Heel 2
... Muscarinic Receptor Antagonists (Parasympathetic depressants) They produce competitive reversible blockade of the actions of A.Ch. at muscarinic (M) receptors. They are classified into: I. Natural Belladonna alkaloids which include Atropine and Hyoscine. They are tertiary amine compounds. ...
... Muscarinic Receptor Antagonists (Parasympathetic depressants) They produce competitive reversible blockade of the actions of A.Ch. at muscarinic (M) receptors. They are classified into: I. Natural Belladonna alkaloids which include Atropine and Hyoscine. They are tertiary amine compounds. ...
PHYSICOCHEMICAL AND PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON THE RHIZOMES GLYCYRRHIZA GLABRA Research Article
... contamination analysis are carried out. The study revealed specific identities for the particular crude drug which will be useful in identification and control to adulterations of the raw drug. Keywords: Glycyrrhiza glabra Linn., Toxic metals, physicochemical studies, Aflatoxin. ...
... contamination analysis are carried out. The study revealed specific identities for the particular crude drug which will be useful in identification and control to adulterations of the raw drug. Keywords: Glycyrrhiza glabra Linn., Toxic metals, physicochemical studies, Aflatoxin. ...
Mind Altering Drugs
... Impact of THC on the Brain 1. It is known that THC affects and influences the activity of cells at specific sites called cannabinoid receptors on nerve cells in the brain. 2. Some areas of the brain have many cannabinoid receptors; others have few or none. 3. Many cannabinoid receptors are found in ...
... Impact of THC on the Brain 1. It is known that THC affects and influences the activity of cells at specific sites called cannabinoid receptors on nerve cells in the brain. 2. Some areas of the brain have many cannabinoid receptors; others have few or none. 3. Many cannabinoid receptors are found in ...
Principles of Metered-Dose Inhaler Design
... is seldom done in clinical practice. When CFC pMDIs are primed, stored valve-down for 3 hours, shaken, and then actuated, the drug content of the first dose may be erratic.25 Improvements in valve design may have largely eliminated this problem, in addition to giving a more predictable dose at the e ...
... is seldom done in clinical practice. When CFC pMDIs are primed, stored valve-down for 3 hours, shaken, and then actuated, the drug content of the first dose may be erratic.25 Improvements in valve design may have largely eliminated this problem, in addition to giving a more predictable dose at the e ...
The Role of Molecular Imaging in Drug Delivery
... Ultrasonography is by far one of the most commonly used clinical imaging modalities because it is safe and cost-effective. Ultrasonic contrast agents, such as microbubbles, have been the subject of active research, especially in recent years. There has been increased interest in developing site-dire ...
... Ultrasonography is by far one of the most commonly used clinical imaging modalities because it is safe and cost-effective. Ultrasonic contrast agents, such as microbubbles, have been the subject of active research, especially in recent years. There has been increased interest in developing site-dire ...
Quenton Tazelaar Abstract 10/25/2012 Malaria is a disease that is
... Plasmodium in Africa is P. falciparum (Worldmalariareport2011)which can invade all types of red blood cells and causes the most potent form of malaria. The Anopheline mosquito specifically female mosquitoes feed on blood, a necessity in the production of eggs. Malaria incident rates hit a low in the ...
... Plasmodium in Africa is P. falciparum (Worldmalariareport2011)which can invade all types of red blood cells and causes the most potent form of malaria. The Anopheline mosquito specifically female mosquitoes feed on blood, a necessity in the production of eggs. Malaria incident rates hit a low in the ...
Protein Binding Drug-Drug Interaction between Warfarin and
... characterized as Sudlow site I and Sudlow site II [8]. These sites bind drugs selectively. Warfarin primarily binds to the site I [9,10]. Because tizoxanide displaced warfarin from its binding site we can suggest that tizoxanide also has high affinity to the albumin binding site I and the both drugs ...
... characterized as Sudlow site I and Sudlow site II [8]. These sites bind drugs selectively. Warfarin primarily binds to the site I [9,10]. Because tizoxanide displaced warfarin from its binding site we can suggest that tizoxanide also has high affinity to the albumin binding site I and the both drugs ...
Methadone - Grand Rapids Medical Education Partners
... for arrythmia: CHF or other medications that predispose to arrythmia Risk is small but rec risk factor screening for cardiac arrythmias,(not EKG), and care if other medications might prolong QT ...
... for arrythmia: CHF or other medications that predispose to arrythmia Risk is small but rec risk factor screening for cardiac arrythmias,(not EKG), and care if other medications might prolong QT ...
Billing and Coding Guide
... This guide is intended solely for educational purposes regarding possible codes that may be available for OTIPRIO. The information provided contains general reimbursement information only and represents Otonomy’s understanding of current reimbursement policies as of July 1, 2016. This coding and rei ...
... This guide is intended solely for educational purposes regarding possible codes that may be available for OTIPRIO. The information provided contains general reimbursement information only and represents Otonomy’s understanding of current reimbursement policies as of July 1, 2016. This coding and rei ...
