t=0
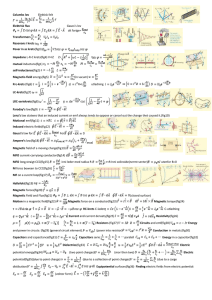
... placed in the uniform magnetic field directed along the x-axis with magnitude 0.500 T. Only the magnetic force acts on the proton. At t=0 the proton has velocity components vx 1.50 105 m / s, v y 0, vz 2.00 105 m / s. Find the radius of the helical path, the angular speed of the proton, and ...
... placed in the uniform magnetic field directed along the x-axis with magnitude 0.500 T. Only the magnetic force acts on the proton. At t=0 the proton has velocity components vx 1.50 105 m / s, v y 0, vz 2.00 105 m / s. Find the radius of the helical path, the angular speed of the proton, and ...
F1004
... The Electricity and Magnetism course has as purpose that the students use the electrical and magnetic charge interactions in the functioning of simple devices, and the knowledge of electricity and magnetism to delve deeper in advanced topics such as electromagnetic fields. Course objective: By the e ...
... The Electricity and Magnetism course has as purpose that the students use the electrical and magnetic charge interactions in the functioning of simple devices, and the knowledge of electricity and magnetism to delve deeper in advanced topics such as electromagnetic fields. Course objective: By the e ...
Columbs lov Elektrisk flux Transformers Resonans i krets
... LC-krets(fig(7) LRC-seriekrets(fig8) Faraday’s law(fig9) Lenz’s law statwes that an induced current or emf always tends to oppose or cancel out the change thet caused it.(fig10) Motional emf(fig11) Induced electric fields(fig12) Gauss’s law for ...
... LC-krets(fig(7) LRC-seriekrets(fig8) Faraday’s law(fig9) Lenz’s law statwes that an induced current or emf always tends to oppose or cancel out the change thet caused it.(fig10) Motional emf(fig11) Induced electric fields(fig12) Gauss’s law for ...
Unit 3_electricity and magnetism_97
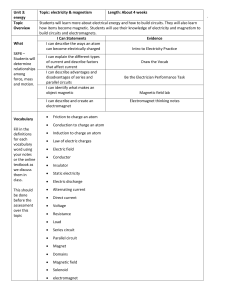
... Students will learn more about electrical energy and how to build circuits. They will also learn how items become magnetic. Students will use their knowledge of electricity and magnetism to build circuits and electromagnets. I Can Statements Evidence I can describe the ways an atom can become electr ...
... Students will learn more about electrical energy and how to build circuits. They will also learn how items become magnetic. Students will use their knowledge of electricity and magnetism to build circuits and electromagnets. I Can Statements Evidence I can describe the ways an atom can become electr ...
I happen to have discovered a direct relation
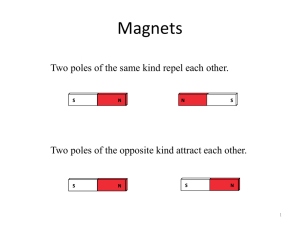
... In permanent magnets, the atomic magnets are lined up. For example, rocks from Magnesia in Asia Minor (town of Tekin in modern day Turkey), from which the term “magnet” is derived, became magnets by being heated inside the Earth and then cooled. ...
... In permanent magnets, the atomic magnets are lined up. For example, rocks from Magnesia in Asia Minor (town of Tekin in modern day Turkey), from which the term “magnet” is derived, became magnets by being heated inside the Earth and then cooled. ...
Paleomagnetism
... Detecting the Field • Earth’s magnetic field can’t be seen by the naked eye, and it also can’t be detected by a compass. • Instead, we use a device called a magnetometer which graphs out the changes in the magnetic field. • It is built into a ship or an airplane. ...
... Detecting the Field • Earth’s magnetic field can’t be seen by the naked eye, and it also can’t be detected by a compass. • Instead, we use a device called a magnetometer which graphs out the changes in the magnetic field. • It is built into a ship or an airplane. ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.