may be sought in order to obtain an improved therapeutic effect. Examples of this include the use of codeine with paracetamol to increase its analgesic effect. Or the combination of clavulanic acid with amoxicillin in order to overcome bacterial resistance to the antibiotic. It should also be remembered that there are interactions that, from a theoretical standpoint, may occur but in clinical practice have no important repercussions.The pharmaceutical interactions that are of special interest to the practice of medicine are primarily those that have negative effects for an organism. The risk that a pharmacological interaction will appear increases as a function of the number of drugs administered to a patient at the same time.It is possible that an interaction will occur between a drug and another substance present in the organism (i.e. foods or alcohol). Or in certain specific situations a drug may even react with itself, such as occurs with dehydration. In other situations, the interaction does not involve any effect on the drug. In certain cases, the presence of a drug in an individual's blood may affect certain types of laboratory analysis (analytical interference).It is also possible for interactions to occur outside an organism before administration of the drugs has taken place. This can occur when two drugs are mixed, for example, in a saline solution prior to intravenous injection. Some classic examples of this type of interaction include that Thiopentone and Suxamethonium should not be placed in the same syringe and same is true for Benzylpenicillin and Heparin. These situations will all be discussed under the same heading due to their conceptual similarity.Drug interactions may be the result of various processes. These processes may include alterations in the pharmacokinetics of the drug, such as alterations in the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of a drug. Alternatively, drug interactions may be the result of the pharmacodynamic properties of the drug, e.g. the co-administration of a receptor antagonist and an agonist for the same receptor.