Drug Use During Pregnancy and Lactation
... –What does a “C” drug really mean –Difficult to assign an “A” to any drug –Does not address lactation safety ...
... –What does a “C” drug really mean –Difficult to assign an “A” to any drug –Does not address lactation safety ...
A Literature Review: Pharmaceutical Care an Evolving Role at
... region becomes dependent on the availability of a pharmacist. It is a well known fact that the conditions of pharmacy practice differ among countries and also vary between different areas within the same country. This is due to the number of pharmacists being lower than required. The direct supervis ...
... region becomes dependent on the availability of a pharmacist. It is a well known fact that the conditions of pharmacy practice differ among countries and also vary between different areas within the same country. This is due to the number of pharmacists being lower than required. The direct supervis ...
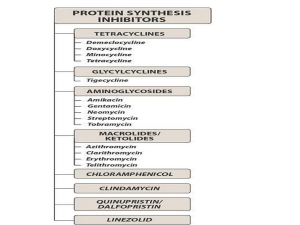
Tobramycin
... mechanism for bactericidal activity is not known. • The initial event is passive diffusion via porin channels across the outer membrane • Drug is then actively transported across the cell membrane into the cytoplasm by an oxygen-dependent process. • Low extra cellular pH and anaerobic conditions inh ...
... mechanism for bactericidal activity is not known. • The initial event is passive diffusion via porin channels across the outer membrane • Drug is then actively transported across the cell membrane into the cytoplasm by an oxygen-dependent process. • Low extra cellular pH and anaerobic conditions inh ...
The Health Effect of Psychostimulants: A Literature Review
... Beyond the worldwide use of caffeine and nicotine, illicit psychostimulants are more used in specific subgroups or cultures. Cocaine may be used in private parties as a mood and energy enhancer, methamphetamines (speed, ice) in raves or techno culture for the same reasons, and 3-4-methylenedioxymeth ...
... Beyond the worldwide use of caffeine and nicotine, illicit psychostimulants are more used in specific subgroups or cultures. Cocaine may be used in private parties as a mood and energy enhancer, methamphetamines (speed, ice) in raves or techno culture for the same reasons, and 3-4-methylenedioxymeth ...
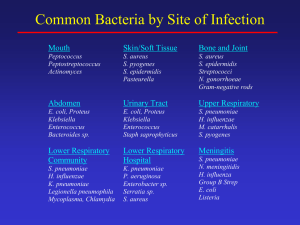
Gram-Negative
... – related to RATE of intravenous infusion; should be infused over at least 60 minutes – resolves spontaneously after discontinuation – may lengthen infusion (over 2 to 3 hours) or pretreat with antihistamines in some cases ...
... – related to RATE of intravenous infusion; should be infused over at least 60 minutes – resolves spontaneously after discontinuation – may lengthen infusion (over 2 to 3 hours) or pretreat with antihistamines in some cases ...
investigator brochure - University Hospitals of Leicester
... Owing to its less pronounced mineralocorticoid activity ……………………. is less likely than cortisone or hydrocortisone to cause sodium retention, electrolyte imbalance, and oedema3. 5.2 Pharmacokinetics and metabolism ……………………………. is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and is in a metabolic ...
... Owing to its less pronounced mineralocorticoid activity ……………………. is less likely than cortisone or hydrocortisone to cause sodium retention, electrolyte imbalance, and oedema3. 5.2 Pharmacokinetics and metabolism ……………………………. is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and is in a metabolic ...
Mechanism-based Inhibition: Deriving KI and kinact
... Inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes is a principle mechanism for drug-drug interactions which may cause severe complications in the clinics (Kalgutkar et al., 2007). It is the underlying mechanism of some of the most notable drug-drug interactions of greatest magnitude (Venkatakrishnan et al., 200 ...
... Inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes is a principle mechanism for drug-drug interactions which may cause severe complications in the clinics (Kalgutkar et al., 2007). It is the underlying mechanism of some of the most notable drug-drug interactions of greatest magnitude (Venkatakrishnan et al., 200 ...
December - National Association of Boards of Pharmacy
... Administration (DEA) statement whereby a pharmacist may use his or her professional judgment in addressing a prescription drug order for a Schedule II controlled substance (CS) that is incomplete or deemed incorrect, pursuant to the following updated Board policy. A pharmacist may change or add the ...
... Administration (DEA) statement whereby a pharmacist may use his or her professional judgment in addressing a prescription drug order for a Schedule II controlled substance (CS) that is incomplete or deemed incorrect, pursuant to the following updated Board policy. A pharmacist may change or add the ...
