Magnetic Fields and Electromagnetic Induction --
... 18. What is the difference between a generator and a motor in view of energy utilization and conversion? Can these devices create energy? ...
... 18. What is the difference between a generator and a motor in view of energy utilization and conversion? Can these devices create energy? ...
Week 2: Current and Intro to Circuits
... • How do they work? • What effects do they have on us? ...
... • How do they work? • What effects do they have on us? ...
Unit 9: Magnetism and Induction Review KEY
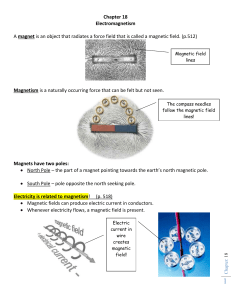
... An electromagnet can be built by wrapping a current-carrying wire around an iron core. Strength can be increased with more current or more turns of wire. ...
... An electromagnet can be built by wrapping a current-carrying wire around an iron core. Strength can be increased with more current or more turns of wire. ...
Magnetic fields
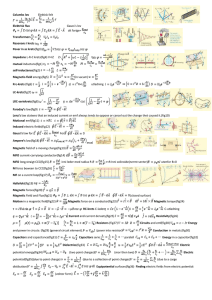
... The direction of the magnetic force is given by the magnetic force right-hand rule (RHR), which states as follows. To find the direction of magnetic force on a positive charge, start by pointing the fingers of your right hand in the direction of the velocity, v. Now curl your fingers forward the dir ...
... The direction of the magnetic force is given by the magnetic force right-hand rule (RHR), which states as follows. To find the direction of magnetic force on a positive charge, start by pointing the fingers of your right hand in the direction of the velocity, v. Now curl your fingers forward the dir ...
615-0335 (10-152) Lenz`s Law Pendulum
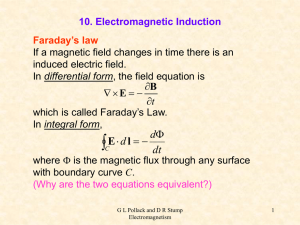
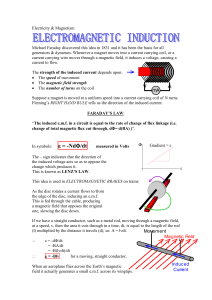
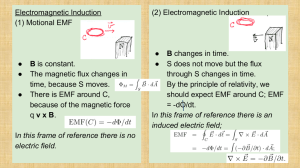
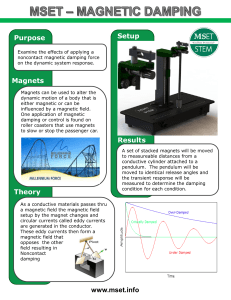
... gives the direction of the electromotive force caused by electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction is a phenomenon caused when a magnetic field interacts with a conductive material. As the material passes through the magnetic field, electrons in the conductor become excited by the magnet. ...
... gives the direction of the electromotive force caused by electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction is a phenomenon caused when a magnetic field interacts with a conductive material. As the material passes through the magnetic field, electrons in the conductor become excited by the magnet. ...
MAGNETISM LESSON 3
... B. A magnetic field does exert force on a wire in which current is flowing . The magnet will either push or pull the wire depending on the pole of the magnet. ...
... B. A magnetic field does exert force on a wire in which current is flowing . The magnet will either push or pull the wire depending on the pole of the magnet. ...
Today: Oscilloscope and Faraday’s Law
... Last week we put a voltage on a coil of wire. The resulting current in the coil made it act like a magnet. In other words a current can produce an magnetic field – evidence that electricity and magnetism are connected. Q. Can a magnetic field produce a current? A. Yes… but it is not as easy. A const ...
... Last week we put a voltage on a coil of wire. The resulting current in the coil made it act like a magnet. In other words a current can produce an magnetic field – evidence that electricity and magnetism are connected. Q. Can a magnetic field produce a current? A. Yes… but it is not as easy. A const ...
1. A bar magnet is broken in half. Each half is broken in half again
... A) work is required to move a magnetic pole through a closed path surrounding a current B) a time-varying electric flux acts as a current for purposes of producing a magnetic field C) the speed of light could be determined from simple electrostatic and magnetostatic experiments (finding the values o ...
... A) work is required to move a magnetic pole through a closed path surrounding a current B) a time-varying electric flux acts as a current for purposes of producing a magnetic field C) the speed of light could be determined from simple electrostatic and magnetostatic experiments (finding the values o ...