Chapter 18
... Magnetic fields can produce electric current in conductors. Whenever electricity flows, a magnetic field is present. ...
... Magnetic fields can produce electric current in conductors. Whenever electricity flows, a magnetic field is present. ...
∫
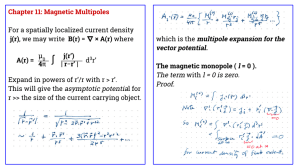
... Chapter 11: Magnetic Multipoles For a spatially localized current density j(r), we may write B(r) = ∇ × A(r) where A(r) = ...
... Chapter 11: Magnetic Multipoles For a spatially localized current density j(r), we may write B(r) = ∇ × A(r) where A(r) = ...
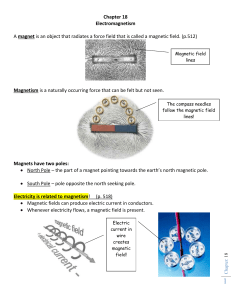
Chapter 18 Vocabulary Magnet – Any material that attracts iron or
... Chapter 18 Vocabulary Magnet – Any material that attracts iron or materials containing iron Poles – The parts of the magnets where the magnetic effects are strongest Magnetic Force – The force of repulsion or attraction between the poles of magnets Electromagnetism – The interaction between electric ...
... Chapter 18 Vocabulary Magnet – Any material that attracts iron or materials containing iron Poles – The parts of the magnets where the magnetic effects are strongest Magnetic Force – The force of repulsion or attraction between the poles of magnets Electromagnetism – The interaction between electric ...
By Erik,Brianna,michael,wyatt
... as the Earth's magnetosphere. That region contains a mix of electrically charged particles, and electric and magnetic rather than gravity determine its structure. We call it the Earth's atmosphere. ...
... as the Earth's magnetosphere. That region contains a mix of electrically charged particles, and electric and magnetic rather than gravity determine its structure. We call it the Earth's atmosphere. ...
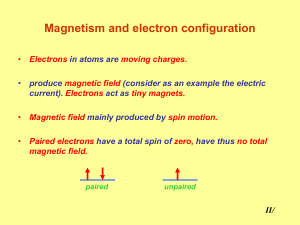
Magnetism and electron configuration
... Magnetism and electron configuration • Electrons in atoms are moving charges. • produce magnetic field (consider as an example the electric current). Electrons act as tiny magnets. ...
... Magnetism and electron configuration • Electrons in atoms are moving charges. • produce magnetic field (consider as an example the electric current). Electrons act as tiny magnets. ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.