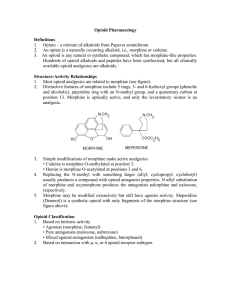
Opioid Pharmacology Definitions 1. Opium – a mixture of alkaloids
... Chronic administration of opioids frequently necessitates the administration of laxatives and stool softeners to treat constipation. Recent evidence that poorly-absorbed quaternary opioid antagonists are also effective in reversing this local effect. Constipating effect is used therapeutically for t ...
... Chronic administration of opioids frequently necessitates the administration of laxatives and stool softeners to treat constipation. Recent evidence that poorly-absorbed quaternary opioid antagonists are also effective in reversing this local effect. Constipating effect is used therapeutically for t ...
PDF: 1177 KB - Department of Infrastructure and Regional
... alcohol. The results of these studies have been mixed and it appears that any effects may be dose-specific. The effectsof amphetamine and amphetamine derivatives on many behaviours have been studied, some of which are relevant to driving. Vigilance performance is improved with ingestion of d-ampheta ...
... alcohol. The results of these studies have been mixed and it appears that any effects may be dose-specific. The effectsof amphetamine and amphetamine derivatives on many behaviours have been studied, some of which are relevant to driving. Vigilance performance is improved with ingestion of d-ampheta ...
PHYTOSOMES: A NOVEL DOSAGE FORM FOR ENHANCEMENT OF BIOAVAILABILITY OF BOTANICALS AND NEUTRACEUTICALS Review Article
... flavonoids (e.g., anthocyanidins from bilberry, catechins from green tea, silymarin from milk thistle). However, many flavonoids are poorly absorbed; the poor absorption of flavonoid nutrients is likely due to two factors. First, they are having multiple‐ring molecules that ar ...
... flavonoids (e.g., anthocyanidins from bilberry, catechins from green tea, silymarin from milk thistle). However, many flavonoids are poorly absorbed; the poor absorption of flavonoid nutrients is likely due to two factors. First, they are having multiple‐ring molecules that ar ...
Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility
... the small number of known drug-like compounds and the vastness of chemistry space, there are only several possibilities on the distribution of drugs in chemistry space. At the extremes, either drugs are found in small, infrequently distributed clusters in the vastness of chemistry space (the authors ...
... the small number of known drug-like compounds and the vastness of chemistry space, there are only several possibilities on the distribution of drugs in chemistry space. At the extremes, either drugs are found in small, infrequently distributed clusters in the vastness of chemistry space (the authors ...
Drug interaction

A drug interaction is a situation in which a substance (usually another drug) affects the activity of a drug when both are administered together. This action can be synergistic (when the drug's effect is increased) or antagonistic (when the drug's effect is decreased) or a new effect can be produced that neither produces on its own. Typically, interactions between drugs come to mind (drug-drug interaction). However, interactions may also exist between drugs and foods (drug-food interactions), as well as drugs and medicinal plants or herbs (drug-plant interactions). People taking antidepressant drugs such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors should not take food containing tyramine as hypertensive crisis may occur (an example of a drug-food interaction). These interactions may occur out of accidental misuse or due to lack of knowledge about the active ingredients involved in the relevant substances.It is therefore easy to see the importance of these pharmacological interactions in the practice of medicine. If a patient is taking two drugs and one of them increases the effect of the other it is possible that an overdose may occur. The interaction of the two drugs may also increase the risk that side effects will occur. On the other hand, if the action of a drug is reduced it may cease to have any therapeutic use because of under dosage. Notwithstanding the above, on occasion these interactions may be sought in order to obtain an improved therapeutic effect. Examples of this include the use of codeine with paracetamol to increase its analgesic effect. Or the combination of clavulanic acid with amoxicillin in order to overcome bacterial resistance to the antibiotic. It should also be remembered that there are interactions that, from a theoretical standpoint, may occur but in clinical practice have no important repercussions.The pharmaceutical interactions that are of special interest to the practice of medicine are primarily those that have negative effects for an organism. The risk that a pharmacological interaction will appear increases as a function of the number of drugs administered to a patient at the same time.It is possible that an interaction will occur between a drug and another substance present in the organism (i.e. foods or alcohol). Or in certain specific situations a drug may even react with itself, such as occurs with dehydration. In other situations, the interaction does not involve any effect on the drug. In certain cases, the presence of a drug in an individual's blood may affect certain types of laboratory analysis (analytical interference).It is also possible for interactions to occur outside an organism before administration of the drugs has taken place. This can occur when two drugs are mixed, for example, in a saline solution prior to intravenous injection. Some classic examples of this type of interaction include that Thiopentone and Suxamethonium should not be placed in the same syringe and same is true for Benzylpenicillin and Heparin. These situations will all be discussed under the same heading due to their conceptual similarity.Drug interactions may be the result of various processes. These processes may include alterations in the pharmacokinetics of the drug, such as alterations in the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of a drug. Alternatively, drug interactions may be the result of the pharmacodynamic properties of the drug, e.g. the co-administration of a receptor antagonist and an agonist for the same receptor.