Physical Science
... Only negative charges move Electric Force – push or pull between two objects (#14) – negative and positive charges attract; – positive-positive charges repel; – negative-negative charges repel ...
... Only negative charges move Electric Force – push or pull between two objects (#14) – negative and positive charges attract; – positive-positive charges repel; – negative-negative charges repel ...
Science Demos for Carden Elementary
... Current is how many electrons actually flow (analogous to the volume of water per second). Magnets Show Lode Stones (Magnetic Rocks). All magnets have North pole and a South Pole. Test them to see that S-S attracts, but N-N repels. Draw an Electric Field (monopole). Draw a Magnetic Field (Dipole). M ...
... Current is how many electrons actually flow (analogous to the volume of water per second). Magnets Show Lode Stones (Magnetic Rocks). All magnets have North pole and a South Pole. Test them to see that S-S attracts, but N-N repels. Draw an Electric Field (monopole). Draw a Magnetic Field (Dipole). M ...
Used to determine the direction of emf induced in a conductor
... This emf causes a current flow if the conductor circuit is closed . ...
... This emf causes a current flow if the conductor circuit is closed . ...
Document
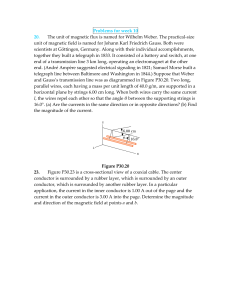
... A single rectangular loop of wire with the dimensions inside a region of B=0.5 T and part is outside the field. The total resistance of the loop is 0.2Ω . The loop is pulled from the field with a constant velocity of 5m/s. 1)What is the magnitude and direction of the induced current? 2) In which par ...
... A single rectangular loop of wire with the dimensions inside a region of B=0.5 T and part is outside the field. The total resistance of the loop is 0.2Ω . The loop is pulled from the field with a constant velocity of 5m/s. 1)What is the magnitude and direction of the induced current? 2) In which par ...
F1004
... The Electricity and Magnetism course has as purpose that the students use the electrical and magnetic charge interactions in the functioning of simple devices, and the knowledge of electricity and magnetism to delve deeper in advanced topics such as electromagnetic fields. Course objective: By the e ...
... The Electricity and Magnetism course has as purpose that the students use the electrical and magnetic charge interactions in the functioning of simple devices, and the knowledge of electricity and magnetism to delve deeper in advanced topics such as electromagnetic fields. Course objective: By the e ...
Magnets and Electricity
... Magnets are used to generate, or produce, electricity. Spinning a coil of wire inside a magnetic field produces an electric force between the ends of the coil. In a similar way, an electric current produces a magnetic field around it. A compass placed next to a wire carrying an electric current will ...
... Magnets are used to generate, or produce, electricity. Spinning a coil of wire inside a magnetic field produces an electric force between the ends of the coil. In a similar way, an electric current produces a magnetic field around it. A compass placed next to a wire carrying an electric current will ...
EMT MODEL SET 2
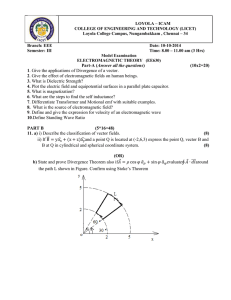
... b) Derive expressions for i) Lorentz force ii) Force on a current element and ii) Force between two current elements. ...
... b) Derive expressions for i) Lorentz force ii) Force on a current element and ii) Force between two current elements. ...
Maxwell`s Equations (4)
... that magnetic monopoles do not exist. The law asserts that the net magnetic flux ΦB through any closed Gaussian surface is zero: ...
... that magnetic monopoles do not exist. The law asserts that the net magnetic flux ΦB through any closed Gaussian surface is zero: ...
1 William Gilbert William Gilbert was born in
... The following are now the accepted magnetic field drawings. You need to know these ...
... The following are now the accepted magnetic field drawings. You need to know these ...
ECE 341: Electromagnetic Fields I Concepts: Maxwell’s Equations
... currents Can analyze RLC circuits in time-harmonic regime Has command of power and energy relations for circuit elements, in both instantaneous and timeaverage forms Can analyze electric circuits with time-harmonic currents using phasors and complex variables ...
... currents Can analyze RLC circuits in time-harmonic regime Has command of power and energy relations for circuit elements, in both instantaneous and timeaverage forms Can analyze electric circuits with time-harmonic currents using phasors and complex variables ...